A ResNet is a type of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) that is composed of multiple layers of residual blocks. Residual blocks are a type of bottle-neck block that contain two 3×3 convolutional layers, where the second layer is connected to the first layer via a skip-connection. The skip-connection allows the ResNet to learn an identity mapping, which is the mapping between the input and the output of the ResNet. The identity mapping is important because it allows the ResNet to be trained on much deeper networks than other types of CNNs.
The residual network (avolutional neural network) was introduced in the aftermath of CNN (Convolutional Neural Network). Additional layers are added to the DNN to improve accuracy and performance. Depth is reached at a specific level with the traditional Convolutional Neural Network model. The idea that LeNet is a baseline architecture does not apply in practice. NLP and IR tasks have benefited greatly from the rapid development of word embedding and neural networks. We describe a staged hybrid model in this paper, which consists of Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks (RCNNs) and highway layers. In each region, there is a significant difference in financial and economic development. We will use neural networks to design the economic benefit model of financial depth and breadth in this paper.
FCN-ResNet is made up of a ResNet-50 or ResNet-101 backbone. It is a fully convolutional network model.
The error rate decreases dramatically as the CNN architecture (AlexNet) that won ImageNet 2012 is replaced by a new CNN architecture (the next winning architecture) with more layers in a deep neural network.
Shaoqing Ren, Kaiming He, Jian Sun, and Xiangyu Zhang published a paper on residual network (ResNet) in May 1995, which is regarded as one of the most famous deep learning models. The paper was first published in 2015 under the title “Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition.”
ResNet is a method of dealing with the vanishing gradient problem in deep CNNs. As a result, they are able to skip some layers by assuming that very deep networks are not capable of producing training errors that are higher than those found at the shallower end. They can be thought of as a model similar to LSTM in RNNs as a whole.
Is Resnet A Cnn Or Ann?
Deep residual networks, such as the ResNet-50 model, are CNN networks with 50 layers deep, as opposed to the general-purpose networks that are typically used today. An Artificial Neural Network (ANN) with residual blocks stacked on top of each other is known as a Residual Neural Network (ResNet).
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) can detect visual patterns directly from pixel images without having to process them preprocessing. Several banks have used the LeNet-5 convolutional network, which was designed to classify digits at the seven levels, to recognize handwritten numbers on checks. AlexNet won the challenge in 2012 after outperforming all previous competitors. VGGNet, which was created by Simonyan and Zisserman as a runner-up at the ILSVRC 2014 competition, is now widely available. The network, like CNN, used a novel element known as an inception module. A few days of training gave the human expert (Andrej Karpathy) a top-5 error rate of 5.7% (single model) and 3.6% (ensemble).
Create A Basic Resnet Model
You can begin with the tutorials once you have downloaded and installed the necessary software. In the first step, we’ll go over how to create a basic Resnet model. The model will then be used to classify images.
Is Resnet A Cnn Architecture?
A ResNet is a type of CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) architecture that is designed to improve upon the traditional CNN architecture through the use of skip connections. These skip connections allow for the gradient to flow more freely through the network, which in turn leads to improved performance on tasks such as image classification.
Convolutional Neural Networks are a type of Deep Neural Network that performs well at the highest level. CNNs have evolved significantly in recent years by not only stacking layers but also creating their own. This article will show you how to create and implement state-of-the-art CNN architectures in Pytorch in their entirety. It is the first architecture to incorporate ReLU non-linearity, dropout for regularization, and multi-GPU training. VGG stands for “deeper form of Alexnet” and can be referred to as such. This network uses the same ReLU activation function, but there are fewer parameters. InceptionNet was the 2014 Imagenet challenge winner and was introduced in the paper Going Deeper With Convolutions as part of the challenge.
It is based on flowchart, in which we use four convolution branches to create a new component: the Inception Module. The kernel sizes 3*3 are layered in the above code, followed by inverse blocks. The most significant feature of these Inception blocks is that they are not only deeper, but they also have a wider Resnet. In ResNet, residual output from the previous layer is added to the current layer’s output. This architecture is ideal for training networks deeper in depth. Using the above steps, we can create our own Residual Network from scratch.
Because of its speed and accuracy when distinguishing objects, the ResNet model is an excellent choice for image classification. They have less memory than other models, allowing them to be used in larger models.
For our encoder/downsampling section of the U-Net, we will use ResNet 34. Researchers at Fastai discovered that this model outperformed the ResNet-50 model in terms of efficiency and speed of training. The system uses less memory and is capable of running larger models, which means it can do more with less.
Our U-Net model can be successfully implemented using the ResNet model.
