To understand the overwhelming sea of data in today’s digital age, one must first recognize a transformative force that is shaping the future of analytics. You can imagine a world where massive datasets are not just possible but efficient, opening up unparalleled insights and possibilities; brace yourself for that world, because Hadoop already exists.
Essentially, Hadoop is the foundation of modern data analytics, allowing for the analysis of vast amounts of complex data at the speed and complexity of modern analytics. Discover how this game-changing framework contributes to scalable data processing, fault tolerance, and cost-effectiveness as we look at its inner workings. Imagine a situation in which your organization can handle terabytes or even petabytes of data without experiencing hardware failure, ensuring data integrity while protecting its integrity. Not only are the possibilities intriguing, but they are also revolutionary.
We’ll go over the layers of Hadoop’s architecture and how it stacks up against traditional databases in this session to get an understanding of why Hadoop is so important for businesses in a variety of industries. As we embark on the journey into the realm of Hadoop, we should all make a point of fastening our seatbelts because data isn’t simply a challenge, but it’s also a way to make better decisions. Hadoop has vast potential, so we’ll take a closer look at its benefits and discover how it’s already reshaping the way we think about and make use of big data.
Understanding Big Data
In the vast expanse of the digital universe, the concept of Big Data has emerged as a defining force, reshaping the way we perceive, manage, and derive insights from information. To comprehend the magnitude of Big Data, one must first grapple with its multifaceted nature. Defined by its sheer volume, variety, velocity, and veracity, Big Data transcends the conventional boundaries of data processing, ushering in an era where traditional methods find themselves inadequately equipped for the task at hand.
Definition and Characteristics of Big Data
At its core, Big Data refers to datasets that surpass the capacity of conventional databases and demand advanced, innovative processing techniques. It’s not merely about the quantity of data but the complexities that arise from its diverse forms and the speed at which it accrues. In essence, Big Data encapsulates a spectrum of structured and unstructured data, ranging from text and images to videos and sensor data. This diversity, coupled with the unprecedented speed at which data is generated, forms the foundation of its defining characteristics.
Volume, Variety, Velocity, and Veracity
Delving into the defining aspects of Big Data, it’s imperative to acknowledge the four Vs that delineate its essence:
-
Volume: The sheer scale of data generated daily is staggering. With the digital footprint expanding exponentially, organizations find themselves grappling with datasets that measure in terabytes, petabytes, and beyond.
-
Variety: Big Data is not a monolithic entity; it’s a mosaic of diverse data types. Structured data from databases, unstructured data from social media, and semi-structured data from sources like XML files collectively contribute to the intricate tapestry of Big Data.
-
Velocity: In a world driven by real-time interactions, the speed at which data is generated and needs to be processed is unprecedented. From online transactions to social media updates, the demand for instantaneous analytics necessitates a shift from traditional batch processing to real-time solutions.
-
Veracity: The reliability and accuracy of data are paramount. With the influx of data from varied sources, ensuring the trustworthiness of information becomes a formidable challenge. Veracity underscores the importance of discerning signal from noise in the data landscape.
Challenges Posed by Traditional Data Processing Methods
As we navigate the realms of Big Data, the inadequacies of traditional data processing methods become glaringly apparent. Conventional databases, designed for structured data with predefined schemas, falter when confronted with the unstructured and rapidly evolving nature of Big Data. The rigid structure that once facilitated efficient processing now becomes a hindrance, necessitating a paradigm shift in approach.
-
Scalability: Traditional databases struggle to scale seamlessly with the exponential growth of data, leading to performance bottlenecks and system failures.
-
Complex Data Types: The variety of data encountered in Big Data, including multimedia content, geospatial data, and social media interactions, poses a significant challenge for databases optimized for tabular structures.
-
Real-time Processing: The demand for real-time insights is incompatible with batch processing models, compelling a transition towards solutions capable of handling data on the fly.
In navigating the complexities of Big Data, organizations are compelled to embrace technologies that not only grapple with the scale and variety but also accommodate the need for rapid, real-time analysis. It’s in this dynamic landscape that the role of innovative frameworks like Hadoop becomes not just relevant but indispensable. As we traverse the data-driven frontier, the significance of understanding Big Data, with all its intricacies and challenges, becomes the compass guiding us toward a future where insights are as vast as the data they originate from.
Evolution of Hadoop
In the ever-accelerating realm of big data, the evolution of Hadoop stands as a testament to the transformative power of innovation. The origins of Hadoop can be traced back to the early 2000s when engineers at Yahoo, notably Doug Cutting and Mike Cafarella, conceptualized a groundbreaking framework designed to process vast amounts of data efficiently. This open-source juggernaut, named after Cutting’s son’s toy elephant, swiftly evolved into a pivotal force, reshaping the landscape of data processing and analytics.
