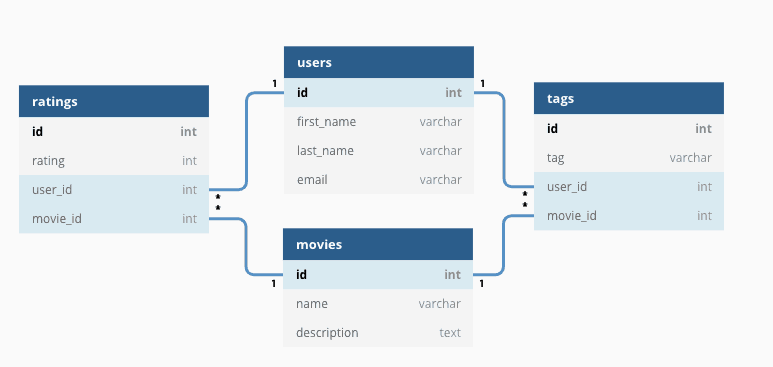
There’s a solution that not only manages vast datasets effortlessly but also provides valuable insights. Imagine a tool that manages huge volumes of data while also efficiently navigating them. Panther, a game-changer in the world of data analytics, is about to hit the market. Can Panther analyze large data sets with finesse and precision?
It is far more than capable of carrying out a given task. With its robust capabilities, this tool can handle massive datasets while maintaining scalability and efficiency. Panther’s ability to solve complex data puzzles no matter how large or small your data is demonstrates its dependability. The key to big data analysis is not just a tool; it is also a key that opens doors to a wealth of actionable insights.
As we embark on this exploration, you will be taken on a journey that will alter your life. Panther’s ability to analyze large data sets is discussed in greater depth in this article, and you will discover how you can take advantage of its full potential through case studies and real-world examples. Using Panther for data-driven decision-making provides you with insights into the nuances, challenges, and successes that come with it. Panther is a powerful tool that assists you in navigating the vast landscape of Big Data with confidence and precision. The power of Panther is to be unlocked in order to revolutionize the field of big data analysis.
Understanding Panther
In delving into the intricacies of Panther, one finds a formidable ally in the vast arena of big data analysis. The overview of Panther’s capabilities reveals a tool designed not merely for analysis but for mastery of expansive datasets. Its key features, akin to a well-tailored suit, seamlessly cater to the demands of data exploration and deciphering complex patterns. Picture a tool that not only navigates through voluminous datasets but does so with finesse, unlocking the doors to a treasure trove of insights.
Panther’s Versatility in a Glance:
-
Scalability Beyond Boundaries: Panther’s prowess lies in its ability to scale effortlessly, accommodating datasets of varying magnitudes. From terabytes to petabytes, this tool stands resilient, offering a panoramic view of data landscapes without compromising efficiency.
-
Intuitive Data Visualization: Navigating the labyrinth of data is made simpler through Panther’s sophisticated data visualization tools. It’s not just about numbers; it’s about translating data into visual narratives that are both insightful and actionable.
-
Statistical Wizardry: Panther emerges as a statistical virtuoso, equipped with tools that delve into the depths of data intricacies. It’s more than just algorithms; it’s a guide through the statistical jungle, helping users decipher trends, correlations, and outliers.
Key Features: Unveiling Panther’s Arsenal:
-
Machine Learning Capabilities: Panther goes beyond traditional analytics, incorporating machine learning seamlessly. This feature empowers users to not just analyze historical data but predict future trends, a valuable asset for strategic decision-making.
-
Compatibility with Big Data Frameworks: In the dynamic landscape of big data, Panther seamlessly integrates with popular frameworks like Hadoop and Spark. This compatibility ensures a smooth interplay between Panther and distributed data storage systems, enhancing its effectiveness in diverse ecosystems.
-
Real-time Analytics: Panther’s ability to provide real-time insights is a game-changer. In a fast-paced world, where decisions are made in the blink of an eye, Panther ensures that the insights generated are not just accurate but timely.
