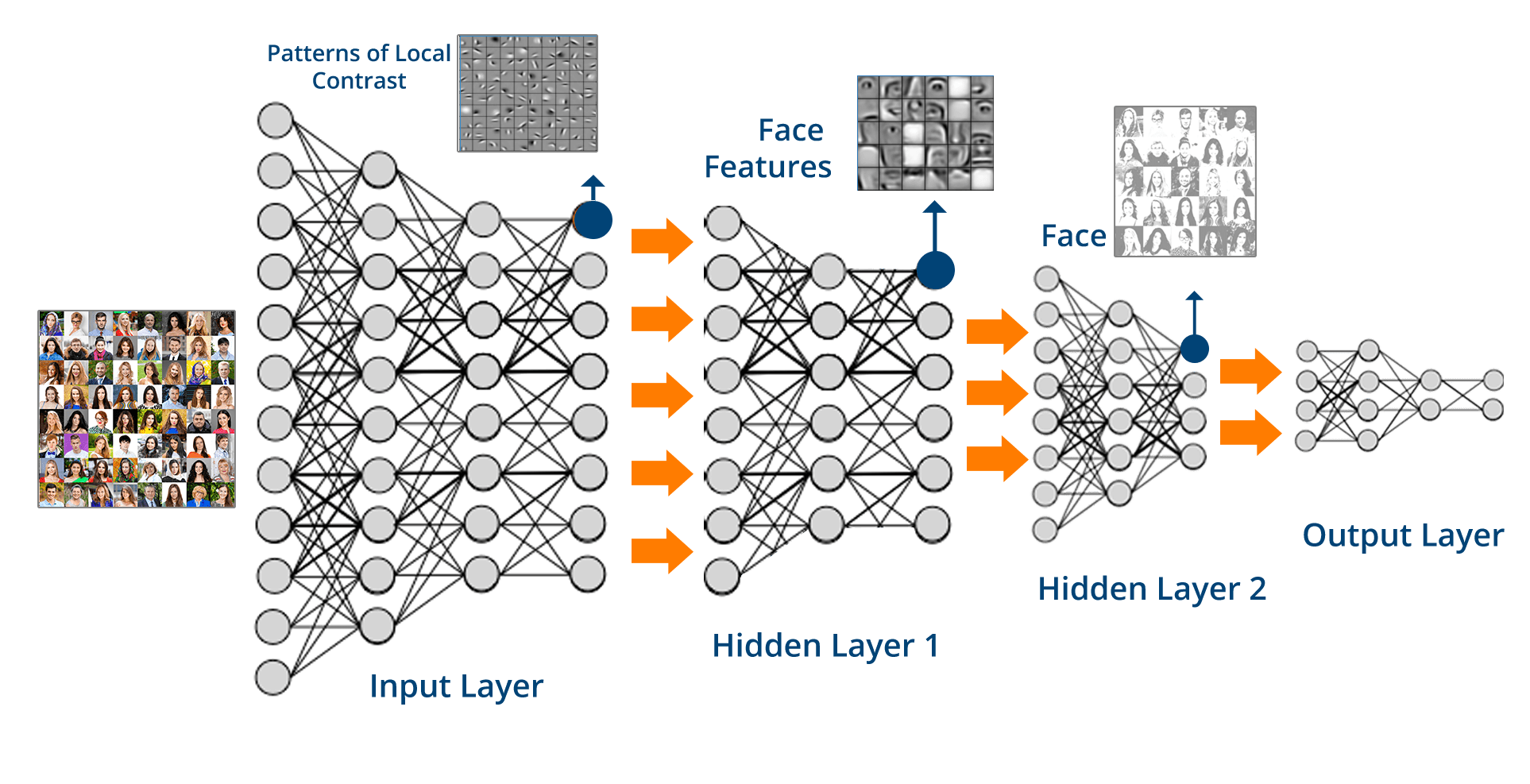
Imagine a world in which your computer creates melodies that touch your emotions and stir your soul, and your music will be a symphony conductor. Music generation through deep learning has emerged as an exciting frontier in this digital age thanks to the intersection of technology and art. Can machines compose music that is comparable to the best of our forefathers?
To summarize, this article will examine the fascinating world of creating music with deep learning and piano rolls. This course will cover deep learning fundamentals, as well as the magic of piano rolls and how to design an AI composer. We’ll cover advanced techniques for incorporating emotions into your compositions, musically blending styles, and using user feedback in our next class. As you read the book, you will begin collaborating with AI as a creative partner on your musical journey.
As we discover the secrets of creating music with deep learning piano rolls, where innovation meets artistic expression in perfect harmony, are you ready to unlock the potential of artificial intelligence to compose melodies that resonate with your heart?
Understanding Deep Learning and Music Generation
In the fascinating realm of music generation powered by deep learning, understanding the fundamentals is akin to deciphering the intricate notes of a symphony. Subsection 1 of our exploration delves into the bedrock of this technology, offering a glimpse into the symphony of neural networks and training that underpin the creative process.
Deep Learning Fundamentals
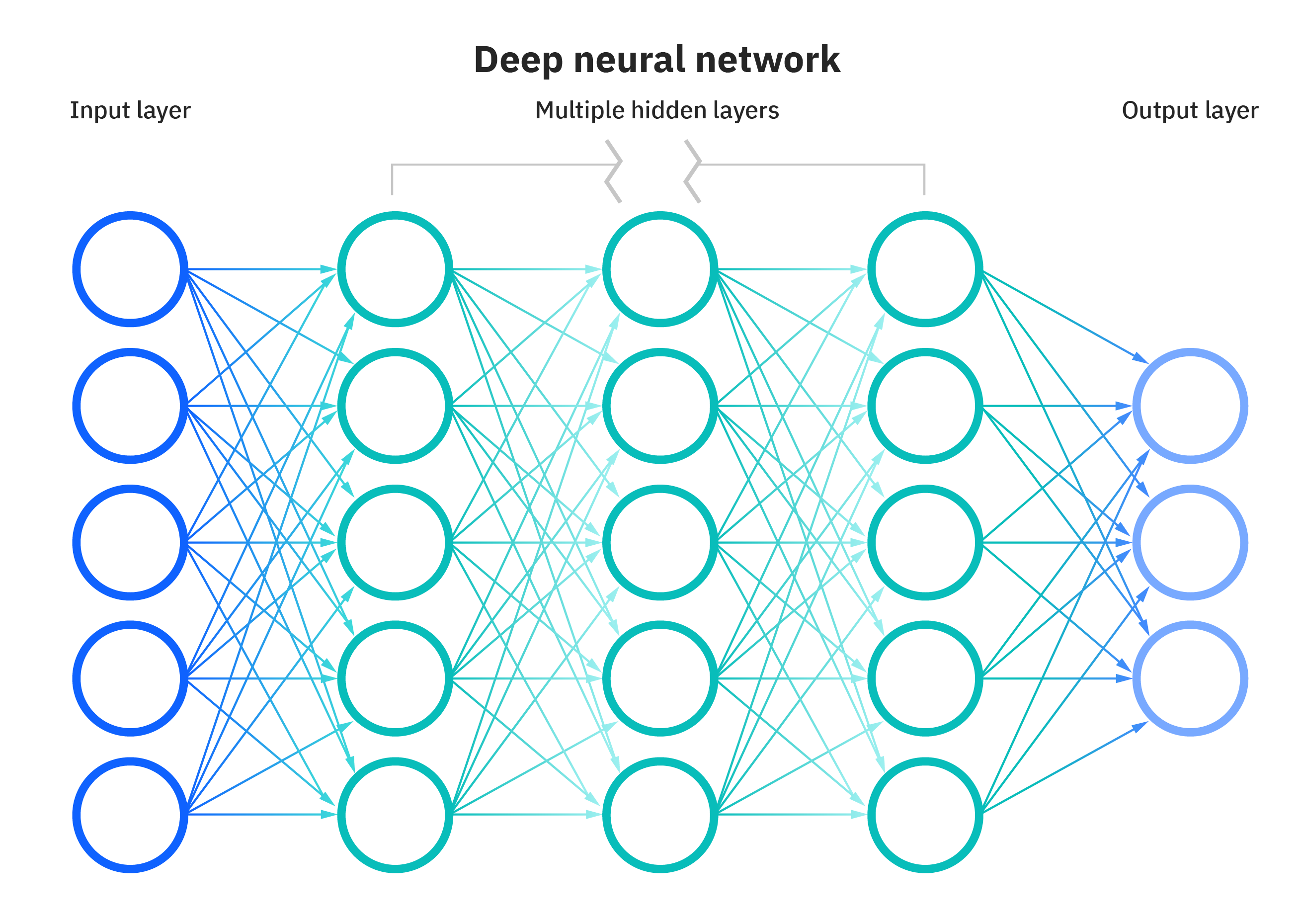
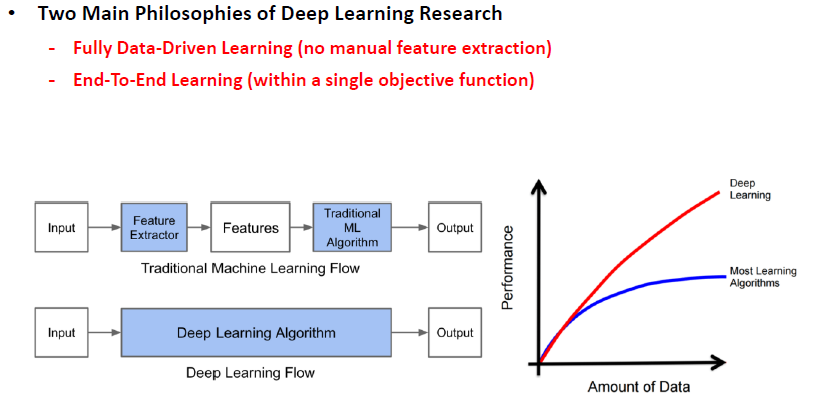
At its core, deep learning is an orchestra of algorithms and mathematical models inspired by the structure of the human brain. Neural networks, the instrumental players in this orchestra, are composed of interconnected nodes, or neurons, that process and transmit information. They have a remarkable ability to learn patterns and representations from vast datasets, a quality analogous to a musician honing their skills through practice and exposure to diverse melodies.
Training these neural networks involves a meticulous process of feeding them copious amounts of data, much like a musician rehearsing countless scales and compositions. As the neural network encounters a multitude of musical examples, it learns to extract features and nuances, akin to a musician discerning the subtleties of tempo, pitch, and dynamics. It’s this learning process that equips the neural network with the proficiency to compose music that not only mimics existing genres but can also venture into uncharted sonic territories.
Subsection 2 of our exploration introduces an instrumental element that fuels the creative engines of deep learning - piano rolls as data.
Piano Rolls as Data
In the world of music, piano rolls are akin to the sheet music that guides a musician’s performance. They are a specialized notation system that represents musical notes as they unfold over time. But in the context of deep learning, piano rolls take on a new role as a rich source of data, akin to a treasure trove of musical inspiration.
These digital representations encapsulate the essence of a musical piece, capturing every note’s timing, duration, and pitch. They serve as the raw material that feeds into the neural network’s learning process. The advantages of employing piano rolls as input for deep learning models are manifold, resembling the advantages a skilled musician gains from having a diverse repertoire at their fingertips.
Firstly, piano rolls provide a structured format that aligns with the sequential nature of music. Just as a musician follows a score from start to finish, deep learning models can process piano rolls chronologically, allowing them to grasp the narrative arc of a composition. Furthermore, the discrete nature of piano roll data, with each note neatly categorized, facilitates the neural network’s ability to identify and recreate these musical components.
Secondly, the use of piano rolls introduces an element of universality to the creative process. Much like a musician can adapt and reinterpret a piece of music across various instruments, deep learning models trained on piano rolls can generate music that spans genres, styles, and instruments. This versatility is a testament to the power of piano roll data in nurturing the AI’s capacity to transcend musical boundaries.
Building Blocks of Music Generation
In the intricate tapestry of music generation through deep learning, the foundation lies in the meticulous construction of its building blocks. Subsection 1, which we embark upon, is the cornerstone - Data Preparation.
Data Preparation: The Crucible of Creativity
To craft melodies that resonate with the human soul, the journey begins with an unassuming yet indispensable step: the collection and preparation of piano roll data. This process parallels a composer meticulously selecting the finest instruments and tuning them to perfection before embarking on a symphony.
Here, data is the muse. It involves curating extensive datasets of piano rolls, which serve as the primary source material for the AI composer. These piano rolls encapsulate the essence of musical compositions, each note meticulously encoded with information on timing, duration, and pitch. The process of collecting this data is akin to assembling a vast library of musical manuscripts, where each piece contributes to the AI’s musical vocabulary.
Yet, the quest for quality transcends mere quantity. The importance of high-quality training data is paramount. Just as a virtuoso demands precision from their instrument, the deep learning model relies on clean and accurate data to compose harmonious melodies. Errors or inconsistencies in the training data can lead to discordant compositions, undermining the very essence of AI-generated music. It’s akin to a composer striving for perfection in every note, knowing that the slightest imperfection can disrupt the symphony’s flow.
Subsection 2, “Choosing the Right Model,” takes us into the realm of architecture and design, where the choice of the AI composer’s framework is a pivotal decision.
Choosing the Right Model: Crafting the Composer’s Core
In this subsection, we embark on an exploration of the varied deep learning architectures suitable for music generation. Just as composers select different instruments to evoke distinct emotions, choosing the right model sets the stage for the AI’s creative prowess. There is no one-size-fits-all in this orchestration; it’s about harmonizing the model with the desired musical outcome.
We traverse a landscape rich with options, from recurrent neural networks (RNNs) that embrace sequential data like a sonnet, to generative adversarial networks (GANs) that engage in a duet of creation and critique. Each architecture brings its strengths and weaknesses, akin to different instrumental timbres. RNNs excel in capturing temporal dependencies, while GANs foster creativity through adversarial training.
Highlighting these strengths and weaknesses is akin to a music critic reviewing the merits of a particular performance. It helps composers, or in this case, developers, make informed choices based on the musical nuances they wish to imbue into the AI’s compositions.
Subsection 3, “Training Your Model,” guides us through the intricate process of nurturing the AI composer’s skillset.
Training Your Model: The Art of AI Apprenticeship
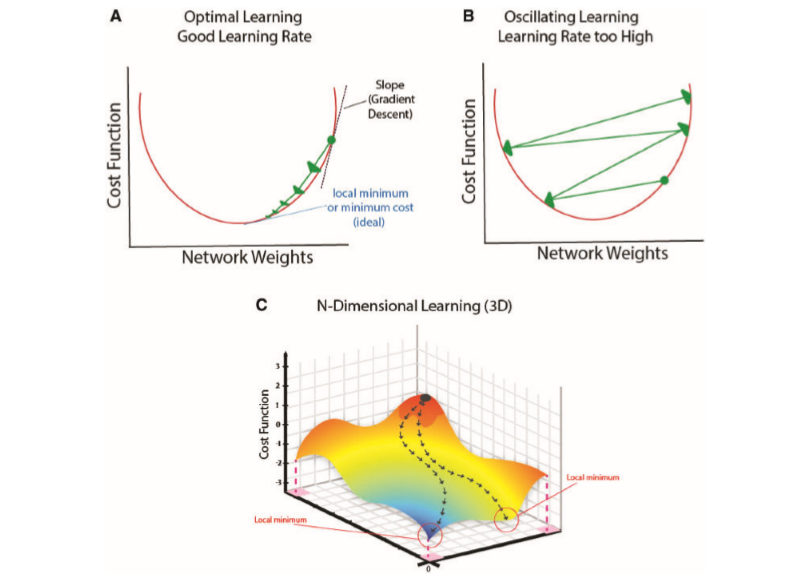
In this phase, we don the mantle of a mentor, providing a step-by-step guide on how to train a deep learning model for music generation. The journey begins with the selection of appropriate hyperparameters, akin to tuning an instrument to the desired pitch. We delve into the intricacies of the training process, likening it to a musical apprenticeship where the AI learns from its musical predecessors.
Hyperparameter tuning is akin to adjusting the conductor’s baton to achieve the perfect tempo and dynamics. It involves optimizing variables like learning rates and batch sizes to ensure that the model learns and adapts effectively. The training process itself unfolds like a musical composition, with each epoch refining the AI’s ability to generate harmonious melodies.
We also explore optimization techniques, drawing parallels with a musician’s dedication to perfecting their craft. Techniques like gradient clipping and learning rate schedules serve as the scales and exercises that strengthen the AI composer’s capabilities.
Lastly, Subsection 4, “Evaluating Model Performance,” sheds light on the critical aspect of assessing the quality of the AI-generated music.
Evaluating Model Performance: The Sonic Litmus Test
Much like a music critic appraises a performance, evaluating the quality of generated music requires a discerning ear. In this section, we elucidate the methods and metrics used to gauge the AI composer’s virtuosity.
We delve into the realm of evaluation metrics, such as FID (Fréchet Inception Distance) and perplexity, which serve as the musical score by which the AI’s compositions are judged. These metrics provide an objective measure of the generated music’s fidelity to the training data and its inherent creativity. It’s akin to scoring a musical composition based on its adherence to established conventions and its innovative flair.
In closing, the building blocks of music generation encompass a symphony of processes, from data preparation to model selection, training, and evaluation. In each phase, we find parallels with the world of music, where precision, creativity, and critical assessment converge to create AI-generated melodies that resonate with the human spirit. As we navigate this intricate composition, we uncover the secrets to harmonizing technology and artistry in a symphony of innovation.
Advanced Techniques and Creative Enhancement
In the ever-evolving landscape of AI-generated music, the quest for creative enhancement and emotional resonance represents an intricate symphony of advanced techniques. Subsection 1, “Adding Emotion to Music,” delves into the artistry of infusing profound emotions and human-like qualities into the fabric of AI-generated compositions.
Adding Emotion to Music: The Heartbeat of Creativity
In this subsection, we embark on a journey to explore the nuanced techniques that breathe life and emotion into AI-generated music. Much like a skilled musician pouring their soul into a performance, the integration of emotions into music is a transformative process.
Here, sentiment analysis emerges as a key conductor of emotion. It serves as the compass, guiding the AI composer to navigate the vast emotional spectrum. By analyzing the sentiment of lyrics, melodies, or even user-generated content, AI can tailor compositions to evoke specific feelings, whether it’s the melancholy strains of a requiem or the euphoric crescendo of a celebratory anthem. It’s akin to a composer channeling their innermost emotions into every note, creating a musical masterpiece that resonates deeply with listeners.
Emotional mapping, on the other hand, is the canvas upon which the AI artist paints its sonic emotions. It involves associating musical elements with specific emotions, much like assigning colors to moods on an artist’s palette. For example, minor chords may be linked to sadness, while major chords might evoke joy. By mapping emotions to musical features, AI can craft compositions that tug at the heartstrings and convey a profound sense of human-like sentiment. It’s akin to a painter using brushstrokes to convey the depth of human emotion on a canvas.
Subsection 2, “Combining Styles and Genres,” ushers us into a realm of musical innovation where deep learning serves as a bridge between diverse musical styles and genres.
Combining Styles and Genres: A Musical Kaleidoscope
In this phase of our exploration, we witness the remarkable capacity of deep learning to blend different musical styles and genres, creating harmonious fusions that defy conventional boundaries. Much like a skilled chef blending diverse ingredients to create a culinary masterpiece, deep learning models combine musical elements to craft genre-defying compositions.
We are presented with examples of successful genre-mixing, where the AI composer orchestrates a symphony that seamlessly weaves together the threads of classical, jazz, and electronic music, producing a unique and captivating sonic tapestry. These genre-blending compositions illustrate the limitless potential of AI in pushing the boundaries of musical creativity.
Subsection 3, “Incorporating User Feedback,” unfolds as a symposium on the collaborative nature of AI-generated music, where the input of users becomes a vital component of the creative process.
Incorporating User Feedback: A Dynamic Dialogue
In the final phase of our exploration, we delve into the dynamic interplay between AI and human creativity. Here, we explore ways to incorporate user feedback into the training process, transforming AI-generated music into a collaborative venture.
Much like a mentor guiding a prodigious talent, user feedback provides valuable insights that enable iterative improvement. By soliciting feedback from musicians, composers, and music enthusiasts, AI composers refine their craft, learning from the diverse perspectives and preferences of their human collaborators. This iterative process is akin to a musical rehearsal, where each session refines the composition until it achieves a harmonious and resonant form.
Reinforcement learning emerges as a powerful tool in this collaborative journey. It enables the AI composer to adapt and evolve based on user interactions, much like a musician refining their performance based on audience reactions. With each interaction, the AI learns to compose music that aligns more closely with the user’s preferences, creating a symbiotic relationship between technology and creativity.