Origins and Development of Hadoop
The journey of Hadoop mirrors the narrative of ingenuity meeting necessity. Originating from the need to manage and analyze the exponentially growing datasets at Yahoo, Hadoop quickly transcended its origins and found resonance across industries. As a distributed storage and processing framework, Hadoop addressed the limitations posed by traditional databases, enabling organizations to harness the power of parallel processing on commodity hardware. The evolution of Hadoop wasn’t merely a technological progression; it was a paradigm shift in how we approached the complexities of big data.
Overview of the Apache Hadoop Framework
At its core, the Apache Hadoop framework represents a distributed, scalable, and fault-tolerant solution for processing and storing vast amounts of data. The framework is underpinned by the robust Apache Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), a cornerstone that facilitates the storage and retrieval of data across a network of machines. Hadoop’s architecture, designed for horizontal scalability, ensures that organizations can seamlessly expand their infrastructure to handle growing datasets.
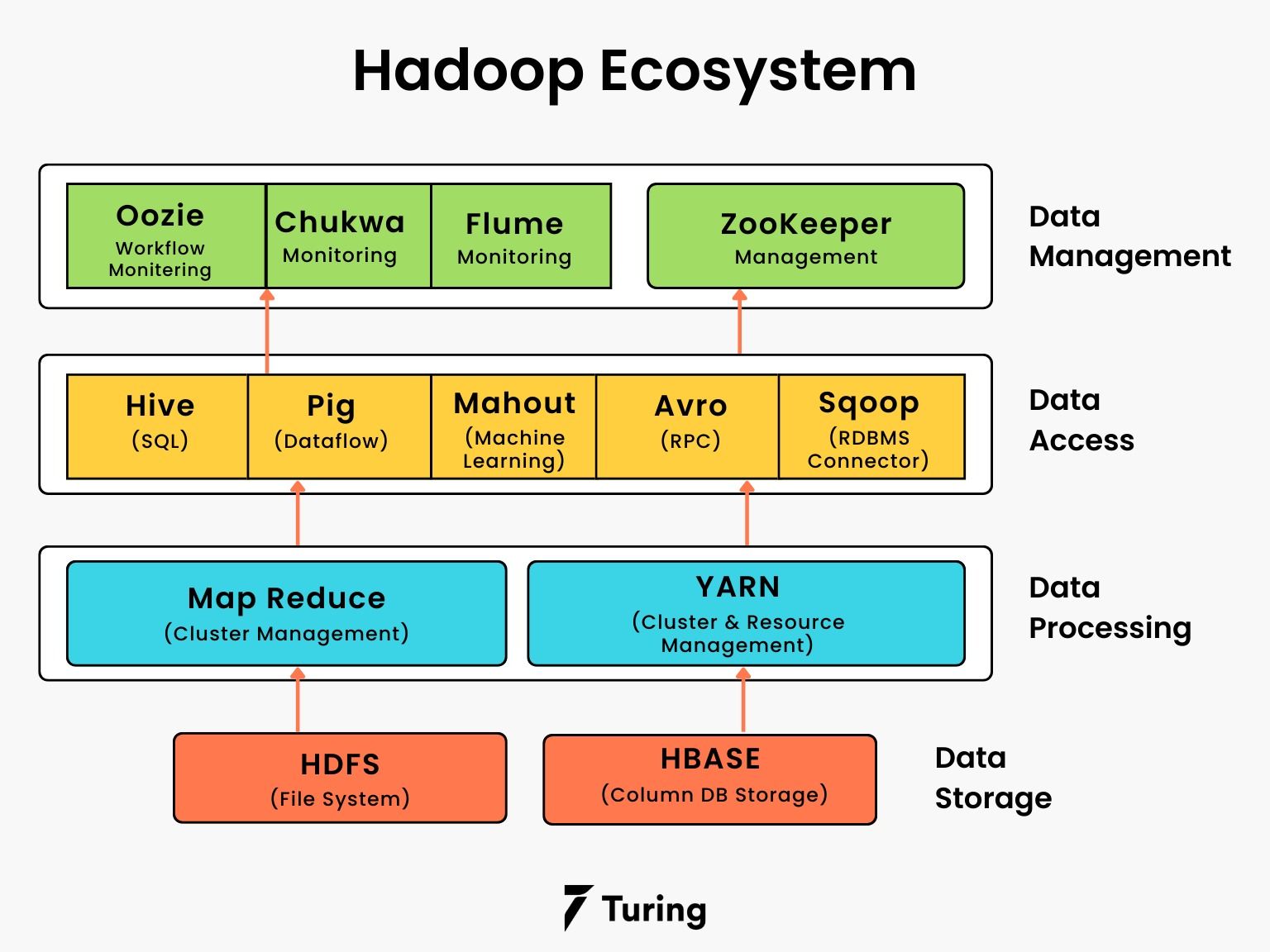
Key Components of Hadoop Ecosystem: HDFS, MapReduce, YARN, and More
The Hadoop ecosystem, akin to a dynamic ecosystem in nature, thrives on diversity and interdependence. Its key components synergistically contribute to the framework’s efficacy:
-
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS): Serving as the bedrock of Hadoop, HDFS divides large datasets into smaller blocks, distributing them across nodes for parallel processing. This distributed storage architecture ensures both fault tolerance and high availability.
