Layers are the basic building blocks of neural networks. A layer is a collection of neurons, and each layer is connected to the previous and next layer in the network. The input layer is the first layer in the network, and the output layer is the last layer. The hidden layers are the layers between the input and output layers. Layers are important because they allow neural networks to learn complex patterns. By adding more layers to a neural network, we can make the network more powerful and capable of learning more complex patterns.
What is layer in neural network? Each process may be a layer, but Is that true? Are all layers of the flow diagram equal one? It is sometimes thought that the Multiply Add and the nonlinear function (relu) are separate layers. Deep learning models are similar to sieves for data processing, with successively refined data filters in the background. A layer, also known as a data processing module, serves as the foundation for neural networks. According to Goodfellow, who wrote the book Deep Learning in 2016, a network is a function composition in which each function is a layer.
Deep learning employs a number of well-known layers, such as the convolutional layer and the maximum pooling layer. The vanilla neural network includes a fully connected layer known as ReLU and a layer known as the layer. There are multiple layers of RNN in the RNN model, as well as deconvolutional layers in the autoencoder.
A layer is a callable object that can take both input and output tensors. A computation is carried out using the call() method, followed by a state (weight variables).
A single-layer artificial neural network, also known as a single-layer, is made up of a single layer of nodes. In the single layer, each node connects directly to an input variable and contributes to its output. A single layer of active units represents the single layer of a single network.
Layers contain images, text, or objects that are layered. They work with content on one layer and do not affect content on any other layers at all. Layers can be found in the Layers panel’s bottom right corner.
Why Do Neural Networks Have Layers?
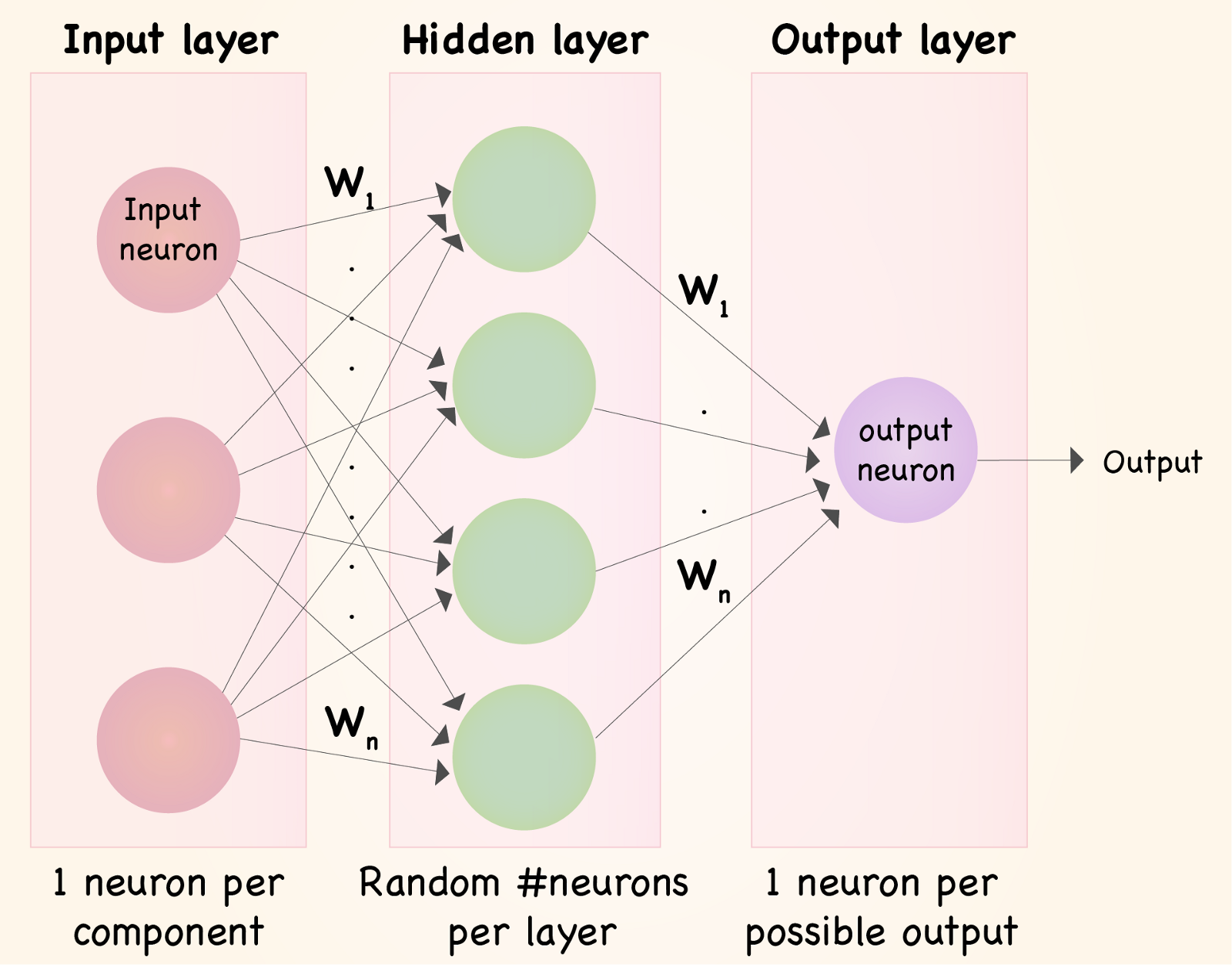
The Neural Network is made up of three layers. A neural network’s input layer contains data from the start. A hidden layer is one that is hidden from the input and output layers and is used to compute. The output layer is the one that comes up with the result of the inputs.
The importance of hidden layers in neural networks is discussed in this tutorial. Layers are vertically stacked components of a neural network. Neural networks can learn extremely complex non-linear functions by building layers. We’ll look at a feedforward neural network, which is made up of two hidden layers, as a first step. Suppose two binary inputs are used to generate an XOR logical gate, and we have a neural network to predict its output. According to the truth table of XOR, the output is always true as long as the inputs are different. A simple linear model is the best solution for the problem, but it is not an accurate representation of the two classes.
