Are you ready to unlock the secrets of how Augmented Reality (AR) tags are shaping the future of Robotics? If you want to learn more about the possibilities provided by AR tags in computer vision robotics, this is the place to go.
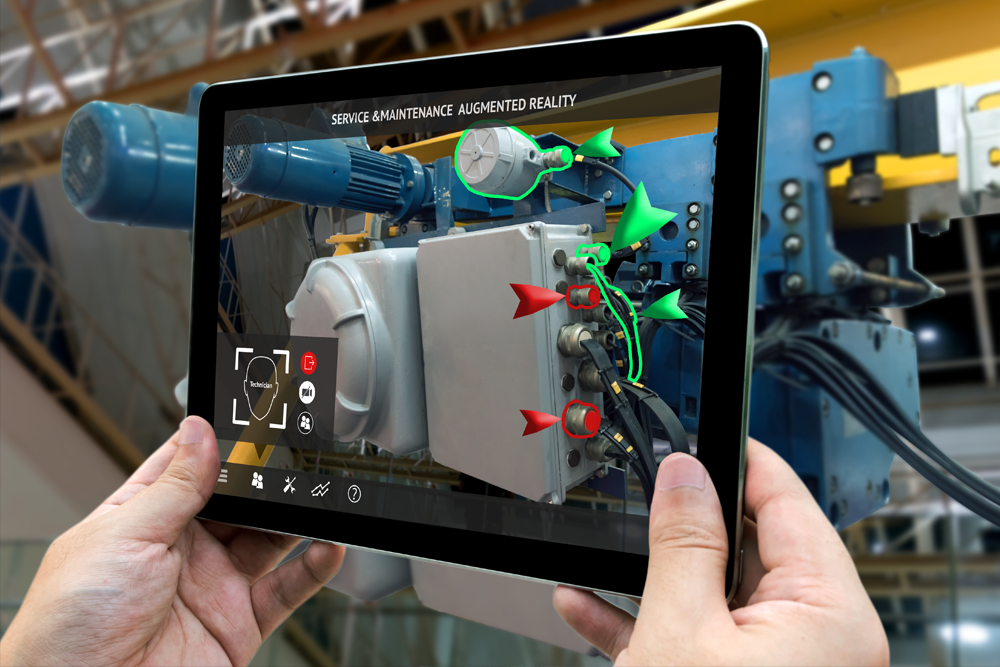
AR tags, which are digital markers, give robots a wealth of information when they are viewed through a camera lens. Robotics have the ability to recognize objects, calculate their positions, and navigate with unprecedented precision thanks to these systems. While the eye may be drawn to this fascinating technology, there is much more to it than meets the eye.
Continue reading to learn more about the inner workings of AR tags in computer vision robotics. AR tags’ potential in revolutionizing the robotics field is breathtaking, ranging from their role in improving object recognition to their application in precision surgeries. Let’s get to work and begin exploring the future of robotics with the help of AR tags.
What are AR Tags
In the vast and ever-evolving landscape of technology, Augmented Reality (AR) tags have emerged as a fascinating and integral component. They represent a pivotal aspect of modern computer vision and robotics, offering a rich tapestry of functionalities and applications. To truly comprehend the significance of AR tags, one must begin with a well-defined understanding of what they are and how they have evolved over time.
Definition of AR (Augmented Reality) Tags:
At its core, an AR tag is a digital marker designed to be recognized and interpreted by computer vision systems. These tags serve as points of reference for augmented reality applications, enabling digital content to be overlaid onto the real world when viewed through the lens of a camera-equipped device. Augmented Reality itself involves enhancing the physical world with digital information, and AR tags are the anchors that make this possible. These markers come in various shapes and sizes, often resembling black and white patterns, and can be affixed to physical objects or surfaces. When detected by a compatible camera, they trigger specific actions or augment the user’s perception of reality.
Distinction between AR Tags and QR Codes:
It’s crucial to distinguish AR tags from QR (Quick Response) codes, as they share some visual similarities but serve fundamentally different purposes. While both may appear as square patterns of black squares on a white background, their functions diverge significantly. QR codes are primarily designed for data storage and retrieval, linking to websites, contact information, or other digital content when scanned. In contrast, AR tags are all about enriching the real world with digital overlays, providing context or interactivity to the physical environment. AR tags act as triggers for augmented reality experiences, whereas QR codes are more akin to direct links to information.