-
MapReduce: An innovative programming model that revolutionized data processing, MapReduce divides tasks into smaller sub-tasks, processes them in parallel, and then consolidates the results. This parallel processing capability is instrumental in handling large-scale data analytics.
-
YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator): Introduced in Hadoop 2.x, YARN decouples the programming logic from resource management, enabling more diverse and dynamic processing workloads. It serves as the resource manager, enhancing scalability and flexibility.
-
Hadoop Common: Providing the foundational utilities and libraries for other Hadoop modules, Hadoop Common ensures seamless integration and interoperability within the ecosystem.
-
Hadoop MapReduce 2 (MR2): The second version of MapReduce in Hadoop 2.x brings improvements in terms of performance, scalability, and resource management.
Navigating the evolutionary path of Hadoop unveils a narrative of continuous enhancement and adaptation to the ever-evolving demands of big data analytics. As organizations worldwide grapple with data deluge, Hadoop remains a linchpin, offering not just a solution but a dynamic ecosystem that empowers enterprises to turn data challenges into strategic advantages. The evolution of Hadoop is an ongoing saga, promising innovations that will shape the future of data processing and analytics, steering us toward a landscape where the boundaries of possibility are continually redefined.
Hadoop Architecture
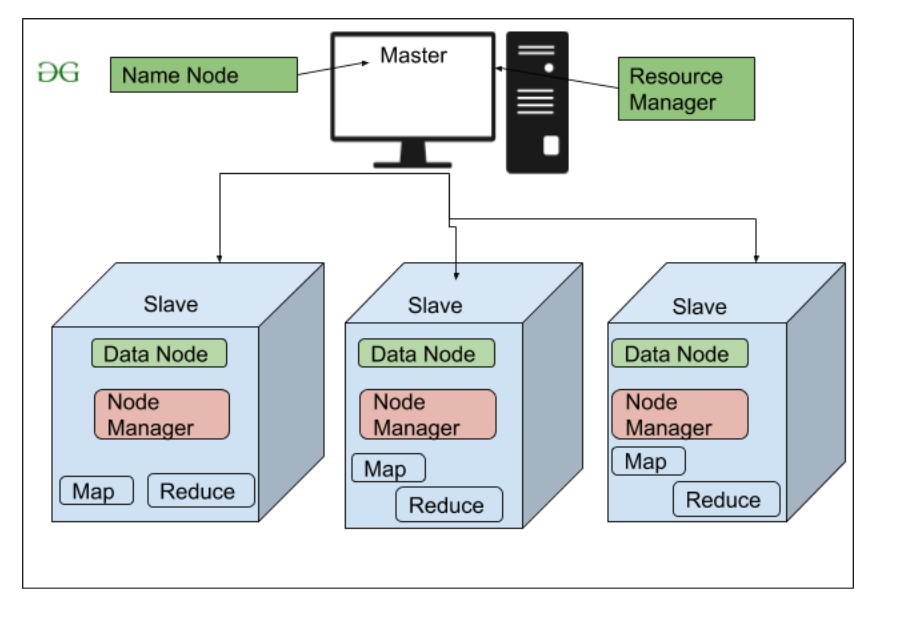
Embarking on a journey into the intricate architecture of Hadoop unveils the blueprint behind the colossal capabilities that make it a juggernaut in the realm of big data analytics. This deep dive into Hadoop’s architecture reveals a carefully crafted framework that orchestrates the processing and analysis of vast datasets, redefining the possibilities of data-driven decision-making.
The Foundation: Understanding the Distributed File System (HDFS) and Its Advantages
At the core of Hadoop’s architecture lies the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), a distributed and fault-tolerant file storage system that serves as the linchpin for managing immense volumes of data. The architectural prowess of HDFS can be dissected into key facets:
-
Distributed Storage: HDFS divides massive datasets into smaller blocks, distributing them across a cluster of machines. This distributed approach not only ensures efficient data storage but also facilitates parallel processing, a fundamental principle for handling colossal datasets.
-
Fault Tolerance: HDFS is designed to anticipate and mitigate hardware failures. By replicating data across multiple nodes, it ensures that even if one node fails, data integrity is maintained. This fault-tolerant design is pivotal for the reliability of Hadoop in real-world applications.