Panther’s Journey Ahead:
As we traverse the landscape of big data analysis, Panther stands as a beacon of innovation. The journey doesn’t end with its current capabilities; it’s a continual evolution. The future promises enhancements and updates, setting Panther on a trajectory to redefine the benchmarks of excellence in data analysis tools. The world of big data is dynamic, and Panther is not merely keeping pace; it’s setting the pace.
In the grand tapestry of data analytics, Panther’s role transcends being a tool; it’s a companion for those seeking not just answers but a deeper understanding of their data. With its scalability, intuitive features, and compatibility, Panther etches its mark as a vital asset in the arsenal of organizations navigating the vast seas of big data. It’s not just about analysis; it’s about mastery, and Panther stands poised at the forefront of this data-driven revolution.
Panther’s Compatibility with Big Data Sets
In the ever-expanding universe of big data, Panther emerges as a titan, seamlessly navigating the intricacies of massive datasets with unparalleled compatibility and efficiency.
Scalability Unleashed:
Panther’s scalability is nothing short of extraordinary, resembling a digital Hercules effortlessly carrying the weight of colossal datasets. This is not just a tool; it’s a powerhouse designed to scale seamlessly from terabytes to petabytes, providing organizations with the flexibility to handle diverse data magnitudes.
Efficiency Beyond Measure:
When it comes to handling large volumes of data, Panther is the maestro orchestrating a symphony of efficiency. Its algorithms dance through the complexities of extensive datasets, ensuring that every bit of information is processed with speed and precision. This isn’t just about managing data; it’s about doing so with finesse and effectiveness, setting Panther apart as the go-to solution for organizations grappling with data deluge.
Benchmarking Excellence:
In the realm of big data, performance benchmarks are the yardsticks of success, and Panther not only meets but exceeds expectations. Imagine a tool that doesn’t just analyze data but does so at a pace that redefines industry standards. Panther’s performance isn’t a mere claim; it’s substantiated by concrete benchmarks that showcase its prowess in delivering results with exceptional speed and accuracy.
Real-world Triumphs:
Case studies serve as the real litmus test for any tool’s efficacy, and Panther emerges triumphantly in this arena. Organizations across diverse sectors have harnessed the power of Panther to unravel the complexities of their data. From financial institutions managing vast transaction records to healthcare providers deciphering patient trends, Panther’s compatibility has been validated in the real-world crucible, where results matter the most.
Strategic Integration:
Panther’s compatibility extends beyond its standalone capabilities. Imagine a tool that seamlessly integrates with popular big data frameworks like Hadoop and Spark. This isn’t just compatibility; it’s strategic integration that ensures Panther plays harmoniously in the larger orchestration of distributed data storage systems. It’s about being part of a bigger picture, where every element works in concert to deliver a symphony of data insights.
Future-Proofing Data Analytics:
As we gaze into the future, Panther’s compatibility becomes a linchpin for organizations aiming to future-proof their data analytics endeavors. The scalability, efficiency, and benchmark-setting performance lay the foundation for an ever-evolving tool that adapts to the dynamic landscape of big data technologies. Panther doesn’t just analyze the present; it paves the way for the future of data analytics.
In the grand narrative of big data, Panther’s compatibility is not a feature; it’s a narrative of triumph over the challenges posed by vast and intricate datasets. It’s about scalability that transcends limits, efficiency that defines excellence, and benchmarks that set new standards. Panther is not just a tool; it’s a testament to the evolution of data analytics, where compatibility is the key to unlocking the boundless potential within the realm of big data.
Panther’s Analytical Tools
In the intricate landscape of big data analysis, Panther doesn’t merely offer tools; it presents a sophisticated arsenal that transforms data into actionable insights. Let’s embark on a journey through the intricacies of Panther’s analytical tools, uncovering the layers of innovation that set it apart in the realm of data analytics.
Exploring Data Visualization:
Imagine data not as numbers on a spreadsheet but as a vibrant tapestry of insights. Panther’s data visualization tools are the palette that brings this vision to life.
- Interactive Dashboards: Panther crafts interactive dashboards, providing a visual narrative that transcends the limitations of traditional data representation.
