Skip connections are a type of connection between layers in a neural network that allow information to bypass intermediate layers. This can be useful for training very deep neural networks, since it can help prevent the network from getting “stuck” in a local minimum. Additionally, skip connections can help improve the network’s generalization performance by making it easier for the network to learn the identity function.
Deep learning is the study of algorithms that are inspired by the brain and the neural network. Skip connections avoid some neural network layers and feed the output of one layer to the next, with the input of one layer feeding the output of the other. The module is a standard module that is used to provide gradient support along backpropagation. Degradation problems in deep neural nets can be resolved by skipping connections. The ability to reuse features is ensured by the use of skip connections for residual networks or ResNets. The non-sequential layer contains both addition and concatenation of skips. ResNet is widely regarded as a game-changer in the deep learning community.
The main goal of ResNets is to stack skip residual blocks together and preserve gradient by using identity functions. Deep learning is known to be based on DenseNet, which is the most widely used deep learning architecture. Rather than simply summarising the output feature maps, it concatenates them to the next layer. Skip connections solve the problem of vanishing gradient by providing continuous gradient flows from the first layer to the final layer. A feature map can be dimensionalized by using convolutional layers within the decoder. Skip connections can be used to maintain feature reuse while also stabilizing training and convergence. The Ronneberger et al. proposed the use of U-Nets for biological picture segmentation.
The Residual Connections method of skipping back and forth between layer inputs rather than learning unreferenced functions is referred to as a skip-connection.
Why Do Skip Connections Help?
Skip connections are a way of providing shortcuts for information to flow between layers in a neural network. By providing a skip connection, the network can learn to better propagate information between layers, which can improve the overall performance of the network.
Deep neural networks, as opposed to shallow neural networks, are better suited to learning complex functions more efficiently. Deep neural nets’ performance decreases as the model’s depth is increased. A degraded material is referred to as a problem. People in the Deep Learning community have developed solutions to these problems. When training accuracy degrades, it indicates that there aren’t as many systems that can be optimized similarly. Skip connections were used to solve problems in a variety of architectures. In this manner, some layers in the neural network are bypassed, while some are passed along as an input to the next layer.
The sections that follow will provide a thorough explanation of each topic. In Neural Networks, Skip Connections can be added and subtracted in two fundamental ways. He et al. proposed a set of residual networks in their paper. It was developed in 2015 to solve a problem with image classification. Next, we’ll go over a DenseNets variant of skip connections that is based on ResNets. In this section, we will use Skip Connections to create ResNets and DesNets from scratch. The PyTorch tool enables us to load ResNet models with weights trained using the ImageNet data set. In the following step, we’ll construct a dense block that includes an arbitrary number of DenseNet layers.
What Is The Use Of Skip Connection In Image Denoising Networks?
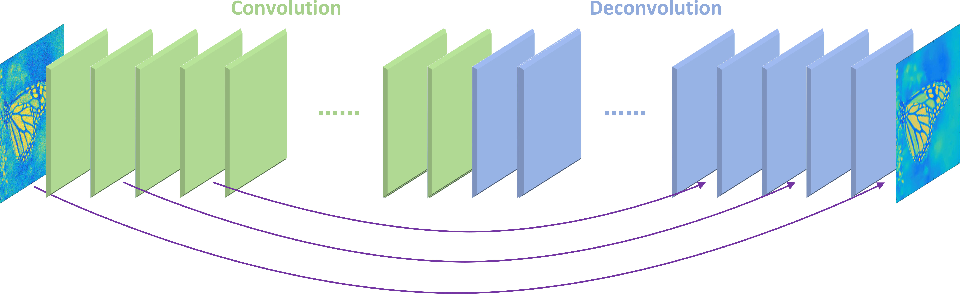
Skip connection is a technique used to improve the performance of image denoising networks by providing a shortcut for information to flow between layers. This allows the network to learn more complex patterns and improve the quality of the final output.
It is an example of a’self-supervised’ algorithm in which the input data is used to generate targets. An autoencoder is made up of the following components: an Encoder, a Bottleneck, and a Decoder. In images, noise is the result of a random variation in color or brightness, which degrades the image’s quality. As an alternative,’skip connections’ can be added from the encoder to the decoder, which can significantly improve performance. The input image will have a more clearly defined decompression. Images were taken from a Flickr set of images that was published on Kaggle. Because of computational limitations, images have been scaled down to a smaller size (128,128,3).
