There are multiple ways to convert a BERT model to PyTorch. The most common method is to use the “hugging face” library. This library has a wide range of functions that can be used to convert BERT models to PyTorch. Another common method is to use the “transformers” library. This library also has a wide range of functions that can be used to convert BERT models to PyTorch.
In 2018, Google published a paper titled “Pre-training of deep bitonal transformers for language understanding.” As part of this paper, they used a language Encoder model called BERT (Bidirectional Representation with Transformers) to achieve high performance in tasks such as Question Answering, Natural Language Inference, Classification, and General Language Understanding Evaluation. The BERT transformer architecture is made up of a transformer architecture based on inverse linear switch mode technology (LSTM). Because it considers both words from different angles, it can distinguish between words that are spelled similarly but have different meanings. Jeremy Howard and Sebastian Ruder published a paper in 2018 titled Universal Language Model Fine-tuning or ULM-FiT, which argued that transfer learning can be used inNLP just as effectively as computer vision. The OpenAI team developed the OpenAI GPTrative Gene Pre-trained Transformer, or GPT. BERT’s self-monitoring mechanism is self-replicating.
We can generate inputs and labels from raw corpus without explicitly programming them by leveraging it. During the training, BERT employs a wide range of tokens, including [CLS], [MASK], [SEP], and so on. These methods enable it to distinguish between a sentence that begins with a single word and is masked, as well as between two sentences that separate. Next, we’ll need to create a function that formats embedded sequences in three different ways. Embedding symbols, segments, and positions is a type of embedment. The cat is moving in the sentence The cat is walking. This function should generate a sequence in the following manner when the dog barks.
Albert’s logic is complex, so it is difficult to understand when it is perceived slowly. As a result, it makes more sense to explain each component in its entirety and its function. It is the first layer that takes the input and generates a lookup table. In addition, because BERT is bifunctional, it will maintain contextual relationships. BERT Encoders can be applied to three inputs: values, context vectors, and attention. Scaled dot product attention is calculated using a softmax function that ranges from 0 to 1. As part of the feed-forward network, the output from the multihead is forwarded to the encoder.
However, the transformer’s decoder section is replaced with a shallow network that can be used for classification purposes. There is no doubt that BERT is one of the most advanced NLP models available today. BERT can be created by itself, or it can be downloaded as a pre-trained version. If you do this, you do not need to use softmax; instead, you will get a clean feed-forward neural net result without it. The parameters and dataset can be used to mimic SOTA performances over a 3 to 10 epoch period.
As part of the new version, we must import the appropriate modules and models from TF, TF-Hub, and TF-text; then load the input into the preprocessor model; and finally load the preprocessed input into the BERT encoder.
How Do I Load A Pretrained Bert Model In Pytorch?
To load a pre-trained BERT model in PyTorch, you will first need to install the PyTorch BERT package. Once you have installed the package, you can then use the “bert-base-uncased” model that is included in the package. To use the model, you will need to specify the path to the model weights file and the path to thevocabulary file.
This repository contains op-for-op PyTorch reimplementations, pre-trained models, and fine-tuning examples for: BERT, OpenAI GPT, and Transformer-XL. The implementation was tested on multiple datasets and should perform as well as the TensorFlow implementation. More details about the examples can be found in the Examples section. PyTorch pretrained bert can be installed through pip by following the steps below. If you want to recreate the original tokenization process of the OpenAI GPT model, you must install ftfy (if you’re using Python 2) and SpaCy (if you’re using Java). Pytest can be used to run tests that are in the tests folder. Python includes the following classes: Bert PyTorch models (torch.nn.
Module) with pre-trained weights (in the modeling.gpt2.py file) will be used. There are three openai GPT PyTorches, two transformer-xli models, three bert models, and three transformer-xli models. Command-line interface that allows you to convert TensorFlow checkpoints (openai.py, modeling_transfo_xl.py). As a result of these resources, the repository now contains: The following are five examples of how to use BERT in addition to three notebooks that were used to check that they behaved similarly (the notebooks folder). Using WikiText-103 as a reference, you can build this quick-start example by using TransfoXLTokenizer, TransfoXLModel, and OpenAIGPTLMHead classes. Detailed information about these classes can be found in the doc section below. BERT_CLASS can be instantiated as a tokenizer for a Google AI, an OpenAI model, or a PyTorch-trained model; for a saved model or a pretrained model, BERT_CLASS can be instantiated as a tokenizer.