-
Scalability: As data continues its exponential growth, HDFS scales horizontally, allowing organizations to seamlessly expand their storage infrastructure. This scalability is crucial for enterprises dealing with the challenges of ever-expanding datasets.
The Engine Room: The Role of MapReduce in Processing and Analyzing Large Datasets
Within the intricate architecture of Hadoop, MapReduce emerges as the powerhouse, driving the processing and analysis of large datasets with unparalleled efficiency. MapReduce, akin to a conductor orchestrating a symphony, operates on a simple yet powerful principle:
-
Parallel Processing: MapReduce breaks down complex data processing tasks into smaller, manageable sub-tasks that can be executed in parallel across the distributed nodes of a Hadoop cluster. This parallelism is the key to expediting data processing, allowing organizations to derive insights at unprecedented speeds.
-
Flexibility in Programming: MapReduce’s programming model is not only scalable but also flexible. Its ability to process data in a distributed environment is language-agnostic, offering organizations the freedom to use programming languages they are most comfortable with, a significant advantage for diverse teams.
-
Distributed Computing Efficiency: By executing tasks close to where the data resides, MapReduce minimizes data transfer across the network, optimizing efficiency in distributed computing. This locality-aware processing is a strategic approach to enhance performance and reduce latency.
Navigating the Complexity: Hadoop Ecosystem Components
Beyond the foundational elements of HDFS and MapReduce, the Hadoop architecture expands into a diverse ecosystem, each component playing a distinctive role. Some noteworthy components include:
-
YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator): Acting as the resource manager, YARN enhances the scalability and flexibility of Hadoop by decoupling resource management from the programming logic.
-
Hadoop Common: Providing the foundational utilities and libraries for other Hadoop modules, Hadoop Common ensures seamless integration and interoperability within the ecosystem.
As organizations grapple with the intricacies of big data, understanding the architecture of Hadoop becomes a compass guiding them through the complexities. The synergy of HDFS, MapReduce, and the broader ecosystem creates a dynamic framework that not only tackles the challenges of today but also lays the foundation for the data-intensive future. It’s within this architectural marvel that the possibilities of big data analytics unfold, offering a roadmap for organizations to navigate the ever-expanding landscape of data-driven insights.
Advantages of Hadoop for Big Data Analytics
Navigating the complex landscape of big data analytics, Hadoop emerges not just as a solution but as a strategic powerhouse offering distinct advantages that propel organizations into the forefront of data-driven innovation.
Scalability: Handling the Data Deluge with Ease
In the ever-expanding universe of digital information, scalability isn’t merely an option; it’s a necessity. Hadoop, with its distributed architecture, stands as a beacon of scalability, effortlessly handling the mammoth volumes of data traversing the digital realm. The scalability of Hadoop can be dissected into key facets:
-
Horizontal Scaling: Hadoop’s architecture facilitates the addition of nodes to a cluster seamlessly, ensuring that organizations can scale their infrastructure horizontally. This horizontal scaling capability is pivotal for accommodating the exponential growth of data without compromising performance.
-
Parallel Processing: The genius of Hadoop lies in its ability to divide tasks into smaller, manageable sub-tasks processed concurrently across multiple nodes. This parallel processing not only expedites data analysis but also enables organizations to scale their analytical capabilities proportionally with their data.
Fault Tolerance: Safeguarding Data Integrity in the Face of Challenges
In the dynamic world of data processing, where hardware failures are an inevitability, fault tolerance becomes a linchpin for ensuring data reliability and availability. Hadoop’s fault tolerance mechanisms are the guardians of data integrity:
-
Data Replication: Hadoop employs a strategic approach of replicating data across multiple nodes within a cluster. In the event of a hardware failure or node malfunction, the replicated copies ensure that the data remains accessible, safeguarding against potential loss.
-
Job Recovery: Hadoop’s resilience extends to the recovery of processing tasks in the event of node failures. The framework can reroute tasks to healthy nodes, minimizing disruptions and ensuring the continuity of data processing workflows.
Cost-Effectiveness: The Economic Benefits of Hadoop’s Approach to Storage and Processing
In a business landscape driven by efficiency and cost-effectiveness, Hadoop emerges as an economic ally, offering a strategic approach to storage and processing that optimizes resources:
-
Commodity Hardware: Hadoop’s architecture is designed to operate on low-cost, commodity hardware, negating the need for expensive, specialized infrastructure. This approach democratizes access to big data analytics, enabling organizations of varying sizes to leverage its power.
-
Storage Efficiency: Hadoop’s Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) optimizes storage efficiency by distributing and replicating data across nodes. This not only enhances fault tolerance but also reduces the need for high-end storage solutions, contributing to overall cost savings.