This decoder was built using a convolution or deconvolutional layer structure. Both models were tested for 200 epochs with a mini-batch size of 32 units. The first three convolutional layers’ activation outputs show that most of the image information is retained. If this is the case, the image’s noise would be retained as well. The model’s information is now quite abstract as we move deeper into the model. By starting with lower-level features, such as borders, corners, and angles, the model gains a higher level of realism. In order to perform skip connections, it must first connect the encoder’s third and fifth convolutional layers before it can connect the decoder’s sixth and final deconvolutional layer. In addition to denoising images, this can be used for any image reconstruction application using autoencoders. In addition to training the model with varying levels of noise factor, it is possible to generalize its results.
Resnet’s Skip Connections Speed Up Training And Improve Accuracy
The skip connections in ResNet solve the problem of vanishing gradient in deep neural networks by facilitating this alternate shortcut path for the gradient to flow through. The network can learn faster and more accurately as a result of this because it can ignore parts of the network that may be causing the gradient to decrease. Similarly, in u net segmentation architectures, skip connections assist in recovering the full spatial resolution displayed on the network output. The main advantage of fully convolutional methods is that they do not rely as heavily on feature extraction. Using skip connections allows us to maintain a high level of accuracy while still providing a quick learning experience.
Why Are There Skip Connections In Unet?
Skip connections are used in U-Net models to help the model learn to classify images by providing a shortcut between the input and output layers. The skip connections help the model to learn the relationships between the pixels in the input image and the class labels.
A skipped connection serves to reconnect the network of the initialy that the user is attempting to learn. Skip connections may result in a significant loss of information from one layer to the next. In order to detect an emergency vehicle, you must detect both a larger feature (vehicle) and a more finelygrained feature (siren), which are combined in later networks. Unet was designed to segment images to achieve very precise segmentation, which meant it had to be able to segment an image to the highest quality in order to achieve this. The various layers of convolutions used to decode the exact line features would be extremely difficult, and this task would be even more difficult. Because of the larger and smaller convolutional sizes, you can get features at different resolutions using them.
What Purpose Did The Skip Connection Solve In Resnet?
ResNet’s skip connections, which solve the problem of vanishing gradient in deep neural networks by allowing the gradient to flow through an alternate shortcut path, are implemented using this method.
Some research has claimed that ResNet or Highway networks can reduce the vanishing/explosing problem in deep neural networks. Skipping connections, I suppose, makes the function appear smoother and less convoluted, which is unrelated to the exploding gradient problem. As previously stated, residual connections reduce the amount of feature space a network can search for.
Noise In The Output Of The Previous Laye
H (x) is a function that can only be written as a function of x from the previous layer if x from the previous layer is only counted as input to the function:
To find the input to the current layer, go to the location where the current layer is located.
Consider the case in which there is some noise in the output of the previous layer. As illustrated below, the noise will cause the error to be additive. Where does the noise from the previous layer go?
As a result, br> is used to learn a function of this residual connection. In the activation section, the residual connection’s function is located.
Skip Connections Neural Network
A skip connection neural network is a type of neural network that uses skip connections to improve the flow of information between different layers of the network. Skip connections are simply connections that skip over one or more layers, and they can be used to improve the performance of a neural network by reducing the amount of information that is lost as it is propagated through the network.
Why Use Skip Connections
Skip connections are used in computer vision architectures to help improve performance by providing a direct path between two parts of the network. This can help to improve the flow of information and prevent overfitting.
The Benefits Of Skip Connection-based Neural Networks
A skip connection neural network is a powerful tool for scene comprehension that is used in a variety of applications such as image recognition, video encoding, and text recognition. Dense block neural networks can also be used to aid in scene understanding, but their training is more difficult.
Why Skip Connections Improve Performance Of Cnn
Skip connections are beneficial to CNN performance as they enable the network to learn from previous layers and improve the accuracy of predictions. By having a connection between the layers, the network can better learn patterns and improve the overall performance of the CNN.
Since the introduction of neural networks (NNs) to denoising techniques, their performance has steadily improved. The use of skip connections in speech enhancement systems has been shown to increase the performance of NNs. We present an architectural design of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) with no connections for speech enhancement. With the help of speech enhancement, environmental noises can be avoided from negatively impacting the target’s voice. As a result of speech enhancement, NNs with skip connections have better denoising abilities than baseline NNs, allowing speech applications such as Man-Machine speech interaction, hearing aids, and so on to function more effectively. More accurate methods are possible if the improvement method reaches 85%, 90%, and 92% accuracy, which is higher than SVM, VGG-16, andBPNET algorithms. To improve image quality, a GAN network is used in this method to enhance the image and to increase the integrity of the image data set.
In contrast to image extraction and fusion, which are processes that combine multiple images, convolution neural networks use extracted and fused images as their input. Speech enhancement and recognition can be performed more easily using deep learning models than they can in the real world. Based on this model, parameters and linear prediction coefficients (LPCs) for clean speech and noise signals are modeled. When noise levels are impacted, they fluctuate. It is possible to incorporate a bidirectional GRUs network into an input sequence to predict parameters both in the present and in the future. The proposed model was able to improve word quality, intelligibility, and word error rates by 37.5%, 18.79%, and 19.13% when using various noisy environments. The CNN Deep Web enhanced speech method is superior to the Wiener filtering method.
According to the metrics, Deep CNN is outperforming conventional CNN techniques. In the case of speech separation, there is a distinction between target and background noise. Signal processing problems that involve speech separation are traditionally studied. A more recent approach considers speech separation as a supervised learning issue. Automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems have been shown to be increasingly effective in everyday life. Systems are frequently used in noisy environments where they are used. This can lead to a poor recording of speech and an impaired performance of speech recognition systems.
The purpose of this book is to provide a comprehensive review of current state-of-the-art techniques for improving the robustness of ASO systems. This study describes a novel deep neural network architecture with a multi-objective learning and ensembling (MOLE) framework that is intended to enhance speech. Using the concept of combining weak models with powerful classifiers, MOLE is formed by two compact deep neural networks (DNNs) that combine strong and weak models. We develop a new objective function that incorporates the clean phase into model training in order to better estimate spectral magnitudes. MOLE can achieve consistent improvements over long-term memory (LSTM) based approaches as well as over short-term memory (LSM) based approaches because its model size is very small and latency is low. A single frame MOLE-based SE system outperforms an LSTM-based SE system with a 7-frame input expansion at a 3-frame delay. We introduce deep convolutional generative adversarial networks (DCGANs), a class of CNNs with architectural constraints that we demonstrate are ideal for unsupervised learning.
Skip Connections Vs Residual Connections
A residual connection is the same thing as a skip connection. They eliminate the need for a network to use non-linear activation methods by allowing gradient flows directly through the network.
Deep neural networks are networks of connections that send information from a specific layer to other layers over time. It reduces the issue of vanishing gradient and degrading accuracy that frequently accompany deep neural networks. We will learn about skip connections in depth in sections on how they aid neural networks. You add x to F(x) because it adds an identity mapping to the input. As a result, it has a rough idea of what it will need to learn in order to function properly. To determine how much weight is lost during backpropagation, we use the loss function. Because the model can ignore the mapping of specific layers, it can implement this method for deep networks.
Deep neural networks can pass semantic information at the lower level to the network’s remaining layers without connecting to the network’s upper layers. We can save information that would have gone away if we had passed it through too many layers of abstraction. The primary architectures that utilize skip connections are ResNet50 and DenseNets. ResNets defeated AlexNet in the imagenet classification challenge in 2015. In this architecture, the image is inputted with a 224x224x3 file and a 33 filter, followed by a MaxPooling layer. After that, there are 16 more blocks. Each residual block contains three convolutional layers that transform the dimensionality of the data.
Advantages Of Residual Connections
In other words, if layer i’s output is fed into layer i+1, layer i’s output is fed into layer i+2. In the following table, we can represent the residual connection between layers i and i+n. This corresponds to (1- F)x_i, where x_i is the input layer for layers b, c, and d. Using residual connections allows data to flow more directly from the input to the output, circumventing some layers that are typically present in a typical output connection.
Skip Connections Keras
In computer vision, a skip connection, or shortcut connection, is a connection between layers of a neural network that allows the gradient signal to bypass one or more layers. This can be useful in training very deep neural networks, which are otherwise difficult to train due to the vanishing gradient problem.
Skip connections are also useful in creating models that are easier to interpret, as they provide a direct path from the input to the output. This can be helpful in understanding how the model is making predictions.
U-net Skip Connections
U-net skip connections are a type of connection used in neural networks. They are used to improve the accuracy of the network by providing a direct connection between the input and output layers. This allows the network to learn the input and output data more accurately.
The Benefits Of Skip Connections
A full convolutional method capable of semantic segmentation is a fully convolutional method that has been shown to recover the full spatial resolution at the network output after Skip connections. These connections are referred to as long skip connections, as defined by us. Skip connections, in short, serve as an inverse of gradient generators to solve the problem of vanishing gradient and provide more context to the network’s layers later on. The more context you have at each layer, the better your network will perform. Deep features are the most important aspect of network security. Rather than learning unreferenced functions through skip connections, residual connections refer to residual functions with reference to the layer inputs. A formal way to achieve the desired underlying mapping is to allow the stacked nonlinear layers to fit another mapping of F ( x ). The letter H (x) is also known as the letter x.