- Intuitive Graphical Representations: Charts, graphs, and heatmaps become not just visual aids but intuitive guides, allowing users to decipher trends with a mere glance.
Mastering Complex Statistical Analysis:
The true litmus test for any analytics tool lies in its ability to unravel the complexities of statistical analysis. Panther doesn’t shy away from this challenge; it embraces it with finesse.
- Advanced Statistical Models: Panther houses advanced statistical models that delve into the nuances of data, extracting meaningful patterns and correlations.
- Predictive Analytics: Beyond historical analysis, Panther enables users to peer into the future through predictive analytics, foreseeing trends and making informed decisions.
Machine Learning Capabilities Unleashed:
In a world where data is dynamic and ever-evolving, Panther’s machine learning capabilities emerge as the beacon guiding organizations through the intricacies of big data.
- Automated Insights: Panther’s machine learning algorithms don’t just analyze data; they learn from it. The result is automation that sifts through vast datasets, extracting insights with unparalleled efficiency.
- Pattern Recognition: Identifying patterns within the data labyrinth is not just a capability; it’s a strength. Panther’s machine learning excels in recognizing intricate patterns, providing a deeper understanding of data dynamics.
Practical Application in Big Data Analysis:
Panther’s analytical tools aren’t confined to theoretical prowess; they find practical application in the real-world challenges of big data analysis.
- Financial Forecasting: Picture a tool that not only analyzes financial data but forecasts future trends with precision. Panther’s analytical tools empower financial institutions to make strategic decisions based on accurate predictions.
- Healthcare Insights: In the healthcare sector, Panther’s machine learning capabilities become a lifeline, predicting disease trends, optimizing patient care, and revolutionizing the way medical decisions are made.
Strategic Integration for Maximum Impact:
The true power of Panther’s analytical tools lies not just in their standalone brilliance but in their strategic integration.
- Seamless Collaboration: Panther seamlessly collaborates with other analytical tools, creating a synergistic ecosystem where each tool enhances the capabilities of the other.
- Cross-Functional Insights: From marketing departments deciphering consumer behavior to supply chain professionals optimizing logistics, Panther’s analytical tools offer cross-functional insights that redefine the dynamics of decision-making.
In the grand symphony of big data analytics, Panther’s analytical tools aren’t just instruments; they are virtuosos that transform data into a masterpiece of insights. From visualizing complex datasets to harnessing the predictive power of machine learning, Panther stands at the forefront of innovation. It’s not just about tools; it’s about a transformative approach to data analytics that empowers organizations to navigate the complexities of the data landscape with confidence and precision.
Integration with Big Data Technologies
In the dynamic landscape of big data, Panther doesn’t stand alone; it dances seamlessly with the giants, integrating with popular frameworks and navigating distributed data storage systems with a finesse that redefines the benchmarks of compatibility.
Compatibility with Big Data Frameworks:
Panther’s compatibility isn’t a mere checkbox; it’s a strategic integration that amplifies its capabilities, making it a versatile player in the orchestra of big data technologies.
- Harmony with Hadoop: Panther’s compatibility with Hadoop is akin to a well-synchronized duet. It effortlessly navigates the distributed processing power of Hadoop, unlocking the potential for analyzing massive datasets with unparalleled efficiency.
- Spark Integration: Picture Panther as a spark that ignites the possibilities within big data. Its compatibility with Spark adds a layer of agility, enabling users to harness the speed and in-memory processing capabilities that Spark offers.
Interaction with Distributed Data Storage Systems:
Panther’s prowess extends beyond compatibility; it’s a maestro in interacting with distributed data storage systems, ensuring that the flow of data is not just seamless but optimized for maximum impact.
- Distributed File Systems: Panther seamlessly interacts with distributed file systems, ensuring that data, regardless of its volume, is stored and retrieved with efficiency. Think of it as a librarian that effortlessly locates the right data in the vast library of distributed storage.
- Data Warehouses: Panther’s interaction with data warehouses is not just transactional; it’s transformational. It optimizes the way data is stored, facilitating quick and accurate retrieval, turning data warehouses into dynamic repositories of actionable insights.
