In 1950, Alan Turing published a paper titled “Computing Machinery and Intelligence” in which he proposed a test for determining whether or not a machine could be said to possess artificial intelligence. The test, now known as the Turing Test, involves a human judge engaging in a natural language conversation with a human and a machine, each of which is hidden from the judge. If the judge cannot tell which is which, then the machine is said to have passed the test. In 1966, Joseph Weizenbaum created ELIZA, a computer program that could mimic human conversation. ELIZA was not truly intelligent, but it was able to convincingly imitate human conversation by following a set of simple rules. In 1974, Roger Schank and Robert Abelson developed the Script Applier Mechanism (SAM), a computer program that could understand and generate stories. SAM was able to understand the plot of a story and generate new stories with the same plot. In 1980, Terry Winograd and Fernando Flores developed the SHRDLU program, which could understand and respond to natural language commands. SHRDLU was able to understand the meaning of commands and carry out the desired actions. In 1982, Walter Freeman and Dennis Bray developed the Cog project, which was designed to create a robot that could think and act like a human. The Cog project was unsuccessful, but it demonstrated that artificial intelligence was possible. In 1997, IBM’s Deep Blue computer beat world chess champion Garry Kasparov in a six-game match. Deep Blue was the first computer to beat a human world champion in a game of chess. In 2011, IBM’s Watson computer won the game show Jeopardy! Watson was the first computer to beat human champions in a game that required natural language understanding. These are just a few of the milestones in the history of artificial intelligence. Artificial intelligence is an active area of research and there have been many successful demonstrations of artificial intelligence.
By the 1950s, scientists, mathematicians, and philosophers had culturally integrated artificial intelligence (or AI) into their brains. Turing: Can machines make good decisions? In 1957, McCarthy convened the DSRPAI conference, which set the stage for the next twenty years of AI research. Artificial Intelligence flourished in the 1960s and 1970s as computers became more powerful, cheaper, and more accessible. There was a high level of optimism and expectations. McCarthy’s expectations were not met; many people attended and came to enjoy themselves. Many of the most significant artificial intelligence goals were achieved between the 1990s and the 2000s.
When Moore’s Law was first published in the 1920s, it predicted that computer memory and speed would double every year. Dragon Systems launched speech recognition software on the Windows platform in the same year. The age of big data is upon us, which means that we now have the ability to collect huge amounts of information that is too large for a human to process. Artificial intelligence has been extremely effective in the fields of technology, banking, marketing, and entertainment in the past. I’m assuming that in the next twenty years (and that is conservative), driverless cars will be on the road. In the long run, the goal is to develop general intelligence, which is a machine capable of performing all cognitive tasks that a human can. As soon as that time comes, there will be a serious discussion about machine policy and ethics.
To make sense of their relationship, visualize them as concentric circles with AI – the idea that came first – the largest, followed by machine learning – which grew later, and finally deep learning – which is driving the AI revolution.
According to Strachey, who was later director of the Programming Research Group at the University of Oxford, the first successful AI program was written in 1951. Strachey’s checkers (draughts) program was developed on a Ferranti Mark I computer at the University of Manchester in England.
Given how quickly technology advances, it’s possible that we’ll only have a few decades left. Artificial general intelligence is expected to be the first to be developed by around 2030. Experts predict that AGI will not be able to pass a consciousness test until at least 2060.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) was a term coined by Dartmouth College in 1956. According to cognitive scientist Marvin Minsky, the future of artificial intelligence is bright. When a number of scientists criticized progress in the field in the 1974-1980 period, government funding for the field dropped, which was known as AI winter.
What Was The First Successful Ai?
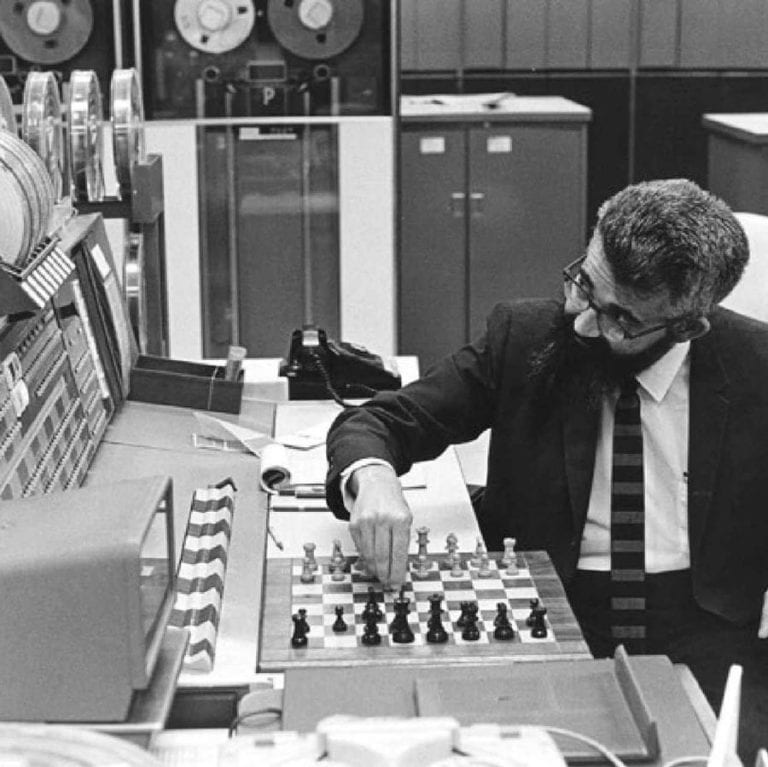

The first successful AI was developed in the 1950s by a team of researchers at Dartmouth College. The AI, called SHRDLU, was able to communicate in natural language and perform simple tasks.
