Neural networks are a type of machine learning algorithm that are used to model complex patterns in data. In order to train a neural network, the data must be prepared in a specific format. The data must be split into input and output values, and the input values must be scaled to a range between 0 and 1. The output values must be one-hot encoded, which means that each value must be represented as a vector of zeros with a single 1 in the position of the value. For example, if the output values are classes 1, 2, and 3, then the one-hot encoded vectors would be [1,0,0], [0,1,0], and [0,0,1].
Data preparation is an important step in neural network analysis and should be done at the very beginning. Because there are so many sources and large amounts of data to prepare, it has become more difficult. The time and effort required to prepare data for analysis is 50%-70% of the total time and effort involved in a data analysis project. The most commonly used research method for biodiesel is artificial neural networks (ANN). The model-based nature of biodiesel research has traditionally required modeling of (trans)esterification processes, the physical properties of biodiesel, and the design of biodiesel internal combustion engines. A diamine ligand with an electron-pulling group was discovered in this study, according to the researchers. The Cu(I) complex was studied and discussed using various techniques, including nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), single crystal analysis, density functional theory calculations, and photophysical measurements.
Metal-to-ligand-charge-transfer (MLCT) and ligand duality are present, as shown by the electronic transition of the Cu(I) complex. The polymer immobilization effect, in addition to reducing MLCT geometric distortion, could improve emissive performance by increasing emission blue shift, long excited state lifetime, and photostability. A methyl group was attached to this diamine ligand in order to improve its steric scavenging potential. Ca2MgSi2O7: Eu2+ fibers are expected to be used in a wide range of optical detectors, bio-labeling, and full-color displays. The oxygen sensing properties of the cylinders were evaluated by exposing them to a silica molecular sieve SBA-15. composite sensors had better sensitivity and photostability than non-composite sensors.
How Is Data Prepared For Analysis?
Data preparation refers to the process of cleaning and transforming raw data prior to analysis and processing. It is a critical step in the process because it involves reformatting data, making changes to data, and combining data sets to enrich them.
A data preparation process converts raw data into solid information. It is intended to help reduce errors and inaccuracies during data processing. Preparing data is a long-term process that must be completed in order to complete analysis. The goal of this post is to go over data integration, data profiling, data cleaning, and data governance. Data that cannot be transformed or manipulated for reliability may be subject to manual transformation. The questions that you should ask are intended to clarify the significance of data quality. Because the tools required technical knowledge, data preparation is initially restricted to IT teams. The data preparation software has evolved and, as of today, allows business users to make their own preparations.
How Does Neural Network Process Data?
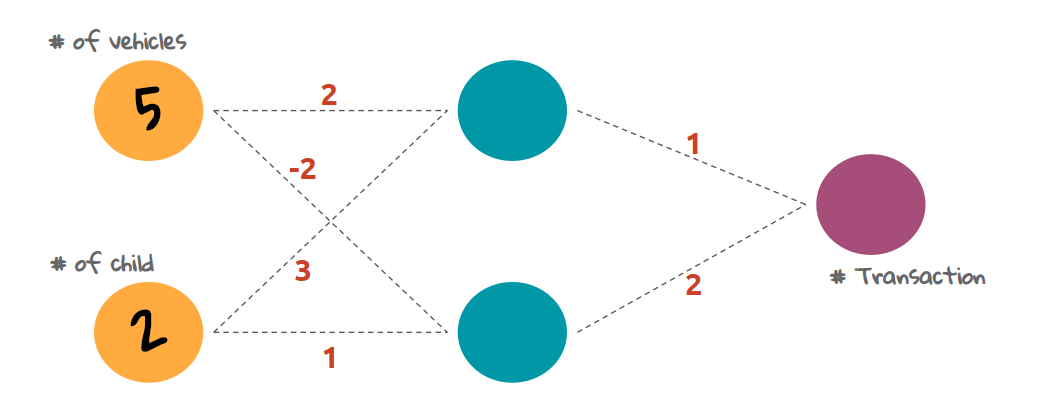
A neural network processes data by creating a series of layers, each of which is made up of a set of neurons. The first layer of neurons takes in the raw data, and each subsequent layer processes the data further. The final layer of neurons produces the output of the neural network.
The four major components of a neural network are layers (the row of neurons), neuron (blue, orange, and purple circles), weight (arrow), and bias (not shown in the figure). A neuron is made up of three types: an input neuron, a hidden neuron, and a production neuron. The processing of neural networks is very simple, in contrast to the algorithm used for learning it. The activation function of a Neuron converts values it receives into instructions that it processes. There are two types of activation functions: 1. All of these operations can be re-written in the form of matrix operations. A pair of neurons will be added to the output layer if we want to solve the classification problem.