Historical Context and Development of AR Tags:
To appreciate the evolution of AR tags, it’s worthwhile to delve into their historical context. AR tags, also known as fiducial markers, first gained prominence in academic and research circles as tools for tracking and identifying objects in computer vision applications. Over time, they transcended their academic origins and found applications in industries such as gaming, marketing, and, most notably, robotics. The development of AR tags has been closely intertwined with advancements in computer vision, including improved algorithms for pattern recognition and the increased availability of camera-equipped devices.
Key Features of AR Tags:
AR tags possess several key features that make them invaluable in the realms of computer vision and augmented reality. Firstly, they are designed to be easily detectable by camera systems, ensuring quick and accurate recognition. The distinct visual patterns and high contrast between black and white elements aid in this detection process. Secondly, AR tags can encode information within their pattern, allowing them to convey specific data or instructions to the system. This information may include details about the object to which the tag is attached, its orientation, or the type of augmented reality content to be overlaid. Lastly, AR tags are scalable and adaptable, meaning they can be created in various sizes and configurations to suit the needs of a particular application.
The Role of AR Tags in Computer Vision
In the intricate landscape of computer vision, Augmented Reality (AR) tags emerge as a pivotal element, bestowing a remarkable transformation upon the capabilities of this technology. Understanding the role of AR tags in computer vision unveils a world of possibilities, wherein these digital markers act as the linchpin for the convergence of the virtual and the physical. This section delves into three vital aspects of AR tags: how they enhance computer vision capabilities, their seamless integration with robotic systems, and the manifold benefits they usher into the realm of robotics applications.
How AR Tags Enhance Computer Vision Capabilities:
The integration of AR tags within computer vision is akin to adding a finely-tuned lens to a high-resolution camera. These unassuming markers provide context and structure to the visual data captured by cameras. By doing so, AR tags enable a deeper level of understanding, allowing computer vision systems to not only “see” but also “comprehend” the environment. Through the recognition of AR tags, computers can gauge the position, orientation, and identity of objects, thus enhancing object recognition, tracking, and overall understanding of the physical world. This is akin to giving a computer the ability to understand the world in much the same way we do, albeit through the lens of code and data.
Integration of AR Tags with Robotic Systems:
The synergy between AR tags and robotic systems is a testament to the remarkable progress made in the fields of automation and artificial intelligence. These digital markers serve as guides and navigational aids for robots, acting as beacons that allow precise localization and orientation. In essence, AR tags become the lighthouses in the vast sea of data, enabling robots to navigate complex environments with unparalleled accuracy. This integration is particularly vital in scenarios where robots are required to operate in unstructured or dynamic surroundings, such as warehouses, medical facilities, or even on the surface of other planets.
Benefits of Using AR Tags in Robotics Applications:
The advantages bestowed by AR tags in the realm of robotics are multifaceted. Firstly, they enhance safety by enabling robots to make well-informed decisions in real-time. For example, in a medical setting, AR tags can guide surgical robots to precisely target and remove a tumor while avoiding healthy tissue. Secondly, AR tags contribute to efficiency and precision in manufacturing and logistics. Robots equipped with AR tag recognition can swiftly and accurately assemble products or navigate warehouses for inventory management. Furthermore, these digital markers are invaluable in collaborative human-robot environments. By providing robots with a better understanding of human intent and actions, AR tags facilitate more natural and safer interactions between humans and machines.
AR Tag Encoding and Data
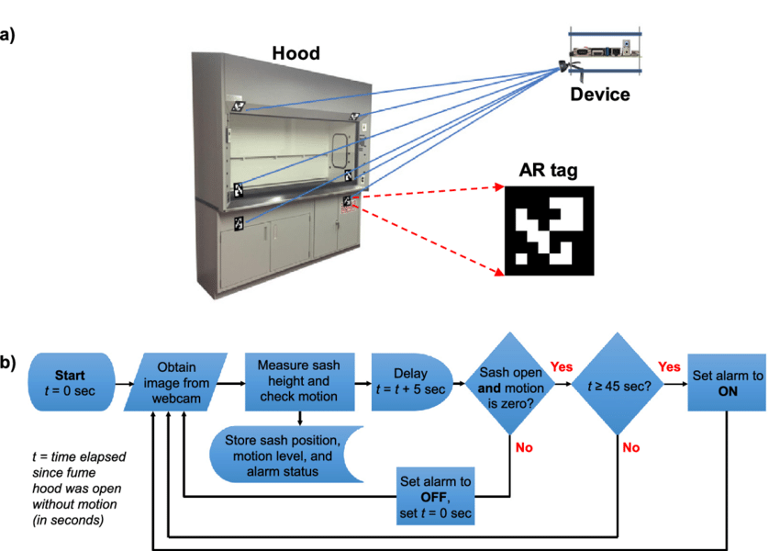
In the intricate world of Augmented Reality (AR) tags, the encoding and management of data are fundamental aspects that underpin their functionality and versatility. To appreciate the inner workings of AR tags, one must delve into the intricate web of data encoding, the types of data they commonly store, the structure of AR tag data, and the real-world applications where these digital markers truly shine.
How Information is Encoded in AR Tags:
AR tags are masters of encoding information in a visually intuitive manner. They do this through a system of high-contrast patterns, typically consisting of black and white elements. These patterns, when deciphered by a camera or computer vision system, translate into meaningful data. The encoding process relies on precise arrangements of these elements, akin to a digital language, that the system can interpret. Each combination of black and white squares conveys specific information, whether it’s an identifier, spatial coordinates, or instructions for augmented reality applications. It’s akin to a secret code that only the machines can comprehend, seamlessly bridging the gap between the physical and the digital.
Types of Data Commonly Stored in AR Tags:
AR tags are not one-trick ponies; they possess the ability to store a diverse array of data types. This can encompass basic information such as serial numbers, labels, or coordinates in a 2D space. However, AR tags can also carry more complex data, including three-dimensional positioning, rotation, and scaling information, making them essential for tasks like object tracking and pose estimation. Furthermore, AR tags are used to trigger augmented reality content, which can range from textual overlays to 3D models and animations. The flexibility of data storage within AR tags renders them indispensable in various applications, from industrial settings to gaming and marketing.
The Structure of AR Tag Data:
The structure of AR tag data is akin to a well-organized database, with each element serving a specific purpose. Within the visual pattern of an AR tag, you’ll find synchronization bits that help the camera lock onto the tag’s orientation and size. Next comes the data bits, the heart of the AR tag, where the encoded information resides. Error correction bits ensure that even if the tag is partially obscured or damaged, the system can still extract the correct data. These bits act as a safety net, ensuring the reliability of AR tag recognition in diverse conditions. Finally, checksum bits validate the integrity of the data, guaranteeing that what’s decoded matches what was originally encoded. This intricate structure ensures that AR tag data remains accurate and robust.
Examples of Real-World Applications Using AR Tag Data:
The real-world applications of AR tags are nothing short of astonishing. In the field of manufacturing, AR tags are used to precisely align components during assembly, reducing errors and increasing efficiency. In healthcare, AR tags aid in surgical navigation, guiding medical instruments with remarkable precision. Robotics benefits immensely from AR tags, as they enable robots to identify objects, calculate their position, and navigate complex environments. Moreover, in the realm of education and entertainment, AR tags bring textbooks to life and enhance gaming experiences through interactive content. Their utility extends to logistics, where they streamline inventory management, and even to art, where they trigger augmented reality exhibits. In essence, AR tags are the silent enablers of a world where the physical and digital realms coexist seamlessly.
In sum, the world of AR tags is a realm where data encoding is an art, where information is tucked away in intricate patterns, and where the applications are as diverse as the human imagination. They are the digital keys that unlock a universe of possibilities, from precision surgery to immersive gaming. AR tags are more than markers; they are the bridges connecting the tangible world to the boundless realm of augmented reality.