If you know that case information is critical to your task (e.g., Named Entity Recognition or Part-of-Speech tagging), you should use the Uncased model. The original TensorFlow repository, as well as the Transformer-XL and Multilingual versions of the GitHub, contain information about the Multilingual and Chinese models. To reload a fine-tuned model, you must first save three different types of files. BertForMaskedLM, as the name suggests, is a fine-tuning model that includes the BertModel and a sequence-level (pair of sequences) classifier in addition to the BertModel. The following script demonstrates how to use this class in the run_lm_finetuning.py script. It is used to fine-tune the BERT language model on a specific text corpus byPredictionBertForNextSentencePrediction. BertModel provides token-level classifiers to the entire sequence of last hidden states and is a fine tuning model.
OpenAI GPT employs a single embedding matrix to store the word and its embeddings. By using set_num_special_tokens() function, you can control the number of special tokens that are used. OpenAI GPT-2 Transformer XL employs a layer of tokens and position embeddings, followed by a set of 12 identical self-attention blocks. This tool employs TensorFlow model inputs and outputs in its outputs. In this example, I will show you how to extract the entire hidden states list from the model output. TransfoXLTokenizer can be used for adaptive softmax, and it can be used to count tokens in a corpus with tokens for counting. A GPT2 tokenizer performs byte-level Byte-Pair-Encoding (BPE) tokenization.
OpenAI Adam employs a similar bias-tolerant algorithm to the Adam optimizer. Schedule objects are included with learning rate schedules as well as additional schedules. The NVIDIA team’s testing of pytorch-BERT and my own experiments on reproducing them can be consulted in the relevant PR of the current repository. To use Distributed Training, you must run a single script on each of your machines. This test set is significantly different from the one published on the GLUE website. Several examples of scripts that can be used to fine-tune BERT using the pretraining objective (a combination of masked-language modeling and next-sentence prediction loss) can be found here. The README file contains a list of scripts that can be used for tuning.
SQuAD can be downloaded by following the links to a directory named $SQUAD_DIR, where the data should be saved. Examples of OpenAI GPT, Transformer-XL, and GPT-2 are shown here. It takes 18 hours to fine tune BERT-large on SQuAD with a server with 4 k-80 (these are pretty old now). It’s worth noting that if you have a recent GPU (such as the NVIDIA Volta series), you should run a 16-bit fine tuning implementation (FP16). In contrast to the previous results (which were slightly higher), the results were similarly similar.
Bert: A Better Way To Train Your Models
Import numpy as np import time import GPU_utils import in python. Import sys import argparse import json import bert #Initialize the torch and optimizations with these procedures. # Set the dictionary to local memory by calling torch. The saved items must be loaded in the torch.load(*/dictionaries/bert-base-uncased.json) command. The torch.load (string(‘>/dictionaries/bert-large-uncased.json) print(‘Result: %,%,%,%,%,%) format(result)
Is Bert Available In Pytorch?
At this time, there is no Bert model available in Pytorch.
B.E.R. BERT, or Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers, is a new pre-training method for generating high-quality results for Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks using digital transformers. The BERT model employs the same architecture as the transformer’s encoder. The NVIDIA Volta V100 and NVIDIA Ampere A100 GPUs are used for faster training. The APEX library is used by NVIDIA to enable mixed precision training. Apex, a PyTorch extension with utilities, streamlines mixed precision and distributed training. LAMB can be used on multi-node systems to run up to 1024 graphics cards, allowing for 72x performance improvements. To use mixed precision training, you must first complete a series of steps.