Alan Turing developed the Turing code to crack the enigma code during the Second World War. A machine successfully mastered checkers with the use of an algorithm in 1951. The Dartmouth Conference was organized in 1956 by American computer scientist John McCarthy. Algorithm development was a focus of research in the 1960s. WABOT-1, the first intelligent humanoid robot, was created in 1972. In 1997, IBM’s Deep Blue defeated world chess champion Gary Kasparov in what is regarded as the greatest chess victory in history. Machine learning has become a key commercial advantage for Amazon, Google, Baidu, and others over the last 15 years. We now use a variety of online services that incorporate machine learning.
The WABOT project aimed to create humanoid robots that could interact with humans and other robots. The WABOT-1 was the first android developed in Japan. As a result of the project, humanoid robots of a higher level are now possible.
Humanoid robots may be useful in a variety of settings, including assisting people with disabilities, conducting security patrols, and assisting in disaster relief efforts. They are used in a variety of industries, including research and development, manufacturing, and entertainment.
The WABOT project’s success paved the way for the development of more advanced humanoid robots. It can be used for a variety of purposes, including assisting people with disabilities, performing security patrols, and assisting in disaster relief efforts.
The Dartmouth Workshop And The Creation Of Artificial Intelligence
What was the goal of the Dartmouth Workshop? The goal of the Dartmouth Workshop was to develop a general purpose artificial intelligence program capable of addressing problems in a variety of fields.
Who First Invented Artificial Intelligence?
McCarthy, a Stanford professor and seminal figure of artificial intelligence, died at the age of 84. McCarthy developed the term artificial intelligence and was a towering figure in computer science at Stanford University for the majority of his professional life.
The first computers could pass simple human intelligence tests by the late 1960s, but the field really took off in the early 1970s. At this point in time, computers were capable of answering questions in a variety of domains, including knowledge retrieval, natural language processing, and decision-making. Researchers in the late 1970s and early 1980s focused on improving machines that were intelligent. Machine learning and natural language understanding are two examples of technologies that have come to be based on this. Artificial intelligence has remained an extremely important field of research and development over the years, and new advances are being made on a daily basis. John McCarthy and his colleagues have made significant contributions to the development of machines capable of performing complex tasks and thinking more efficiently than humans.
The First Ai Program
In December 1955, two scientists named Herbert Simon and Allen Newell separately develop the first artificial intelligence program. Logic Theorist was developed by Whitehead and Russell as a replacement for their Principia Mathematica, which solved 38 of the first 52 theorems. One of the significant implications of this milestone in artificial intelligence is that pure mathematical reasoning can now be modeled on a digital computer, paving the way for more sophisticated AI programs.
When Was Artificial Intelligence First Used?

Artificial intelligence was first used in the late 1950s and early 1960s. Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) created the first artificial intelligence program, called the Logic Theorist. This program was designed to solve problems in symbolic logic.
A few years ago, artificial intelligence was a relatively new concept, but its applications are only just beginning to emerge. There are numerous advantages to its use, and it has the potential to profoundly improve our lives. Commerce is one of the most important applications of AI. The use of artificial intelligence will improve product selection, inventory management, and logistics. AI, in addition to commerce, is applicable to a wide range of other tasks. The application is useful in a variety of other domains, such as healthcare. It is becoming increasingly important to incorporate artificial intelligence into healthcare in order to improve the quality of care. AI can also help doctors diagnose patients more accurately, and it can also help nurses provide better care. AI can also aid in the provision of healthcare in addition to billing and record-keeping. We’ve compiled a list of a few of the many ways that AI can help us. The field of artificial intelligence has enormous potential, and its applications are only just beginning to emerge. Many of us have the opportunity to improve our lives by utilizing it.
When Was Artificial Intelligence Invented
The term “artificial intelligence” was first coined by computer scientist John McCarthy in 1955. McCarthy and other early AI researchers were inspired by recent successes in the field of cybernetics, which had demonstrated that simple systems could be designed to exhibit complex behaviour. They began to explore the possibility of creating similar systems that could reason, learn, and solve problems.
The term “artificial intelligence” first appeared at a 1956 conference at Dartmouth College. It wasn’t as simple as it appears to be to artificially intelligent an intelligent being. Several reports have called into question AI’s progress, prompting a drop in government funding and interest. The British government began funding it again in the 1980s, at a time when the field was also revived. This year, the Turing test was fooled by a computer chatbot, which fooled judges into thinking it was a real human. The accomplishment has been met with skepticism, with artificial intelligence experts claiming that only a third of the judges were fooled. Experts are now concerned that the Turing test is no longer a reliable measurement of artificial intelligence.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the science of developing intelligent agents, which are computers that can reason, learn, and act autonomously. AI is a branch of research. WABOT-1, the first humanoid robot capable of intelligent behavior, was developed in Japan in 1972. Artificial intelligence has since evolved into a sophisticated field that deals with the design and construction of computer programs that can reason, learn, and act independently. Artificial intelligence is used in a variety of industries today, including manufacturing, finance, health care, and search engines. Intelligent chatbots, which are computer programs that can talk to humans in natural language, are also being created as a result of artificial intelligence. AI is still in its early stages, and significant knowledge remains to be gained. However, as research and development continues, AI will soon play an important role in our lives.
Who Invented Ai For The First Time?
Artificial Intelligence was founded in 1952 and 1955. The year 1955 is one of the most recent years. Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon created the first artificial intelligence program, which was known as Logic Theorist. This program proved 38 of 52 Mathematics Theorems, and it discovered new and better proofs for some of them.