-
Scalable Processing Model: The parallel processing paradigm embraced by Hadoop allows organizations to scale their processing power based on demand. This scalability ensures that resources are allocated efficiently, preventing unnecessary expenditures on idle infrastructure.
As organizations navigate the data-rich landscape, the advantages of Hadoop become indispensable. Its scalability tackles the challenges of data expansion, fault tolerance safeguards against disruptions, and cost-effectiveness transforms big data analytics from a luxury to a strategic imperative. Hadoop is not just a tool; it’s a cornerstone, paving the way for organizations to harness the true potential of their data in an era where insights are the currency of innovation.
Hadoop Use Cases in Big Data Analytics
In the dynamic landscape of big data analytics, the adoption of Hadoop transcends mere technology implementation; it represents a strategic imperative for organizations seeking to extract actionable insights from the vast tapestry of digital information. Through compelling case studies and real-world examples, the multifaceted utility of Hadoop in diverse industries comes to the forefront, illuminating its role as a transformative force in the era of data-driven decision-making.
Case Studies Showcasing Successful Implementations
-
Retail Revolution:
- Challenge: Managing and analyzing customer transaction data in real-time.
- Hadoop Solution: Implemented Hadoop to process and analyze large volumes of transaction data, enabling personalized marketing strategies.
- Result: Increased customer engagement and revenue through targeted promotions and personalized recommendations.
-
Healthcare Innovation:
- Challenge: Analyzing vast datasets of patient records for predictive healthcare analytics.
- Hadoop Solution: Deployed Hadoop to process and analyze diverse healthcare data, facilitating predictive modeling for disease prevention.
- Result: Enhanced patient care, reduced healthcare costs, and improved treatment outcomes.
Real-World Examples of Data-Driven Decision-Making
-
Financial Forecasting:
- Scenario: A global financial institution grappling with the challenge of real-time risk assessment.
- Hadoop Solution: Leveraged Hadoop’s scalability to process and analyze massive datasets for real-time risk modeling.
- Result: Improved risk management, timely decision-making, and a competitive edge in the volatile financial market.
-
E-commerce Optimization:
- Scenario: An e-commerce giant seeking to enhance customer experience and optimize inventory.
- Hadoop Solution: Implemented Hadoop for processing and analyzing customer behavior data and inventory patterns.
- Result: Improved personalized shopping experiences, efficient inventory management, and increased customer satisfaction.
Illustration of Hadoop’s Analytics on Unstructured and Structured Data
-
Social Media Insights:
- Unstructured Data: Analyzing social media feeds, comments, and images.
- Hadoop’s Role: Hadoop’s ability to handle unstructured data allows organizations to derive sentiment analysis, customer feedback trends, and improve brand perception.
-
Supply Chain Optimization:
- Structured Data: Processing structured data from supply chain transactions.
- Hadoop’s Role: Hadoop enables organizations to analyze structured data for supply chain optimization, demand forecasting, and inventory management.
In these real-world applications, Hadoop emerges as a versatile tool, seamlessly adapting to the unique challenges of different industries. Its scalability empowers organizations to tackle data at scale, while fault tolerance ensures the reliability of insights even in the face of hardware failures. These use cases underscore how Hadoop transforms raw data into actionable intelligence, catalyzing innovation, and driving strategic decision-making across diverse sectors.
As organizations continue to navigate the complexities of big data, the Hadoop framework stands as a beacon, illuminating pathways to innovation, efficiency, and competitive advantage. These use cases serve not just as testimonials but as a testament to the pivotal role Hadoop plays in shaping the data-driven future.
Hadoop vs. Traditional Databases
In the ever-evolving landscape of data management, the clash between Hadoop and traditional databases unfolds as a pivotal narrative, shaping the contours of how organizations grapple with the challenges posed by big data. A comparative analysis sheds light on the strengths and nuances that differentiate these two paradigms, illuminating scenarios where Hadoop emerges as a transformative force in handling vast datasets.
A Comparative Analysis of Hadoop and Traditional Database Systems
-
Data Processing Paradigm:
- Traditional Databases: Follow a structured, schema-based approach optimized for transactional processing.
- Hadoop: Embraces a schema-less, distributed processing model, enabling it to handle diverse data types and massive volumes with ease.
-
Scalability:
- Traditional Databases: Vertical scaling often involves investing in more powerful hardware, limiting scalability.
- Hadoop: Horizontal scaling allows organizations to expand their infrastructure by adding commodity hardware, providing seamless scalability for growing data needs.
-
Data Storage:
- Traditional Databases: Centralized storage systems with predefined schemas can be restrictive for accommodating diverse data formats.
- Hadoop: Distributed storage in the form of Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) facilitates the storage of structured and unstructured data, promoting flexibility.
Exploring Scenarios Where Hadoop Outperforms Traditional Databases
-
Large-Scale Data Processing:
- Scenario: Organizations dealing with massive volumes of data requiring parallel processing.
- Hadoop Advantage: Hadoop’s MapReduce paradigm excels in parallelizing tasks, making it ideal for processing large-scale data efficiently.
-
Unstructured Data Handling:
- Scenario: Dealing with diverse data sources such as social media feeds, images, and text documents.
- Hadoop Advantage: Hadoop’s ability to handle unstructured data provides a competitive edge, allowing organizations to derive valuable insights from varied data formats.
-
Cost-Effective Scaling:
- Scenario: Organizations with a need for cost-effective scaling to accommodate data growth.
- Hadoop Advantage: Hadoop’s ability to scale horizontally on low-cost commodity hardware is a cost-effective alternative to the vertical scaling requirements of traditional databases.
The Complementary Relationship Between Hadoop and Relational Databases
-
Data Warehousing:
- Relational Databases: Efficient for structured data warehousing, supporting complex queries.
- Hadoop’s Role: Acts as a complementary layer for processing and analyzing vast datasets before feeding refined insights into relational databases for further analysis.
-
Real-Time Processing:
- Relational Databases: Excel in real-time transactional processing.
- Hadoop’s Role: Complements by handling batch processing efficiently, providing insights that can be integrated into real-time systems.
In the dynamic interplay between Hadoop and traditional databases, it becomes evident that each has its unique strengths, making them suited for specific scenarios. While Hadoop thrives in handling massive, diverse datasets and promoting cost-effective scalability, traditional databases shine in structured data warehousing and real-time transactional processing. The evolving landscape of data management witnesses a symbiotic relationship where organizations strategically leverage the strengths of both paradigms, creating a holistic approach that navigates the complexities of big data analytics. As data continues to surge, this dynamic interplay ensures that organizations are well-equipped to extract meaningful insights and drive informed decision-making in the digital era.
Overcoming Challenges with Hadoop
In the realm of big data analytics, where the promise of insights looms large, navigating the challenges inherent in implementing Hadoop becomes a strategic imperative for organizations aiming to harness the full potential of their data. As Hadoop emerges as a linchpin in the data-driven landscape, addressing common challenges, optimizing performance, and ensuring robust security practices become pivotal aspects of a successful implementation.
Addressing Common Challenges in Implementing Hadoop for Big Data Analytics
-
Complexity of Integration:
- Challenge: Integrating Hadoop with existing systems can be intricate.
- Strategies:
- Leverage connectors and APIs for seamless integration with databases and applications.
- Implement comprehensive training programs for the IT workforce to enhance familiarity with Hadoop technologies.
-
Data Quality and Governance:
- Challenge: Maintaining data quality and ensuring governance can be challenging.
- Strategies:
- Institute data quality checks within Hadoop workflows.
- Establish clear data governance policies and frameworks to ensure compliance and accuracy.
-
Scalability Concerns:
- Challenge: Ensuring scalable infrastructure to accommodate growing data volumes.
- Strategies:
- Implement a robust scaling plan, considering horizontal scaling for cost-effective expansion.
- Regularly assess and optimize the Hadoop cluster to align with evolving data needs.
Strategies for Optimizing Hadoop Performance
-
Tuning Hadoop Configuration:
- Strategy: Fine-tune Hadoop configurations based on the specific requirements of the workload.
- Performance Boost: Optimization ensures that Hadoop resources are allocated efficiently, enhancing overall performance.
-
Utilizing Data Compression:
- Strategy: Implement data compression techniques to reduce storage requirements and expedite data processing.
- Performance Boost: Compressed data requires less storage space, facilitating faster data transfers and processing times.
-
Caching for Frequently Accessed Data:
- Strategy: Implement caching mechanisms for frequently accessed data.
- Performance Boost: Caching minimizes redundant data processing, improving response times for recurrent queries.
Security Considerations and Best Practices
-
Authentication and Authorization:
- Consideration: Ensuring robust authentication and authorization mechanisms.
- Best Practices:
- Implement strong authentication protocols.
- Define granular access controls to restrict data access based on user roles.
-
Data Encryption:
- Consideration: Safeguarding data during transmission and storage.
- Best Practices:
- Implement SSL/TLS for secure data transmission.
- Utilize encryption tools for data-at-rest within the Hadoop cluster.
-
Regular Security Audits:
- Consideration: Proactive identification and mitigation of security vulnerabilities.
- Best Practices:
- Conduct regular security audits to assess the robustness of the Hadoop environment.
- Keep security measures aligned with evolving threat landscapes.
In the dynamic landscape of big data analytics, overcoming challenges with Hadoop demands a strategic approach that combines proactive problem-solving with optimization strategies. From addressing integration complexities to fine-tuning performance and ensuring robust security measures, organizations must navigate these challenges with precision to unlock the true potential of Hadoop. As the data-driven revolution continues, the resilience and adaptability of Hadoop in the face of challenges position it as a cornerstone for organizations aiming to thrive in the era of big data.