Elevating Data Processing Efficiency:
The integration of Panther with big data technologies isn’t a mere convenience; it’s a strategic move that elevates data processing efficiency to new heights.
- Parallel Processing Power: Panther seamlessly taps into the parallel processing power of big data frameworks, ensuring that the analysis of extensive datasets doesn’t become a bottleneck. It’s like having a fleet of processors working in unison to decode the intricacies of data.
- Optimized Resource Utilization: In the world of big data, resources are akin to gold, and Panther ensures their optimal utilization. Whether it’s storage capacity or processing power, Panther’s integration with big data technologies maximizes the utility of resources, ensuring a cost-effective and efficient analytical journey.
Real-world Impact:
The integration of Panther with big data technologies transcends theoretical compatibility; it finds practical application in diverse industries, leaving an indelible mark on real-world challenges.
- Financial Analytics: In the financial sector, Panther’s integration with Hadoop and Spark becomes a strategic advantage. It’s not just about analyzing transactions; it’s about doing so at a speed and scale that redefine real-time financial analytics.
- E-commerce Dynamics: For e-commerce giants grappling with massive datasets of customer behavior, Panther’s interaction with distributed data storage systems becomes a game-changer. It’s about understanding consumer patterns, optimizing recommendations, and enhancing the overall customer experience.
Future-ready Integration:
As we peer into the future of big data technologies, Panther’s integration isn’t a static achievement; it’s a journey that evolves with the dynamics of the data landscape.
- Adaptability to Emerging Frameworks: Panther is not tethered to the present; it’s poised for the future. As new big data frameworks emerge, Panther stands ready to adapt, ensuring that organizations stay at the forefront of technological advancements.
- Scalability for Tomorrow: The integration is not just for today’s challenges; it’s a strategic move for scalability tomorrow. Panther’s compatibility ensures that as data volumes grow, analytical capabilities can scale effortlessly, without compromising efficiency.
In the grand narrative of big data integration, Panther’s dance with frameworks and distributed systems isn’t just a choreography; it’s a symphony. It’s about compatibility that transcends checkboxes, interaction that optimizes data flow, and real-world impact that defines the essence of Panther’s role in the intricate world of big data technologies.
Challenges and Solutions
In the ever-expanding arena of big data analysis, navigating the complexities of massive datasets presents challenges that require both finesse and innovation. Panther, as a stalwart companion in this journey, doesn’t just acknowledge these challenges; it confronts them head-on, offering a repertoire of strategies and features that redefine the paradigm of big data analytics.
Addressing Potential Challenges:
The realm of massive data sets isn’t without its hurdles, and Panther confronts these challenges with a strategic approach.
- Scalability Conundrum: The sheer volume of data can be overwhelming, testing the limits of traditional tools. Panther acknowledges this scalability conundrum, recognizing that analyzing terabytes or petabytes of data requires not just capability but adaptability.
- Data Variety and Complexity: Big data isn’t just about volume; it’s about variety and complexity. Unstructured data, diverse formats, and intricate relationships pose challenges. Panther identifies these nuances as opportunities for growth, understanding that the true power lies in unraveling the intricacies of diverse data types.
Strategies and Features to Overcome Limitations:
Panther doesn’t just address challenges; it transforms them into stepping stones for innovation, offering a suite of strategies and features that redefine the landscape of big data analytics.
- Dynamic Scalability: Panther’s scalability is not a static feature; it’s dynamic. As data volumes grow, Panther scales effortlessly, ensuring that the analytical journey remains seamless. It’s not just about handling massive datasets; it’s about doing so with agility.
- Adaptive Algorithms: The complexity of diverse data types necessitates adaptive algorithms. Panther doesn’t rely on one-size-fits-all approaches; instead, it adapts its analytical algorithms to the intricacies of the data at hand, ensuring accurate insights regardless of data variety.
Real-world Solutions in Action:
The efficacy of Panther’s strategies and features isn’t theoretical; it’s validated in real-world scenarios where the challenges of massive data sets meet practical solutions.
- Predictive Analytics: Panther’s machine learning capabilities, a cornerstone of its analytical arsenal, enable predictive analytics. It’s not just about historical data; it’s about foreseeing trends and making informed decisions in real-time, transforming challenges into opportunities.