To enable mixed precision training, the run_pretraining.py and run_squad.py scripts must both contain the fp16 argument. Tensor operations are performed in the TensorFloat-32 (TF32) mode on NVIDIA A100 GPUs for handling matrix math. If you compare it to single-precision floating-point math (FP32) on NVIDIA Volta GPUs, you will notice that it provides up to ten times faster performance.
Bert Example Pytorch
Bert Example Pytorch is a great tool for deep learning. It is very easy to use and has a lot of features. Bert is a great tool for natural language processing.
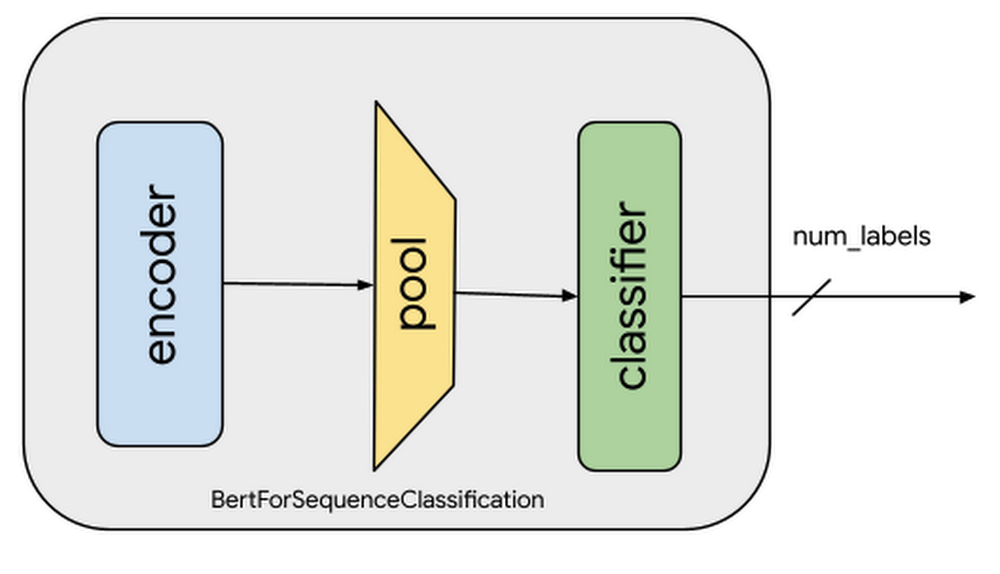
Bert is a state-of-the-art library that trains the model for implementing natural language processing. BERTs are examples or portrayals that are embedded into basic words using an encoder. We may require a pre-trained BERT model to train layers in deep learning and create new models after they are unleveled. The calibration of BERT is essentially a method for preparing a model to perform admirably while preparing information in much less time and effort. The BERT model can be adjusted with only one layer of design changes to achieve best-in-class models for a wide range of assignments, such as question addressing and language deduction, without requiring extensive design changes. The BERT model employs transformer decoders over encoders in a model that is primarily based on transformer decoders. A two-way token, [CLS] and [SEP], are used by BERT. We illustrated the program’s final result by using the following screenshot. As a result of this article, you will gain a better understanding of the Pytorch bert.
Convert Tensorflow Model To Pytorch
There are many ways to convert a TensorFlow model to PyTorch. One way is to use the PyTorch converter tool, which can be found here: https://pytorch.org/tutorials/advanced/super_resolution_with_caffe2.html. Another way is to manually convert the model using the methods described in the PyTorch documentation: https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torchvision/models.html.
In this tutorial, we will look at how to convert a PyTorch model to TensorFlow. On the Open Neural Network Exchange (ONNX), there is a Neural Network Pipeline. ONNX is a free, open-source AI project that aims to make it possible to interchange neural network models among different tools to select the best combination of these tools. Both versions of the neural network use TensorFlow and PyTorch to map FCN ResNet18 blocks. The NCHW (batch size, channels, height, width) format was converted to NHWC by inserting change_ordering=True into it. Because the default TF data format is NHWC, the shape of the input layer has been changed from 3*725*1920 to 725*1920*3. Let’s look at the response map for class A:
