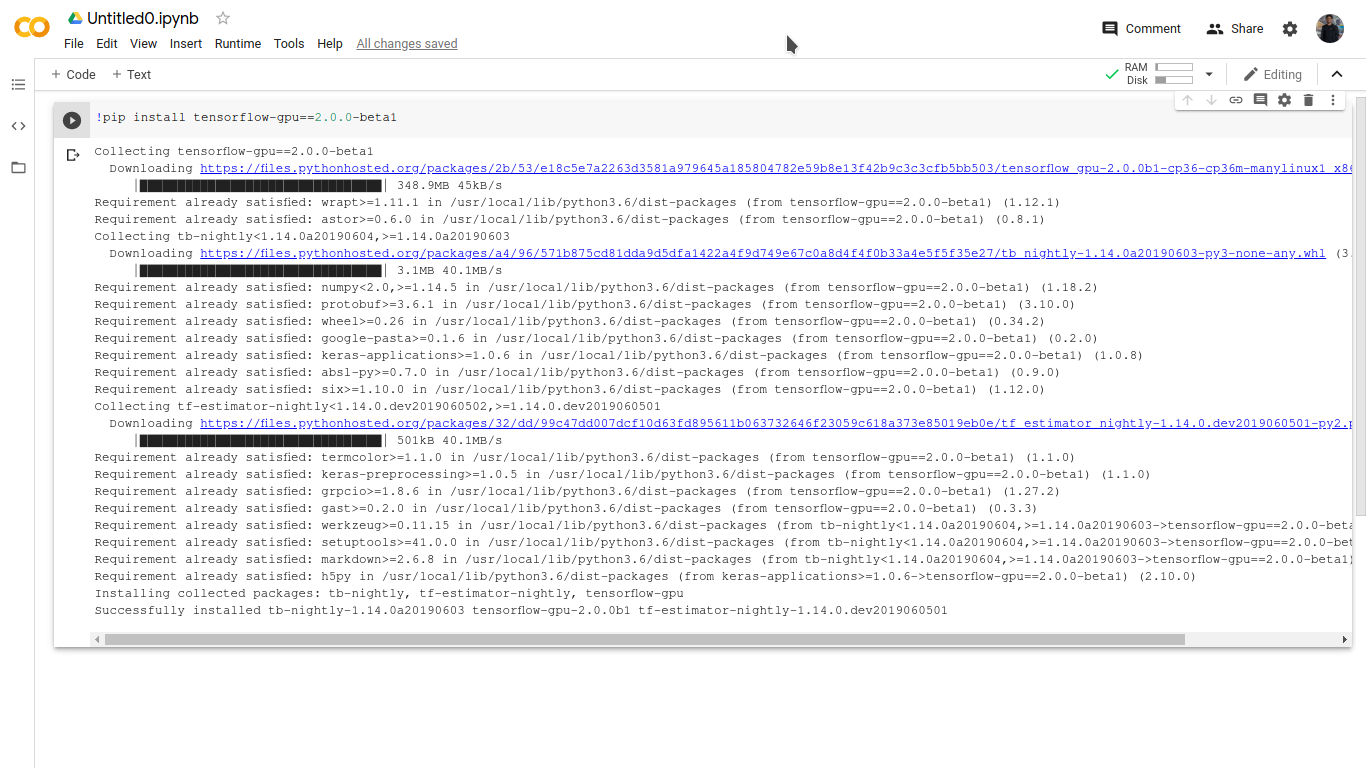
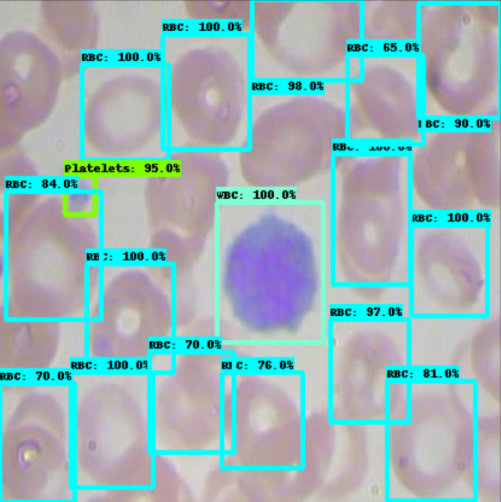
Mint is a free and open source operating system based on Ubuntu. It is one of the most popular Linux distributions and is very easy to use. Many people use it for programming because it is very stable and has a lot of features. TensorFlow is a open source software library for machine learning, developed by Google. It can be used for a wide variety of tasks such as classification, regression, and clustering. TensorFlow is very popular among developers because it is easy to use and has a lot of features. So, will tensorflow work on mint? The answer is yes! TensorFlow is compatible with a wide range of operating systems, including Mint. You can install TensorFlow on Mint using the following instructions: 1. first, you need to add the TensorFlow repository to your sources. list: echo “deb [arch=amd64] https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow-serving-apt stable tensorflow-model-server tensorflow-model-server-universal” | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/tensorflow-serving.list curl https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow-serving-apt/tensorflow-serving.release.pub.gpg | sudo apt-key add – 2. next, you need to update the packages list and install TensorFlow: sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install tensorflow-model-server 3. finally, you need to start the TensorFlow server: sudo tensorflow_model_server –rest_api_port=8501 –model_base_path=/models You can now access the TensorFlow server at http://localhost:8501.
Can Tensorflow Run On Linux?

TensorFlow is used in Python 3.7–3.10 on these 64-bit systems: Python 3.8–3.10. It is recommended that you have Ubuntu 16.04 or later.
Scikit Learn from Google makes it simple to use the TensorFlow fit/predict model by making it as simple as possible. TensorFlow is capable of running computations on a wide range of hardware platforms, including CPUs and graphics processing units. As a result, it can be used by data scientists for a wide range of applications, including machine learning, data analysis, and scientific computing.
Is Tensorflow The Right Tool For Your Data Analysis And Machine Learning Needs?