- Interactive Data Visualization: Confronting the complexity of diverse data formats, Panther’s data visualization tools become a beacon. Interactive dashboards and intuitive graphical representations simplify the understanding of intricate relationships, turning data complexity into a visual narrative.
Efficiency at Scale:
The efficiency of Panther’s solutions isn’t compromised as data volumes surge; in fact, it thrives on the challenge.
- Parallel Processing Power: As data sets grow, Panther’s integration with big data frameworks unleashes parallel processing power. It’s not just about handling more data; it’s about doing so with speed, ensuring that the analytical process remains efficient even as data volumes escalate.
- Optimized Resource Utilization: Panther’s interaction with distributed data storage systems is not just about storage; it’s about optimizing resource utilization. Efficient retrieval, storage, and processing become the pillars of Panther’s strategy to overcome limitations at scale.
Continuous Evolution for Future Challenges:
Panther’s approach to challenges is not static; it’s a continual evolution. As the landscape of big data evolves, Panther remains at the forefront, adapting, innovating, and transforming challenges into opportunities for growth.
In the symphony of big data analytics, Panther’s response to challenges is not just a note; it’s a melody. It’s about acknowledging the intricacies of massive datasets, confronting them with innovative strategies, and transforming challenges into stepping stones for a more efficient, scalable, and future-ready approach to big data analysis.
Use Cases and Success Stories
In the labyrinth of big data analytics, Panther emerges not just as a tool but as a catalyst for transformative insights, as evidenced by the real-world use cases and success stories of organizations harnessing its capabilities. These narratives unfold as compelling testaments to Panther’s impact on decision-making, unveiling a tapestry of success in the realm of big data analysis.
Driving Financial Intelligence:
Panther’s prowess shines brightly in the financial sector, where data is not just a commodity but a strategic asset. Major financial institutions have leveraged Panther’s analytical tools to navigate the complexities of vast transaction records. The result? Accelerated financial intelligence, enabling these organizations to make swift, data-driven decisions in the ever-evolving landscape of global markets.
Revolutionizing Healthcare Analytics:
In the healthcare sector, Panther’s integration with big data technologies has ushered in a new era of analytics. The tool’s machine learning capabilities have empowered healthcare providers to predict disease trends, optimize patient care, and revolutionize medical decision-making. Real-time insights derived from extensive datasets have become a cornerstone in enhancing patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency.
Optimizing E-commerce Strategies:
E-commerce giants grappling with the intricate patterns of consumer behavior have found a strategic ally in Panther. By seamlessly integrating with big data frameworks, Panther enables these platforms to not only analyze but predict consumer trends. This predictive analytics capability has transformed the e-commerce landscape, allowing businesses to tailor their strategies with a foresight that goes beyond conventional analytics.
Enhancing Supply Chain Dynamics:
Supply chain optimization is a critical imperative for industries reliant on efficient logistics. Panther’s analytical tools have become instrumental in decoding the complexities of supply chain dynamics. Through strategic integration with distributed data storage systems, Panther ensures that organizations can glean actionable insights from their vast datasets, optimizing logistics, reducing costs, and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Unraveling Marketing Insights:
Marketing strategies are often crafted in the crucible of consumer insights, and Panther’s data visualization tools have become the artist’s palette for marketers. Through interactive dashboards and intuitive graphical representations, Panther transforms raw data into visual narratives, providing marketers with a holistic view of consumer behavior. This approach has redefined marketing analytics, allowing for more informed and targeted campaigns.
Educational Institutions Harnessing Insights:
Educational institutions grappling with the challenges of student performance data have embraced Panther as an ally in their quest for actionable insights. By addressing the scalability conundrum and leveraging Panther’s adaptive algorithms, these institutions have been able to analyze diverse datasets, identify patterns, and implement targeted interventions to enhance student outcomes.