Three Layers Of A Convolutional Neural Network
In the first layer, each channel is fed into a different convolutional layer, and the input data is broken down into various input channels. A convolutional layer employs a set of filters to transform the input data into a series of output channels. The number of output channels is determined by the number of filters and the size of the input data.
In the second layer, the output channels from the first layer are combined and the outputs from the convolutional layer are added. This layer, known as a pooling layer, is located here. The pooling layer reduces the input data size while decreasing the number of channels.
The third layer, which is fully connected, is referred to as the “connected layer.” It is the fully connected layer that outputs the CNN’s final output. Each neuron in the fully connected layer is counted, as well as the size of the input data, in order to determine the CNN’s accuracy.
Is Cnn And Lstm Same?
There is no definitive answer to this question as it depends on individual interpretation. Some people may believe that CNN and LSTM are similar because they are both deep learning models that can be used for a variety of tasks. Others may believe that they are different because CNN is a convolutional neural network while LSTM is a recurrent neural network.
Data from sequential events can be managed by the LSTM network, which is why it is so popular. In terms of capturing neighborhood information, CNN is a useful tool, but sequences are less effective.
The Cnn-lstm-ml Model Outperforms Other Models In Terms Of Prediction Accuracy
In its most basic form, the CNN Long Short-Term Memory Network, also known as CNN LSTM, is a programming language designed specifically for sequence prediction problems involving spatial inputs.
In its most successful form, the LSTM network, which overcomes the difficulty of training a recurrent network and has been used in a wide range of applications, is one of the most successful RNNs. More information about Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) is available on the RNN Crash Course post.
CNN-LSTM-ML models, on the other hand, consistently outperforms other models in terms of temporal sequence prediction accuracy for both short-term and long-term predictions (1 month and 12 months). It is proposed that the MAE of the proposed model is 33.6% lower than that of LSTM if the training data is reduced by 50%.
Is Resnet Supervised Or Unsupervised?
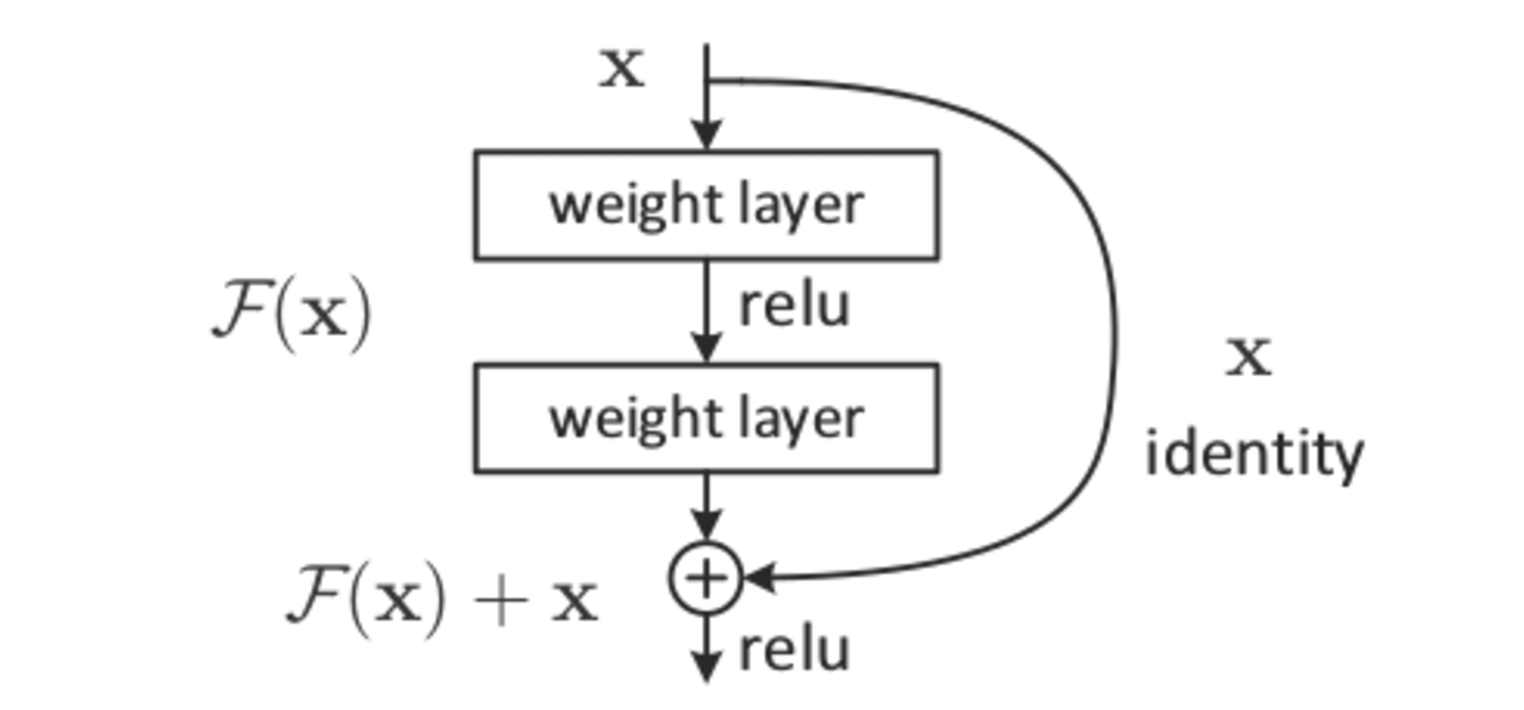
There is no simple answer to this question as it depends on how you define “supervised” and “unsupervised” learning. Generally, though, you can think of ResNet as a supervised learning algorithm, since it relies on a training set of labeled data to learn from. This label data can be provided by humans, or generated by another machine learning algorithm.
The Advantages Of Using Resnet
A CNN is a type of deep learning network in which a number of layers of neurons are present. There are, however, a number of layers in ResNet, which is unusual in that it has a large number of layers. ResNet, on the other hand, is more complicated than CNNs because it is so complex. A ResNet neural network can perform large sums of data processing. Because it has so many layers, it can learn how to deal with complex patterns by doing so. ResNet is one of the most significant advantages of its application due to the “vanishing gradient” problem. It is a problem that arises during backpropagation, and it can be quite difficult to create networks that can learn well from their surroundings. ResNet is able to overcome this issue due to the large number of layers on its platform. ResNet has a lot of power, and it’s definitely worth considering for someone who wants to learn how to process large amounts of data.
Resnet Cnn Architecture
ResNet is a CNN architecture that was introduced in 2015. It is known for its deep learning capabilities and has been used in many image classification tasks. ResNet is also known for its skip connections, which allow the network to learn from previous layers.
After the first CNN-based architecture (AlexNet) that wins ImageNet 2012, every subsequent winning architecture employs more layers of deep neural network to reduce error rates. We use skip connections when we connect to this network. A skip connection connects layer activations to layers further down the chain by skipping some layers between layers. Tensorflow and Keras API can be used to create the ResNet architecture from the ground up. We use the CIFAR-10 data set for this project. 60, 000 3232 color images in ten different classes (airplanes, cars, birds, cats, deer, dogs, frogs, horses, ships, and trucks) were available in this dataset. The fourth step is to define a basic ResNet block that is based on the ResNet V1 architecture in Python3.
Resnet V1 and Resnet V3 are both built using python3 and contain the following code: Resnet V1 >architecture>in python3 def Resnet_v1(inputs, depth, num_classes): If (depth – 2)%6!! ValueError should be raised by adding 6n (‘depth should be 20 32 44′ in [a]). The num_res_blocks output and num_res_blocks output are the same. We can define input as “shape=input_shape.” The inputs are: input (size=3, strides=1, activation=’relu’, batch_normalization=true, conv=Conv2D). In step 6, you must write code to train and test the ResNet 1 and 2 systems. The code that follows is written in C# and will be used for training and testing both the Resnet v1 and v2 versions.
Each stage in the range (3) has a different range of values. In other words, activation is equal to batch_normalization. To get the correct distance, multiply true strides by one. If there is no stage == 0, the stage = 0 is determined by stage = 0 Int (depth – 2) / 9 is the int (depth – 2). activate = activate = activation = activation = Neither batch_normalization nor batch_processing results in any results. I’m not saying that’s true. Filter_out = num.
It will return 2 if the numfilters-out line is filled. An ensemble of ResNets achieved an error of only 3.8% on ImageNet’s test set, a result that earned them the ILSVRC 2015 award. As a result, it improves its relative ability to detect objects by 28% on the COCO object detection dataset because of its very deep representation.
Resnet Architecture
ResNet is a short form for Residual Network. ResNet is an architecture of a neural network used in deep learning. The ResNet architecture was designed by Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, and Jian Sun. The architecture is known for its ability to enable the training of very deep neural networks. The original paper on the ResNet architecture can be found here: https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385.
It may have been the most significant work in the field of computer vision and deep learning. ResNet makes it possible to train up to hundreds or thousands of layers and still produce compelling results. The architecture of convolutional neural networks (CNN) is now deeper and deeper thanks to AlexNet’s state-of-the-art convolutional neural network. ResNet introduced a new identity shortcut connection that eliminates one or more layers. A study conducted by the authors of the Highway Network also incorporated gated shortcut connections. Although the highway network performs no better than ResNet, research shows that it can sometimes be more effective than that. Clearly, the most important thing to do is keep these mature highways clear.
ResNet, one of the most widely used architectures for computer vision tasks, is a popular one. The architecture of this country is being heavily studied as it gains popularity. In this section, I introduce several new architectures based on ResNet and then argue that ResNet should be classified as an ensemble of many smaller networks. Researchers used random layers dropped during training and testing to solve the vanishing gradient problem in deep ResNet. Concatenating feature maps allows them to remain intact and increase the variance of their outputs, allowing them to be reused more frequently. In order to keep the network from expanding out of control, the authors used a hyper-parameter known as growth rate (k). Residual Networks Have the same characteristics as Ensemble Networks, which are more akin to shallow networks.
The purpose of this study is to make it easier to understand ResNet. When you train a 110-layer ResNet with stochastic depth, the performance of your ResNet increases significantly over when you train it continuously. The fact that layers (paths) may be redundant in ResNet raises the possibility that they are. ResNet enables the training of very deep networks in ways that are less efficient than traditional methods. Path lengths ranging from nine to eighteen are the most common source of contributions, but they account for only a fraction of the total. This finding is very interesting because it implies that ResNet was unable to solve the vanishing gradient problem on long paths.
The ResNet architecture was created with the goal of facilitating the efficient operation of large amounts of convolutional layers. The ResNet is distinguished from other networks by its high levels of parallelism, so its output does not suffer as a result of multiple deep layers being added. With ResNet, multiple layers of deep data can be added while maintaining high output accuracy.
Deep neural networks have the ability to layered multiple times for the purpose of detecting threats, according to this discovery. This study confirms the efficacy of deep learning, and it will hopefully lead to more efficient deep learning networks in the future.
The Power Of Residual Blocks
If we want to hold the previous layer’s output in the future, we create a residual block rather than directly feeding the output of the previous layer. This block is then passed on to the next layer, but it is not used to generate the output of the next layer. Because we can skip layers without affecting network performance, we can skip layers in this manner as well.
There is a powerful architecture that can be used to address the vanish gradient issue. Previously, networks with thousands of layers were unable to resolve this problem. This problem is no longer a problem with ResNet.
Resnet Pytorch
ResNet is a short name for Residual Network. ResNet is a Deep Learning model developed by Microsoft Research, which won the first place in the ImageNet Large-Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC) in 2015. The key idea of ResNet is to enable easy and effective training of extremely deep neural networks by using a “residual” learning block. A residual learning block is a building block of a neural network where the input to the block is added to the output of the block. This addition enables the training of much deeper neural networks than was previously possible.
ResNets are neural networks that can be used in computer vision applications such as object detection and image segmentation. Because ResNet solved the vanish gradient problem, a network with up to thousands of convolutional layers is now possible. To work with Convolutional Network patterns, you must first understand ResNet’s original architecture. A Python deep learning framework known as PyTorch includes a variety of options for creating ResNet models. With PyTorch, you can change the architecture of ResNet to meet your specific needs. In this code example, Liu Kuang demonstrates how to use residual blocks and create different ResNet combinations. With Run:AI, you can run as many compute-intensive experiments in PyTorch and other deep learning frameworks as you require.
Resnet Advantages
One of the main advantages of ResNet is its ability to use very deep neural networks. This is made possible by the skip connections that are used throughout the network. These skip connections help to alleviate the problems that are associated with very deep neural networks, such as the vanishing gradient problem. Additionally, ResNet is much more efficient than previous deep neural networks, due to its use of 1×1 convolutions and shortcut connections.
ResNet is a Neural Network architecture with a 50-layer structure that is extremely efficient. It has a low error rate, is built by using a 11 convolution, known as a “bottleneck,” which reduces the number of parameters and matrix multiplications, and performs better than other solutions. It enables much faster training of each layer. Rather than two layers, it employs a stack of three layers. As a result, the 50-layer ResNet is one of the most efficient neural network architectures.
Why Resnet Is The Backbone Of Many Computer Vision Tasks
ResNet is used in a variety of computer vision tasks because it provides extremely deep neural networks up to 150 layers of processing power. The breakthrough, for example, allows us to train models that are previously impossible to construct. In addition, residual blocks create an identity mapping between activations earlier in the network to reduce performance degradation associated with deep neural architectures. Because of the skip connections, the problem of vanishing and exploding gradient has been addressed.