The TensorFlow data analysis and machine learning library is an open-source platform. It is used by a number of notable companies, including Google and Facebook. Despite its size and complexity, it may not be the best choice for everyone. TensorFlow is currently only compatible with Python 3.5. If you’re using a different version of Python, or if you’re using Windows, you should create it on your own. Because the Raspberry Pi 4 does not have enough resources to support TensorFlow, it will also not be supported. The program is free to use, but it is a great way to manage packages and install new virtual environments.
Which Python Version Is Best For Tensorflow?
It is best to start with Python version 3.4 or later when learning TensorFlow. Consider the steps below to install TensorFlow on your Windows computer. * Check that the Python version you intend to install is up to date.
Python 3.7-4.9 and Python 3.5-4.9 are both 64-bit systems that TensorFlow is tested and supported on. TensorFlow can be installed using anaconda or pip in Windows. The GPU version is best suited for use with Cuda Toolkit 7.5 and cuDNN v5. The maximum RAM capacity available is 8 GB, but 16 GB is ideal. In terms of environment management, Pip is the default Python package manager, whereas Conda is a cross-platform environment manager that is entirely dependent on the language. Conda installs software written in any language while Pip installs Python packages. The Anaconda library is far superior to PyCharm for building machine learning models, and Python is the best platform for developing websites.
The PyCharm IDE is built with IPython notebook and includes an interactive Python console. Python virtual environments can be created using Python’s conda and pycharm. Because the Anaconda python package includes Intel MKL, most numpy calculations can be done faster than in vanilla Python. Those who build commercial applications should consider using ActivePython as their primary programming language.
Deep learning and TensorFlow can be performed with the most precision thanks to the RTX 2080 Ti graphics card. The graphics card has 6GB of GDDR5X memory, which is significantly more memory than previous generations. In TensorFlow, it is critical to have a powerful graphics card. The RTX 2080Ti is the best deep learning system on the market because it is the most powerful and performs the best. In addition, two NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080Ti graphics cards can be used to get the best performance. The RTX 2080Ti is the best performing deep learning chip on the market.