Government Agencies and Data-driven Governance:
Government agencies, entrusted with vast datasets related to citizen services, have embraced Panther’s capabilities for data-driven governance. The integration with big data frameworks allows these agencies to process and analyze citizen-centric data efficiently. From optimizing public services to predicting future requirements, Panther has become a linchpin in enhancing the efficacy of government operations.
Empowering Research and Development:
In the realm of research and development (R&D), Panther’s impact has been profound. Research institutions and innovative companies have utilized Panther’s machine learning capabilities to sift through vast datasets, accelerating the pace of discovery. Whether in pharmaceuticals, technology, or scientific exploration, Panther’s adaptive algorithms have become instrumental in driving breakthroughs.
In the symphony of big data success stories, Panther isn’t just a note; it’s the crescendo that transforms data into actionable insights. These real-world use cases stand as a testament to Panther’s versatility, adaptability, and impact on decision-making across diverse industries. As organizations continue to navigate the complexities of big data, Panther remains the maestro, orchestrating a harmonious blend of technology and insights that redefine the possibilities within the realm of data analytics.
Best Practices for Big Data Analysis with Panther
As organizations plunge into the vast ocean of big data, the nuances of efficient analysis become paramount, and Panther emerges as the guiding star in this intricate journey. To harness the full potential of Panther for big data analysis, a set of best practices must be embraced – a curated roadmap that navigates the complexities, optimizes performance, and ensures unwavering accuracy and reliability in the results.
Optimizing Performance:
Panther’s capabilities are vast, and unlocking their full potential requires a nuanced approach to performance optimization.
-
Strategic Data Partitioning:
- Leverage Panther’s prowess in handling distributed data by strategically partitioning large datasets. This ensures that parallel processing power is harnessed effectively, optimizing overall performance.
-
Fine-tuning Machine Learning Models:
- For organizations harnessing Panther’s machine learning capabilities, the key lies in fine-tuning models. Regularly revisit and optimize algorithms based on evolving data patterns to ensure predictive accuracy remains at its zenith.
-
Effective Resource Allocation:
- Panther’s scalability is a virtue, but strategic resource allocation is the key to maintaining optimum performance. Regularly assess data volumes, processing requirements, and allocate resources accordingly to avoid unnecessary bottlenecks.
Ensuring Accuracy and Reliability:
In the realm of big data analysis, accuracy and reliability are non-negotiable, and Panther’s best practices ensure organizations can trust the insights derived.
-
Data Quality Assurance:
- Before embarking on the analytical journey, institute robust data quality assurance practices. Panther thrives on clean, high-quality data; therefore, implementing validation checks and cleansing processes is fundamental.
-
Continuous Monitoring and Validation:
- The dynamic nature of big data necessitates continuous monitoring. Implement validation mechanisms to ensure that the results Panther produces align with the expectations. Regular audits of data sources and outputs fortify the reliability of insights.
-
Adherence to Data Governance:
- Panther’s analytical prowess is most effective when underpinned by strong data governance. Define clear data ownership, establish data quality standards, and ensure that Panther operates within the framework of these governance principles.
Strategic Utilization of Panther’s Features:
Beyond the generic, Panther’s unique features demand strategic utilization to extract maximum value.
-
Dynamic Scaling for Peaks:
- Panther’s dynamic scalability ensures that it can handle peaks in data volumes. Strategically plan for scalability during anticipated peaks to maintain performance standards during data surges.
-
Adaptive Algorithms for Diverse Data:
- Big data comes in diverse formats, and Panther’s adaptive algorithms shine when confronted with this diversity. Ensure that algorithms are adaptive and tuned to handle various data types, from structured to unstructured.
-
Utilizing Data Visualization for Interpretability:
- Panther’s data visualization tools are not just for aesthetics but serve as interpretable narratives. Leverage these tools to communicate complex insights effectively, enhancing the interpretability of analytical results.
Embracing Continuous Learning:
The landscape of big data is dynamic, and a culture of continuous learning ensures that organizations stay ahead of the curve.
-
Training and Skill Enhancement:
- Invest in training and skill enhancement programs for teams working with Panther. An adept team that continually enhances its skills ensures that Panther is leveraged to its maximum potential.