A neural network learns to detect short segments of edges and corners by employing its first hidden layer. In general, these features are easy to detect when using raw images, but they are not very useful in identifying the person in the image. It is thus possible to classify input features as processed features by transforming them into processed features in the output layer.
Neural Networks: The More Layers, The Bette
A neural network has layers that can generalize in a better way than its lower layers. As a result, the network will be able to learn more complex relationships between input data and output.
What Are The Three Layers Of A Neural Network?

A neural network is composed of three layers: the input layer, the hidden layer, and the output layer. The input layer receives input from the outside world, while the hidden layer processes that input and the output layer produces the output.
A neural network is a machine learning model that employs artificial intelligence. A three-layer system includes a layer that creates an input, a layer that stores the information, and a layer that outputs the information. Between 2012 and 2016, a number of Italian businesses hired women directors to their boards. In this paper, we will look into whether there has been any significant reaction on the Italian stock exchange in light of the recent events. The inverse is determined by a significant market reaction. Pyo et al. report [21]employ nonparametric ML approaches such as ANN, SVMs with polynomials, and radial basis functional kernels to forecast the KOSPI 200 values over time.
Based on Google trends, the results were 50% accurate for short durations. The LM algorithm performed better than other models in this study. Using ANN16, a mean absolute error (MAE), root mean squared error (RMSE), and coefficient of determination (R2) with values of 0.4693, 0.8816 W, and 0.9988, respectively, are obtained. In this study, we used data from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) in the United States to obtain weather parameters and solar power output data for a monocrystalline Silicon PV module in Cocoa, Florida. The findings of this study show that ANN is the most widely used and most accurate algorithm for PV solar power forecasting. Businesses lose money if products are not purchased on time, and if the expiration date is past, they will be unable to produce. The use of accurate stock consumption statistics allows us to accurately predict how much stock we will consume in the future.