Future Trends in Hadoop and Big Data Analytics
As the digital landscape continues its exponential growth, the future of Hadoop and big data analytics unfolds with a tapestry of emerging technologies and transformative innovations. The Hadoop ecosystem, once hailed as a game-changer, is undergoing a metamorphosis, adapting to the evolving demands of data processing and analytics capabilities. Here, we delve into the future trends shaping the trajectory of Hadoop and its role in advancing the frontiers of big data analytics.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations in the Hadoop Ecosystem
-
Containerization and Kubernetes Integration:
- Advancement: Integration of Hadoop with containerization technologies.
- Impact: Enhances scalability, agility, and resource efficiency in deploying and managing Hadoop clusters.
-
Enhancements in Real-Time Analytics:
- Advancement: Evolution of Hadoop architectures to support real-time data processing.
- Impact: Enables organizations to glean insights instantaneously, fostering quicker decision-making in dynamic environments.
-
Machine Learning Integration:
- Advancement: Fusion of Hadoop with machine learning algorithms and frameworks.
- Impact: Unleashes the potential for advanced analytics, predictive modeling, and automated decision-making within the Hadoop ecosystem.
The Evolving Role of Hadoop in Advancing Analytics Capabilities
-
Augmented Analytics:
- Transformation: Shifting from traditional analytics to augmented analytics.
- Significance: Integrating machine learning and AI-driven insights directly into the analytics workflow, democratizing data-driven decision-making.
-
Edge Computing Integration:
- Expansion: Extending Hadoop’s reach to the edge of the network.
- Significance: Facilitates data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and enabling real-time analytics for edge devices.
-
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Deployments:
- Adoption: Increasing prevalence of hybrid and multi-cloud Hadoop deployments.
- Significance: Offers flexibility, scalability, and redundancy, allowing organizations to optimize resource utilization and mitigate risks.
Anticipated Developments in Addressing the Evolving Needs of Big Data Processing
-
Focus on Data Governance and Compliance:
- Priority: Heightened emphasis on robust data governance and compliance frameworks.
- Rationale: Addressing concerns around data privacy, security, and regulatory requirements in the era of stringent data protection laws.
-
Sustainability and Green Computing:
- Trend: Integration of sustainable practices in Hadoop clusters and data centers.
- Motivation: Mitigating the environmental impact of data processing through energy-efficient algorithms and eco-friendly infrastructure.
-
Enhanced Security Measures:
- Evolution: Continuous enhancement of security features within the Hadoop ecosystem.
- Objective: Bolstering data protection measures to counter evolving cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities.
In the foreseeable future, the synergy between Hadoop and big data analytics is poised to redefine the contours of data-driven decision-making. The integration of cutting-edge technologies, the evolution of analytics capabilities, and a steadfast focus on addressing the challenges of data governance and security position Hadoop as a linchpin in the data-centric landscape. As organizations embark on this journey of innovation, the trajectory of Hadoop promises not just to keep pace with the data deluge but to lead the charge in shaping the next frontier of insights, intelligence, and innovation.
Some questions and answers
- What is the significance of Hadoop in big data processing?
-
Hadoop’s significance in big data processing lies in its ability to handle vast datasets efficiently. As an open-source framework, Hadoop enables distributed storage and processing across clusters of computers, ensuring scalability and fault tolerance. Its core components—Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and MapReduce—enable parallel data storage and computation, allowing seamless analysis of diverse data types. This scalability accommodates the exponential growth of data, while fault tolerance ensures data integrity. Hadoop’s cost-effectiveness and flexibility make it a cornerstone for organizations seeking actionable insights from massive datasets, fostering informed decision-making in the dynamic landscape of big data analytics.
- Can Hadoop be used for real-time analytics?
-
Hadoop, traditionally designed for batch processing, encounters limitations in real-time analytics due to the inherent latency in data processing. However, the Hadoop ecosystem has evolved to address this gap. Technologies like Apache Spark and Apache Flink provide real-time processing capabilities, complementing Hadoop’s batch-oriented nature. Organizations can integrate these tools with Hadoop, forming a hybrid architecture that caters to both batch and real-time analytics. While Hadoop alone may not be optimal for real-time scenarios, its integration with modern frameworks empowers businesses to glean timely insights from streaming data sources, expanding its utility beyond traditional batch processing paradigms.
- What are the key components of the Hadoop ecosystem and their functions?
-
The key components of the Hadoop ecosystem encompass:
-
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS):
- Function: Splits and distributes large datasets across clusters for parallel storage and processing.
-
MapReduce:
- Function: Facilitates parallel computation by breaking down tasks into smaller sub-tasks across distributed nodes.