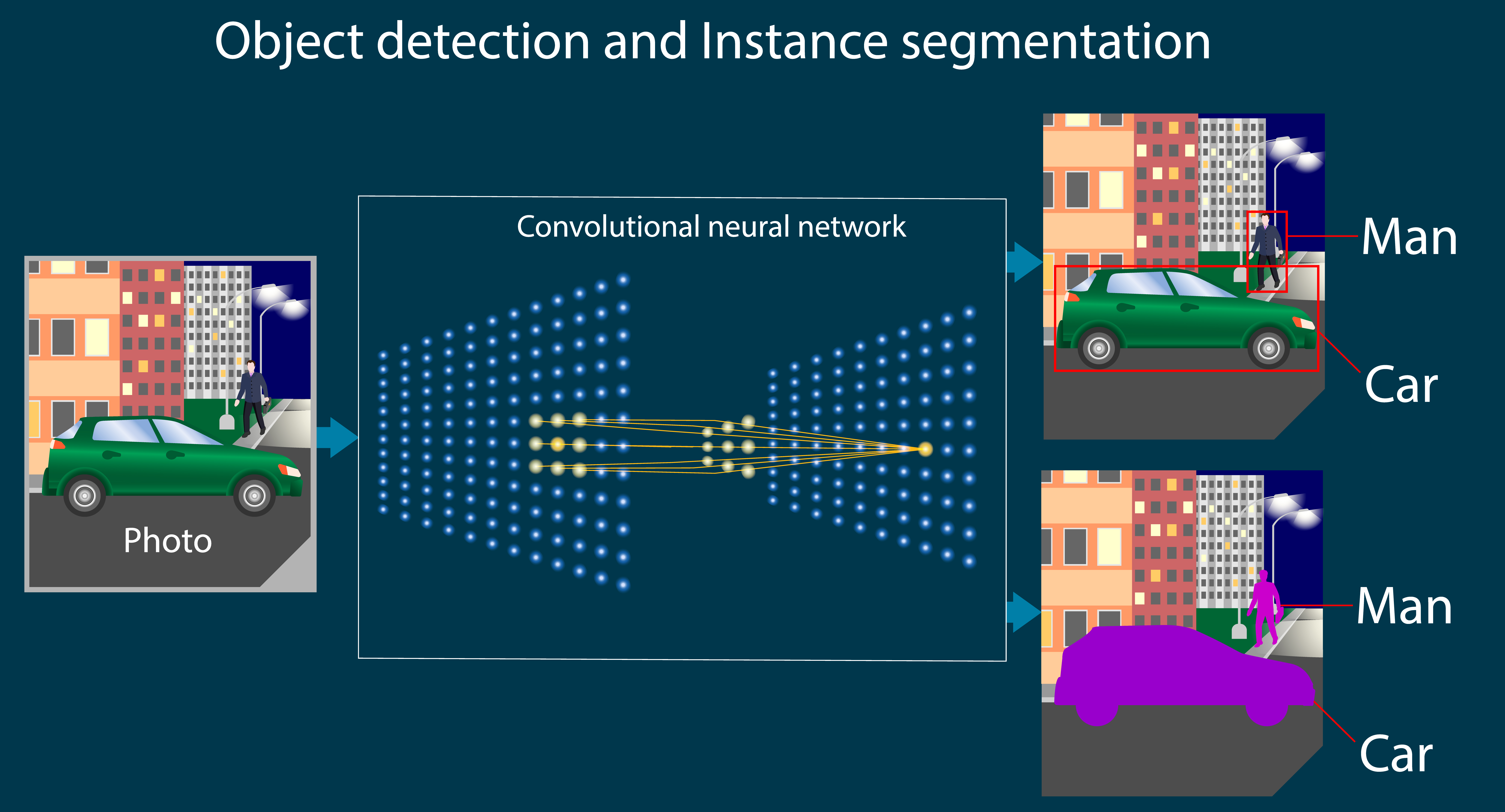
Detection and Recognition
In the dynamic realm of Augmented Reality (AR) tags, the process of detection and recognition stands as a pivotal and intricate component. This vital phase forms the bedrock upon which AR systems spring to life, allowing them to understand and interact with the world in a manner that mirrors human perception. To delve into the process of detecting AR tags in a visual scene, the algorithms and techniques that enable AR tag recognition, and the manifold challenges associated with accurate detection and recognition is to unveil the underlying mechanics that empower AR tags to bridge the realms of the physical and the digital.
The Process of Detecting AR Tags in a Visual Scene:
At the heart of AR tag technology lies the process of detecting these digital markers in a visual scene. When a camera-equipped device scans its surroundings, the detection process begins with the identification of the AR tags’ characteristic patterns. These patterns, often comprising contrasting black and white elements, serve as the visual signature that distinguishes AR tags from the background environment. Cameras seek these patterns, looking for specific spatial arrangements and the presence of synchronization markers that facilitate orientation. Once a potential AR tag is detected, the system moves to the recognition phase, where algorithms decipher the encoded information, determining the tag’s identity, spatial coordinates, and any associated actions or augmentations.
Algorithms and Techniques Used for AR Tag Recognition:
The algorithms and techniques that underpin AR tag recognition are a testament to the sophistication of computer vision and image processing. Within the realm of computer vision, two primary approaches dominate AR tag recognition: template-based and feature-based methods. Template-based recognition involves creating a library of known AR tag patterns and matching the detected patterns with those in the library. Feature-based methods, on the other hand, rely on identifying key points, edges, or contours in the tag’s pattern to determine its identity. Additionally, the use of machine learning and deep neural networks has become increasingly prevalent, allowing systems to recognize AR tags more flexibly and accurately. These techniques, often intertwined, form the backbone of AR tag recognition and are continually evolving to enhance precision and efficiency.
Challenges in Accurate Detection and Recognition:
While AR tag recognition has made significant strides, it is not without its challenges. One of the primary hurdles lies in environmental factors. Lighting conditions, reflections, occlusions, and the distance between the camera and the AR tag can all impact the recognition process. Furthermore, the presence of multiple tags in a single scene can introduce ambiguity and require complex algorithms to disambiguate and accurately identify each tag. Additionally, ensuring real-time recognition in dynamic or fast-paced environments, such as robotics or augmented reality gaming, demands highly efficient algorithms. Overcoming these challenges requires ongoing research and development to refine recognition techniques and adapt them to diverse scenarios.
Pose Estimation and Localization
In the complex and ever-evolving landscape of robotics, the concept of precise pose estimation and localization stands as a critical juncture. Augmented Reality (AR) tags have emerged as silent enablers, playing a pivotal role in enhancing these aspects of robotics. Understanding how AR tags empower precise pose estimation, their role in localization and mapping, and real-world case studies illustrating the significance of accurate pose estimation is essential to appreciate the transformative potential they hold in the field.
How AR Tags Enable Precise Pose Estimation in Robotics:
The essence of precise pose estimation in robotics lies in granting machines the ability to determine their spatial orientation and positioning relative to their environment. AR tags, with their distinct visual patterns and encoded information, become reference points that guide robots in this process. When a robot’s camera detects an AR tag, it immediately recognizes the unique pattern and interprets the encoded data, including the tag’s spatial coordinates and orientation. This information allows the robot to accurately ascertain its position in 2D or 3D space. In essence, AR tags serve as beacons, illuminating the path for robots to navigate with precision.
The Role of AR Tags in Localization and Mapping:
Localization and mapping are fundamental aspects of robotics, and AR tags play a significant role in facilitating these functions. By employing AR tags as reference points in a robot’s visual field, it becomes possible to create maps of the environment. Robots equipped with cameras can detect AR tags within the scene, triangulate their positions, and build a comprehensive map of their surroundings. Additionally, as the robot moves, the continuous detection of AR tags enables it to update its position on the map in real-time. This dynamic localization and mapping are particularly valuable in settings where robots must operate autonomously and adapt to changes in their environment.
Case Studies Demonstrating the Importance of Accurate Pose Estimation:
The importance of accurate pose estimation in robotics becomes vividly apparent when we examine real-world applications and case studies. Take, for instance, the field of manufacturing, where robotic arms equipped with AR tag recognition systems precisely position and assemble intricate components. These systems rely on AR tags to achieve a level of accuracy that human operators would find challenging. In the context of healthcare, surgical robots leverage AR tags to navigate delicate procedures, ensuring that incisions are precise and that the intended target is reached with minimal invasiveness. Furthermore, in the realm of autonomous vehicles, AR tags embedded in road infrastructure serve as markers for self-driving cars, aiding in their navigation and ensuring passenger safety. These case studies exemplify how AR tags are indispensable tools in a spectrum of applications, from precision manufacturing to life-saving medical procedures.
Calibration and Calibration Patterns
Calibration and calibration patterns represent the unsung heroes in the world of computer vision and robotics, quietly ensuring the precision and accuracy of visual data in a myriad of applications. The need for calibration arises from the inherent imperfections in camera and robotic systems, which, when uncorrected, can introduce errors that have far-reaching consequences. This is where Augmented Reality (AR) tags come into play, serving as invaluable calibration patterns that enable the fine-tuning of cameras and robotic systems to ensure they “see” the world accurately. Understanding why calibration is crucial, how AR tags fulfill this role, and the steps involved in camera calibration using AR tags is essential for unlocking the full potential of these technologies.
The Need for Calibrating Cameras and Robotic Systems:
Cameras and robotic systems are designed with precision, but they are not immune to imperfections. Factors such as lens distortion, sensor misalignment, and optical aberrations can introduce distortions in the images they capture. In the context of robotics, errors in spatial positioning can lead to costly mistakes or even safety concerns. Calibration is the process of quantifying and correcting these imperfections to ensure the accuracy of measurements and the fidelity of visual data. Whether it’s a medical robot performing surgery, an autonomous vehicle navigating city streets, or a manufacturing robot assembling intricate components, calibration is the linchpin for success.
How AR Tags are Used as Calibration Patterns:
AR tags, with their unique patterns of high-contrast elements, make for excellent calibration patterns. They possess characteristics that are easy to identify, and their known geometry and dimensions provide a reference framework for correction. During the calibration process, cameras capture images of AR tags placed at various positions and orientations within the field of view. These images are then analyzed to understand how the camera distorts the AR tag’s known geometry. The distortion parameters are calculated, and through a series of complex mathematical transformations, the images can be undistorted and aligned with the real-world coordinates, ensuring accuracy in spatial measurements. In essence, AR tags serve as the known points of reference against which the camera or robotic system can calibrate itself.
Steps Involved in Camera Calibration Using AR Tags:
Camera calibration using AR tags typically involves a series of well-defined steps:
-
AR Tag Placement: AR tags are strategically positioned within the camera’s field of view, ensuring they cover a variety of orientations and positions.
-
Image Capture: Images of the AR tags are captured, with each image containing one or more tags.
-
Image Analysis: The images are analyzed to detect the AR tags and identify their positions and orientations within the image.
-
Calibration Calculation: Based on the detected positions and orientations of AR tags, the calibration algorithm calculates the camera’s distortion parameters.
-
Distortion Correction: The calculated parameters are used to correct the distortion in the captured images, effectively undistorting them.
-
Mapping to Real-World Coordinates: The undistorted images are then mapped to real-world coordinates, providing accurate spatial information.
-
Validation: Finally, the calibration is validated by measuring the accuracy of real-world objects and comparing it to the calibrated measurements.
Limitations and Challenges

While Augmented Reality (AR) tags have carved a significant niche in the realms of computer vision and robotics, they are not immune to limitations and challenges. Understanding these constraints is essential for comprehending the technology’s current state and its potential evolution. Common limitations and challenges associated with AR tags, the environmental factors that can affect their performance, and the promising future developments and potential solutions constitute the trifold exploration of this intricate landscape.
Common Limitations and Challenges Associated with AR Tags:
AR tags, despite their versatility, confront a set of recurring limitations and challenges:
-
Limited Viewing Angle: AR tags must often remain within a certain range of angles and distances for reliable detection and recognition. This limitation can constrain their application in scenarios requiring wide-angle or long-range perception.
-
Environmental Variability: Factors such as varying lighting conditions, reflections, occlusions, and interference can impact AR tag recognition. Real-world environments are dynamic and unpredictable, which presents a challenge for consistent performance.
-
Dependency on Visual Patterns: AR tags primarily rely on their visual patterns for recognition. Alterations or damage to the pattern can hinder their detection, and they may struggle in cases of partial occlusion.
-
Processing Intensity: Achieving real-time detection and recognition of AR tags can be computationally intensive. This places demands on processing power, limiting their use in resource-constrained systems.
Environmental Factors Affecting AR Tag Performance:
AR tags’ performance is intricately linked to the environments in which they are deployed. Several environmental factors can influence their efficacy:
-
Lighting Conditions: Variations in lighting, such as shadows, direct sunlight, or low light, can affect the contrast and visibility of AR tags, impacting their detection.
-
Reflective Surfaces: Highly reflective surfaces, like glass or mirrors, can create reflections that confuse AR tag recognition systems, potentially leading to misinterpretation.
-
Dynamic Environments: In settings with moving objects or people, AR tags may be obscured or appear differently from one moment to the next, posing a challenge for consistent recognition.
-
Interference: Radiofrequency interference or electromagnetic signals in certain environments can disrupt the operation of AR tag detection systems, further compounding the challenge.
Future Developments and Potential Solutions:
The landscape of AR tags is not stagnant; ongoing developments aim to address these limitations and challenges. Potential solutions include:
-
Enhanced Pattern Designs: The development of more robust and adaptable AR tag patterns can improve their resistance to wear and damage, making them more reliable in various scenarios.
-
Advanced Algorithms: Continual advancements in computer vision and machine learning are equipping systems with better algorithms for recognizing AR tags under varying conditions.
-
Multi-Sensor Integration: Combining visual data with data from other sensors, such as depth sensors or inertial measurement units, can enhance AR tag detection and compensate for visual limitations.
-
Environmental Awareness: Systems that adapt to environmental conditions and dynamically optimize their detection processes based on context are under development, promising greater resilience.
-
Efficient Hardware: Hardware advancements, including more powerful processors and specialized vision hardware, enable real-time detection and recognition of AR tags with reduced computational demands.
In conclusion, AR tags, while offering remarkable potential, are not exempt from limitations and challenges. These encompass issues related to their viewing angles, susceptibility to environmental factors, and processing requirements. However, the future holds promise, with innovative solutions on the horizon. These solutions span improved pattern designs, smarter algorithms, multi-sensor integration, environmental awareness, and efficient hardware. As these developments unfold, AR tags are likely to overcome current limitations and become even more versatile and robust tools in the fields of computer vision and robotics, further bridging the gap between the digital and physical worlds.
Practical Applications

The practical applications of Augmented Reality (AR) tags in the realm of robotics are as diverse as they are transformative. These unassuming markers, with their distinct visual patterns, have found their way into a plethora of industries, bringing innovation, precision, and efficiency to a wide array of real-world scenarios. Let’s embark on an exploration of these applications, delve into compelling case studies from various industries, and shed light on the profound impact of AR tags on the landscape of robotics.
Exploration of Real-World Applications in Robotics:
The integration of AR tags into robotics has opened doors to a multitude of practical applications. Here, we take a closer look at some of the sectors where AR tags have made a notable impact:
-
Manufacturing: In the manufacturing industry, AR tags are deployed on the factory floor to guide robotic arms with pinpoint accuracy. Whether it’s the assembly of intricate components or the execution of quality control inspections, AR tags are instrumental in ensuring the precision and efficiency of robotic operations.
-
Healthcare: AR tags find applications in the healthcare sector, particularly in the realm of minimally invasive surgeries. Surgical robots equipped with AR tag recognition systems navigate complex anatomical structures, enabling surgeons to perform procedures with unparalleled precision and minimal invasiveness, ultimately leading to quicker recovery times for patients.
-
Autonomous Vehicles: The autonomous vehicle industry relies on AR tags to enhance navigation and safety. AR tags embedded in road infrastructure serve as markers for self-driving cars, helping them make real-time decisions about their positioning, speed, and route, thereby ensuring the safety of passengers and pedestrians alike.
-
Logistics and Warehousing: In logistics and warehousing, AR tags facilitate the seamless operation of robotic systems responsible for tasks such as inventory management and order fulfillment. These tags serve as beacons that guide robots in navigating labyrinthine warehouse layouts, enabling the efficient movement of goods.
Case Studies Highlighting the Use of AR Tags in Various Industries:
To appreciate the significance of AR tags in practical applications, let’s delve into some intriguing case studies:
-
Precision in Aerospace Manufacturing: In the aerospace industry, AR tags play a pivotal role in assembling intricate aircraft components. The precision required in this sector is awe-inspiring, and AR tags ensure that robotic arms position and attach components with microscopic accuracy, contributing to the safety and performance of aircraft.
-
Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Healthcare is witnessing a revolution in robotic-assisted surgery. Case studies reveal how AR tags guide robotic surgical systems, allowing surgeons to perform complex procedures with unmatched precision. This technology has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by making surgeries less invasive and more accessible.
-
Autonomous Delivery Robots: The emergence of autonomous delivery robots is changing the game for the logistics and e-commerce industries. AR tags placed on sidewalks and at delivery destinations guide these robots, ensuring that they navigate busy urban environments safely and reach their destinations accurately, offering efficient and contactless delivery services.
The Impact of AR Tags on Robotics in Sectors like Manufacturing, Healthcare, and More:
The impact of AR tags on the field of robotics is profound and multifaceted. They offer several key advantages, such as:
-
Precision: AR tags enhance the precision of robotic operations, whether it’s in manufacturing, healthcare, or logistics. This precision results in higher quality and efficiency.
-
Efficiency: By guiding robots with accuracy, AR tags streamline operations and reduce the margin for error. This, in turn, leads to cost savings and increased productivity.
-
Safety: In healthcare and autonomous vehicles, AR tags contribute to safety. They aid in minimizing the invasiveness of surgeries and ensuring safe navigation in dynamic environments.
More questions and answers
- What are the advantages of using AR tags in autonomous navigation systems?
-
The advantages of using AR tags in autonomous navigation systems are manifold. First and foremost, AR tags offer precise localization, allowing autonomous vehicles or robots to pinpoint their exact positions in real-time. This precision leads to enhanced safety, as it enables vehicles to avoid obstacles and make timely, informed decisions. AR tags are also cost-effective, as they provide a reliable means of navigation without requiring expensive infrastructure modifications. Furthermore, these tags are versatile and work in various environments and lighting conditions, ensuring consistent performance. In addition, they facilitate ease of deployment and maintenance. Overall, AR tags significantly improve the efficiency, safety, and reliability of autonomous navigation systems, making them indispensable in a wide range of applications.
- Can AR tags be used for collaborative robot-human interactions?
-
Yes, AR tags can indeed be utilized for collaborative robot-human interactions. By integrating AR tags into collaborative robotics systems, human workers can interact more seamlessly with robots, fostering a safer and more efficient work environment. AR tags enable robots to recognize and respond to human gestures and commands, facilitating intuitive and natural collaboration. They serve as visual cues, guiding robots in tasks that require precise coordination with human counterparts. This technology enhances communication and coordination, allowing for improved teamwork and productivity. Moreover, AR tags can contribute to the overall safety of collaborative workspaces by enabling robots to detect and respond to human presence, thereby reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing the overall collaborative experience.
- How does AR tag technology contribute to the precision of robotic surgeries?
-
AR tag technology significantly enhances the precision of robotic surgeries. These markers are strategically placed on the patient’s body or surgical instruments, serving as reference points for the surgical robot. The system continuously tracks the AR tags’ positions in real-time, enabling the robot to make precise and dynamic adjustments during the procedure. This level of accuracy is paramount in delicate surgeries where millimeter-level precision is essential.
Moreover, AR tags aid in compensating for patient movement or anatomical shifts, ensuring that the robot remains aligned with the surgical plan. This technology minimizes the invasiveness of procedures, reduces trauma to surrounding tissues, and shortens recovery times for patients. In summary, AR tag technology revolutionizes robotic surgeries by providing the critical precision required for complex procedures, ultimately improving patient outcomes and safety.
- What are the potential challenges when implementing AR tags in outdoor robotics applications?
-
Implementing AR tags in outdoor robotics applications presents several potential challenges. First, outdoor environments introduce variable lighting conditions, which can affect tag recognition. Harsh sunlight, shadows, or glare can interfere with the camera’s ability to detect and track AR tags accurately.
Additionally, environmental factors like rain, dust, or snow can obstruct the visibility of AR tags, leading to potential tracking errors. Wind and vibrations, common in outdoor settings, may also impact the stability of the tags, affecting precision.
Furthermore, outdoor navigation often involves uneven terrains and obstacles, which can challenge the robot’s ability to maintain line-of-sight with AR tags.
In summary, while AR tags offer substantial benefits in robotics, outdoor applications require robust solutions to overcome challenges related to lighting, environmental conditions, and terrain. Careful planning and adaptation are essential for successful implementation in outdoor settings.
- How can AR tags improve the efficiency of warehouse automation?
-
AR tags can significantly enhance the efficiency of warehouse automation by providing precise and real-time guidance to robotic systems. These markers, when strategically placed throughout the warehouse, act as beacons for autonomous robots and drones. By recognizing and tracking AR tags, these machines can efficiently navigate the complex and dynamic environment of a warehouse. This results in optimized routes for tasks like inventory management, order fulfillment, and goods transportation, reducing operational bottlenecks and minimizing the time required for tasks.
Moreover, AR tags offer a cost-effective solution compared to other infrastructure modifications. They are versatile, adaptable to changing layouts, and work in various lighting conditions. With the ability to improve accuracy and streamline warehouse processes, AR tags have become a valuable tool in enhancing the efficiency of warehouse automation, ultimately reducing costs and increasing productivity.
Article bottom line
In conclusion, AR tags represent an exciting new force in computer vision robotics. These subtle digital markers can greatly improve the way robots interact with and comprehend the world around them. These tags enable precise object recognition, enhance navigation, and provide a wealth of data, all of which can be used in a variety of industries.
AR tags have a wide range of applications, ranging from increasing warehouse efficiency to reducing the need for complex surgical procedures. In the future, robots will become more versatile, capable, and integrated into our daily lives, promising to be a more autonomous, capable, and intelligent body.
It is critical to address the issues and limitations that AR tags face as we move forward in this new era of augmented reality. Factors such as the environment, system calibration, and the need for robust recognition algorithms must all be considered. Despite these challenges, there are opportunities for advancement and innovation in the field.
The use of AR tags in robotics represents the human element and our ongoing quest to push the boundaries of what machines can do. We are closer than ever to a world in which robots and AR tags work together to make our lives safer, more efficient, and more connected.
The best way to stay up to date is to look for AR tags, whether you’re interested in robotics, a robotics expert, or simply curious about the future. These are the building blocks of a future in which robots will be able to see, understand, and navigate the world with incredible precision.








/ethical-standards-concept-design-1086882024-5c55de2146e0fb0001be6e61.jpg)