-
Staying Informed on Updates:
- Panther evolves, with updates and enhancements released regularly. Stay informed on these updates, understanding how new features can be strategically incorporated to enhance analytical capabilities.
-
Community Engagement and Knowledge Sharing:
- Foster a culture of community engagement and knowledge sharing within the organization. Panther’s vibrant user community provides valuable insights and best practices that can be tailored to specific organizational needs.
In the intricate dance of big data analysis, Panther isn’t just a partner; it’s a virtuoso. By adhering to these best practices, organizations can orchestrate a symphony of efficient, accurate, and reliable insights that transcend the complexities of the big data landscape. It’s not just about harnessing Panther’s capabilities; it’s about orchestrating them into a harmonious analytical journey.
Future Developments
In the dynamic arena of big data, where evolution is the only constant, Panther stands as a harbinger of innovation and adaptability. As organizations traverse the uncharted territories of vast datasets, the roadmap ahead is paved with potential enhancements and updates to Panther, making it not just a tool but a forward-looking catalyst in the ever-evolving landscape of big data technologies.
Potential Enhancements to Panther:
-
Dynamic Machine Learning Advancements:
- The future holds the promise of even more dynamic machine learning capabilities within Panther. Anticipate enhancements that not only fine-tune algorithms in real-time but also empower organizations to seamlessly integrate external machine learning models, ensuring a more holistic approach to predictive analytics.
-
Extended Compatibility with Emerging Technologies:
- As emerging technologies like edge computing and IoT gain prominence, Panther is poised to extend its compatibility. Future developments may see Panther seamlessly integrating with these technologies, providing organizations with the capability to analyze and derive insights from distributed data sources.
-
Enhanced Data Visualization and Interpretability:
- The visual narrative is crucial in deciphering complex data sets. Future updates to Panther may bring forth enhancements in data visualization tools, making them more intuitive and interactive. Expect features that allow for the creation of visually compelling stories from intricate datasets, ensuring better interpretability.
Panther’s Role in the Evolving Landscape:
-
Catalyzing Real-time Analytics:
- The future of big data analysis is synonymous with real-time insights. Panther’s role will transcend batch processing, ushering in an era where organizations can harness its power for instantaneous analytics. Imagine a landscape where decisions are made on the fly, fueled by Panther’s ability to process and analyze data in real-time.
-
Integration with AI Ecosystems:
- The symbiotic relationship between big data and artificial intelligence will become more pronounced, and Panther is set to be at the forefront of this integration. Look forward to seamless interoperability with AI ecosystems, enabling organizations to not just analyze historical data but predict future trends with a level of accuracy that redefines decision-making.
-
Automated Data Governance and Compliance:
- As regulatory landscapes evolve, so will Panther’s commitment to data governance and compliance. Future developments may introduce automated features that ensure data handling aligns with the most stringent regulatory standards. Imagine a scenario where data governance becomes a proactive and automated aspect of big data analytics.
The Road Ahead: A Collective Journey:
-
Community-Driven Innovation:
- Panther’s future developments will be shaped by the vibrant community of users and developers. Expect a more community-driven innovation model, where user feedback and collaborative contributions play a pivotal role in shaping the tool’s trajectory. The collective wisdom of the Panther community will propel it toward new frontiers.
-
Global Scalability and Accessibility:
- The global landscape of big data knows no boundaries, and Panther’s future is geared towards global scalability and accessibility. Envision a scenario where organizations worldwide, irrespective of their scale, can seamlessly adopt and leverage Panther for their big data analytics needs.
-
Education and Empowerment Initiatives:
- Panther’s journey into the future involves not just technological advancements but also educational and empowerment initiatives. Anticipate a focus on user education programs, empowering organizations with the knowledge and skills needed to extract maximum value from Panther’s evolving capabilities.
In the kaleidoscope of big data’s future, Panther emerges as a luminary, illuminating the path ahead with innovations that transcend the boundaries of conventional analytics. As organizations prepare to embrace the ever-expanding realm of big data technologies, Panther stands as a stalwart companion, ready to evolve, adapt, and catalyze a future where insights are not just derived but orchestrated into a symphony of strategic decision-making.