-
YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator):
- Function: Manages resources and schedules tasks, enabling multiple processing engines to operate on Hadoop.
-
Apache Hive:
- Function: Provides a SQL-like interface for querying and analyzing data stored in Hadoop.
-
Apache Pig:
- Function: Offers a high-level scripting language for processing and analyzing large datasets.
-
Apache HBase:
- Function: A NoSQL database for real-time read/write access to Hadoop data.
-
Apache Spark:
- Function: In-memory data processing engine for faster analytics and iterative algorithms.
-
Apache Kafka:
- Function: Facilitates real-time data streaming and messaging within Hadoop.
These components collectively form a robust ecosystem, empowering organizations to store, process, and analyze massive datasets efficiently.
-
- In what industries has Hadoop proven to be a game-changer for analytics?
-
Hadoop has emerged as a transformative force across diverse industries, revolutionizing analytics in the following sectors:
-
Finance:
- Impact: Enhances fraud detection, risk management, and customer insights through the analysis of vast financial datasets.
-
Healthcare:
- Impact: Facilitates advanced medical research, personalized medicine, and predictive analytics, driving improvements in patient care.
-
Retail:
- Impact: Enables retailers to optimize inventory management, personalize customer experiences, and forecast demand more accurately.
-
Telecommunications:
- Impact: Enhances network optimization, customer service, and predictive maintenance through the analysis of telecommunications data.
-
Manufacturing:
- Impact: Improves supply chain management, predictive maintenance, and quality control by analyzing sensor data and production metrics.
-
Energy:
- Impact: Optimizes energy exploration, production, and distribution, leading to improved operational efficiency and resource utilization.
In these industries, Hadoop’s ability to handle massive datasets and perform complex analytics has positioned it as a game-changer, fostering data-driven decision-making and innovation.
-
- How does Hadoop ensure fault tolerance in a distributed environment?
-
Hadoop ensures fault tolerance in distributed environments through a combination of strategic mechanisms:
-
Data Replication in HDFS:
- Approach: Hadoop replicates data across multiple nodes in the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS).
- Function: Redundant copies mitigate the risk of data loss if a node fails, ensuring availability.
-
Task Redundancy in MapReduce:
- Approach: MapReduce tasks are duplicated and executed on different nodes.
- Function: If a node fails during computation, redundant tasks on other nodes ensure uninterrupted processing.
-
Automatic Node Recovery:
- Approach: Hadoop’s resource manager (YARN) monitors node health.
- Function: If a node becomes unresponsive, YARN redistributes tasks to healthy nodes, maintaining system resilience.
By implementing these strategies, Hadoop enhances its fault tolerance, making it robust and reliable in distributed computing environments.
-
- Are there any security concerns associated with implementing Hadoop for big data?
-
Implementing Hadoop for big data introduces security considerations, including:
-
Authentication and Authorization:
- Concern: Ensuring only authorized users access and modify data within the Hadoop cluster.
- Mitigation: Implementing robust authentication mechanisms like Kerberos and defining granular access controls.
-
Data Encryption:
- Concern: Protecting data during transmission and storage to prevent unauthorized access.
- Mitigation: Enabling encryption protocols for data in transit (SSL/TLS) and at rest (HDFS encryption).
-
Audit Trails and Monitoring:
- Concern: Detecting and responding to potential security breaches.
- Mitigation: Implementing comprehensive audit trails, monitoring tools, and real-time alerts for suspicious activities.
-
Securing Hadoop Ecosystem Components:
- Concern: Ensuring the security of individual components like Hive, HBase, and others.
- Mitigation: Regularly updating and patching components, configuring secure defaults, and following best practices.
Addressing these concerns with diligent implementation of security measures enhances Hadoop’s resilience against potential threats in big data environments.
-
- What are the future trends and innovations expected in the Hadoop ecosystem?
-
Anticipated future trends in the Hadoop ecosystem include:
-
Containerization and Kubernetes Integration:
- Innovation: Increasing adoption of container technologies like Docker and Kubernetes for streamlined deployment and management.
-
Enhanced Data Processing Engines:
- Innovation: Continued development of efficient processing engines like Apache Spark, Flink, and Presto for faster analytics and real-time processing.
-
Integration with AI and Machine Learning:
- Innovation: Seamless integration with advanced analytics, machine learning, and AI frameworks for enhanced data-driven insights.
-
Simplified Hadoop Deployments:
- Innovation: Focus on user-friendly deployment options, such as cloud-native solutions and managed services, to lower entry barriers.
-
Evolution of Security Measures:
- Innovation: Ongoing improvements in security protocols, encryption, and compliance features to address evolving cybersecurity challenges.
These trends signify the evolution of Hadoop, ensuring its continued relevance and adaptability in the rapidly changing landscape of big data analytics.
-