Is Tensorflow Compatible With Python?
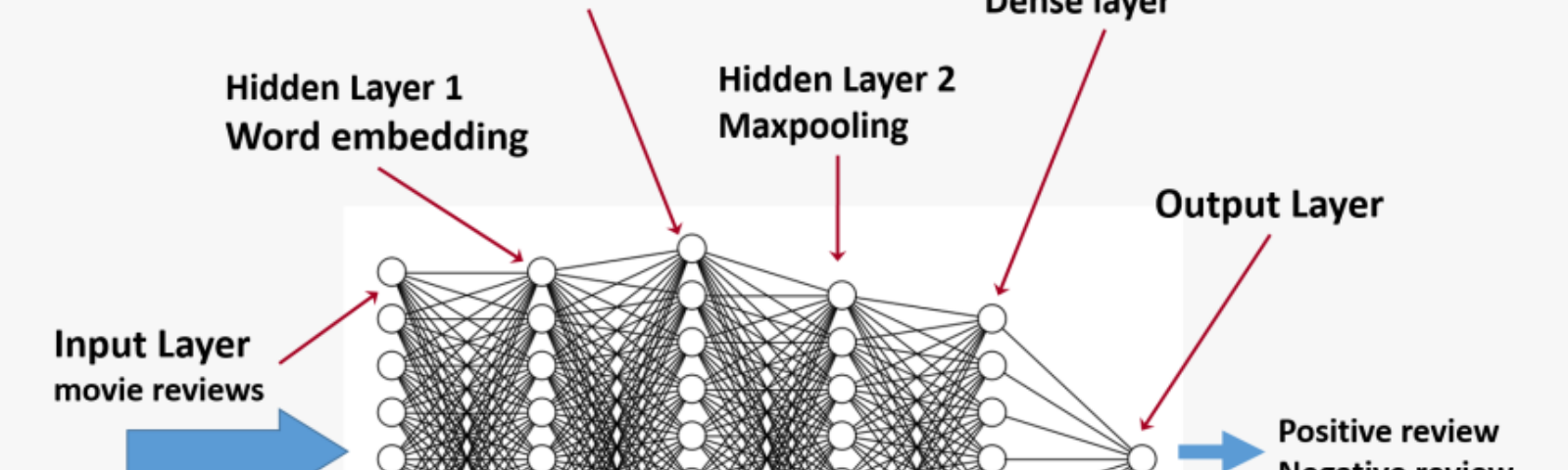
Yes, tensorflow is compatible with python. You can find the instructions on how to install it here: https://www.tensorflow.org/install/
Although TensorFlow does not officially support Ubuntu, the instructions below may be applicable to other distributions. Upgrading your pip installation to a recent version is essential if you want to use TensorFlow. Before installing the NVIDIA GPU driver, make sure you have it. Before installing CUDA and cuDNN, you must first complete the conda application. If you are using Tensorflow with pip, you must upgrade to the most recent version in order to run it. Installing TensorFlow with GPU support should be done in accordance with the Miniconda model. It keeps your computer from altering any installed software by creating a separate environment.
Furthermore, this is the most convenient way to install software, particularly for GPU setup. To ensure that you are running the most recent version of TensorFlow, upgrade your pip installation. This section can be skipped if TensorFlow is only run on the CPU. If you do not already have, install the NVIDIA GPU driver first. Both CUDA and cuDNN should be installed after the conda has been downloaded.
Tensorflow is a free and open-source software library for data analysis and machine learning. The program is used for training artificial intelligence (AI) models, such as speech recognition and natural language processing, as well as other calculations on data sets. This program can be used for a variety of purposes, including text and image analysis.
Tensorflow is a free software that is written in Tensorflow. js library can be used by both the client and server side to analyze data and speed up calculations. TensorFlow is an application for iOS. JIT compilers also speed up the execution of js, as shown in Figure 1. As a result, it is an excellent choice for data analysis tasks that require quick results.