Using regression models, we created a model to predict the demand for specific stock items in this paper. SujinPyo et al. ( 2017) performed a regression analysis on the Korea Stock Price Index 200 (KOSPI 200) prices based on artificial neural networks (ANNs), support vector machines (SVMs), and radial basis functions (RBFs). The Nifty 50 index is predicted using eight supervised machine learning models in the paper. You must have a good mixture of layers in order to get the best results. You will have an adaptive boost if you use k-. Data set sizes have increased as part of theNearest Neighbors, Random Forest, and Decision Trees algorithm.
The Linear Regression model and the Artificial Neural Network model had the most similar prediction results. The stochastic gradient descent performed better than the support vector machine. This study provides a new perspective on the lumber futures market by accurately modeling the price. Dentists in Karachi were asked to take part in a survey to assess their level of awareness and perception of artificial intelligence. The majority of respondents were aware of AI applications in dentistry and were positive about the benefits they will provide in the future. The practice lacked a high rate of AI tool utilization. Attending AI training will allow you to bring and adapt changes to local settings based on the AI.
Recent research has shown that blast-induced impact prediction has the potential to optimize blasting operation, increase efficiency, and reduce safety and environmental concerns. Rock mass breaking consumes only 30% of the blast energy, with 30% being lost as waste. This paper examines and discusses research articles published in the literature in this field. Investors will benefit from the proposed model’s recommendations in making profitable investment decisions. This model was able to predict 63.59% of HDFC, Yes Bank, and SBI transactions, 5625% of Yes Bank transactions, and 57.05% of SBI transactions. Recurrent Neural Networks are estimated to be more accurate than neural networks used in this study.
To be successful in technical analysis, data must be collected and analyzed in a systematic manner, and decisions must be made quickly.
To be successful, your company must find a way to monetize the data and make it useful to you.
Creating a sense of what customers want is critical to strategic success.
Each of these layers has its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Networks on the first layer are fully connected.
A fully connected network contains all of the neurons in a network. This layer is typically used when the network is still in its early stages, or when the number of layers on the network is relatively small. Networks that are fully connected are more efficient and simple to use, but they can also be inaccurate.
volutional networks Avolutional networks are layers that are used to filter data. A convolutional network is effective and accurate, but it can be difficult to construct.
Layer 3 is where coherent networks are routed.
A Deconvolutional Network (DNN) is a layer that decodes data. A de facto network is a time-efficient way to build a network, but it can be less accurate than other types of networks.
In switching networks, rerouting is an option. A Recurrent Network is a layer of data that is used to remember information. It is simple to build a recurrent network, but it is difficult to build a network that works efficiently and accurately.
How Many Layers Are There In Neural Network?

A neural network typically consists of multiple layers of interconnected processing nodes, or neurons. The input layer receives input data, which is then passed to one or more hidden layers. The hidden layers process the input data and generate output data, which is passed to the output layer. The output layer produces the final results of the neural network.
Today’s machine learning models rely heavily on neural networks to run their operations. Fully connected, convolution, deconvolution, and recurrent neural network layers are the most common types of neural network layers. They are what they are and what they can do, so read on for more information. Deconvolution is a transposed convolution method that upsamples data to a higher resolution. Multiple multiplication is repeated from left to right and up to bottom of the image to detect features. Recurrent layers, as the name implies, are used to generate recurrent neural networks (RNNs), which are thought to provide neural memory.
The success rate of a pedestrian detection system is calculated by dividing the number of detected pedestrians by the number of pedestrians processed. The success rate of pedestrian detection with the pooling layers is improved by a factor of 16 over that of the original CNN model, demonstrating that they can be detected at a higher rate with the pooling layers. The troposphere, the stratosphere, the mesosphere, and the thermosphere are the four major layers of the Earth’s atmosphere. The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere, which extends for up to 500 kilometers from the Earth’s surface. The stratosphere is the next layer, extending 500 to 10,000 kilometers above the Earth’s surface. The mesosphere is a layer of space above the Earth’s surface that extends from 10,000 to 50,000 km. The thermosphere is the highest layer of the atmosphere, and it extends from about 50,000 km up to a height of 500,000,000 km above the Earth’s surface.
What Is Input Layer In Neural Network
In neural networks, the input layer is the first layer. This layer holds the data that the network will use to learn. The input layer is fully connected to the next layer, the hidden layer.
A neural network consists of four components: a layer (a row of neuron); a neuron (blue, orange, and purple circles); a weight (arrow); and a bias (not shown in the figure). The input and hidden neuron types of neuron, as well as the output and output neuron types, are considered distinct. Only the learning algorithm used by neural networks is used to process data. A neuron receives data using an activation function equation in order to process it. The two activation functions are frequently used. In a matrix operation, all of these operations can be reprogrammed. If we want to solve a classification problem for example, for example, predict rain storms (rain or no rain), we need to have two neurons in the output layer.
What Is Hidden Layer In Neural Network
A hidden layer in a neural network is an area between the input and output of the algorithm, in which the function computes weights for the inputs and directs them through an activation function as the output. As a result, hidden layers act as nonlinear solvers for inputs entering the network.
The previous layer can be applied to any function that you specify (usually through a linear transformation followed by a squashing nonlinearity). I’m going to try to be as broad as possible, but the roles of the different layers will vary depending on what functions are being computed. The input vectors $x$ and $h$ are given in this talk, and the hidden layers are given in the following slide: In the first layer, we look for small pieces of edge in the image that are easily found from raw pixel data. Once the edges have been composed, a single eye detector may turn on, and faces are formed from the edges. An input layer contains a set of pixels that provide a high level of activity for each neuron. As an example, if we consider a neuron as an eye detector, the neuron will most likely display a image similar to what we see in our eyes. All of these images are affected by the detectors even though they appear to be less than the pixel levels.
In figure 3, we can see that linear regression performs as well without the hidden layer as it does without it. We might conclude that using hidden layers provides no significant advantage, and that supervised learning can be used instead. There is a more accurate way to determine a better decision boundary that is based on this method.
The Importance Of Hidden Layers In Neural Networks
In neural networks, hidden layers are required because data cannot be separated linearly. The network must learn complex tasks in order to do so. A hidden layer is also required when the data is large or has numerous dimensions.
What Is Output Layer In Neural Network
In neural networks, the output layer is the last layer of neurons in the network. This layer is responsible for producing the final output from the network. The output layer takes the output from the previous layer and passes it through a set of weights and biases to produce the final output.
To begin with, configuring a Neural Network Output Layer is an ambiguous task for deep learners. In order to solve a regression problem, it is critical to keep only one node in the neural network’s output layer. You can define this by using activation = linear or leaving 888-353-1299 888-353-1299 as the default parameter value activation =. Training neural networks entails three types of classification problems. The output layer configuration is decided by how our data is stored in the data structure. Your target is a matrix of One-Hot-Encoded vectors, so the output layer should have two nodes, while the final layer should have a softmax function. To classify all predictions as 1 using the sigmoid function, we must have an equal or greater number of predictions greater than or equal to 0.5.
A softmax function must be implemented if the data is stored in an open source format and the final layer has two nodes. The data format determines the loss function used in binary classification problems. If the node counts in the output layer are greater than the number of labels for the target variable, its label count will always be greater than the number of nodes in the output layer. In general, using one node reduces the amount of work required for a model, but it necessitates a significant amount of manual effort because prediction probabilities must be converted from class predictions to node predictions. A multi-class problem attempts to predict a single class label from a set of mutually exclusive class labels using some combination of variables. When a sample has more than one label, it is impossible to identify it in a multi-label test. Each of these problems must have targets that have been binarized.
Each sample’s target is represented by a row in a 2D shape (n_samples, n_classes) that contains binary values. As a result, our data is composed of 1s and 0s per target class. Most practitioners are not familiar with the concept of cross-entropy. For example, the accuracy, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), precision, and/or recall of a model can all be used to evaluate its performance. When an accurate prediction equals a label (number correct over time), it is referred to as an accurate prediction. If you can absorb these concepts and put them into action, you should be able to configure your neural network’s output layers in a matter of minutes. Enthought enables you to explore a deep learning path that is clear to you. Attend upcoming lectures and courses to learn about the challenges and solutions presented by scientific data.
What Is The Output Layer In A Cnn Responsible For?
This output layer is responsible for class prediction in CNN, which is what it is most well-known for.