In essence, the advanced techniques and creative enhancement in AI-generated music represent a harmonious fusion of technology and artistry. As we traverse these subsections, we witness the evolution of AI as a creative collaborator, capable of infusing profound emotions, transcending musical genres, and engaging in a dynamic dialogue with human creators. The future of AI-generated music holds the promise of ever-deepening emotional resonance and artistic exploration, where the boundaries of musical creativity continue to expand, creating a symphony that resonates with the human soul.
Challenges and Future Directions

In the ever-evolving landscape of AI-generated music, we find ourselves at a critical juncture where challenges and future directions shape the destiny of this transformative field. Subsection 1, “Ethical Considerations,” invites us to navigate the moral compass of AI-generated music, addressing profound ethical concerns that demand our attention.
Ethical Considerations: Harmonizing Innovation and Responsibility
As AI-generated music flourishes, it brings with it a symphony of ethical concerns that merit our contemplation. At the forefront of these concerns lies the issue of copyright, where the creative output of AI intersects with intellectual property rights. Much like the legal intricacies of sampling in the music industry, AI-generated compositions often incorporate elements from existing works. This prompts questions about ownership, royalties, and artistic credit. Ethical solutions must be found to ensure that musicians and composers receive due recognition and compensation for their creative contributions while embracing the innovative potential of AI.
Responsibility in AI usage also becomes a defining theme. The power of AI in music creation necessitates careful stewardship, akin to the responsibility of a conductor guiding an orchestra. The creative choices made by AI models, influenced by their training data, require scrutiny to prevent the propagation of biases, stereotypes, or offensive content. Striking a balance between creative freedom and responsible AI usage becomes paramount, ensuring that AI-generated music respects diverse cultures and values.
In Subsection 2, “Future Innovations,” we embark on a visionary journey, peering into the horizon of possibilities that await the world of AI-generated music.
Future Innovations: Orchestrating Tomorrow’s Soundscapes
The future of AI-generated music is a symphony of innovation, where the boundaries of creativity continue to expand. We stand at the cusp of technological breakthroughs that promise to reshape the very nature of music. Deep learning for music generation will likely witness advancements that enable AI composers to craft compositions that evoke not just emotion but deeply resonate with listeners, mirroring the genius of legendary composers.
The impact of AI-generated music on the music industry looms large on the horizon. We may witness a transformation akin to the advent of digital music, where AI composers become collaborators with human musicians, enhancing the creative process. The potential for personalized music experiences tailored to individual preferences and moods could redefine the way we consume and interact with music. This evolution could also lead to new business models, challenging traditional paradigms and revolutionizing music distribution.
As we traverse the challenges and future directions of AI-generated music, we find ourselves at a crossroads of responsibility and innovation. The path forward requires us to harmonize the creative potential of AI with ethical considerations, ensuring that music remains a universal language that respects both its creators and listeners. With technology as our virtuoso, the future of AI-generated music holds the promise of compositions that transcend the ordinary, resonating deeply with the human spirit and enriching the tapestry of musical expression.
Related questions and answers
- How can I get started with deep learning-based music generation using piano rolls?
-
To start with deep learning-based music generation using piano rolls:
- Gather diverse, labeled piano roll data.
- Choose a framework like TensorFlow or PyTorch.
- Design your neural network (e.g., RNNs or GANs).
- Preprocess and normalize the data.
- Train the model with parameter tuning.
- Generate music, adjusting for style and complexity.
- Evaluate quality using metrics.
- Refine with user feedback.
- Address copyright and ethical concerns.
- Stay updated with evolving techniques.
- What are the best practices for collecting and cleaning piano roll datasets?
-
Collecting and cleaning piano roll datasets for deep learning is crucial for successful music generation. Follow these best practices:
-
Diverse Sources: Gather data from diverse musical genres and styles to ensure versatility in your dataset.
-
Metadata: Include metadata such as composer, genre, and tempo to enhance dataset organization.
-
Labeling: Ensure each piano roll is labeled accurately to help the model understand the musical context.
-
Quality Control: Manually review and filter out low-quality or duplicate rolls to maintain data integrity.
-
Data Augmentation: Augment the dataset by applying transformations like pitch shifting or time stretching to increase variety.
-
Normalization: Normalize data to a consistent format, ensuring uniformity in note representation, time signature, and tempo.
-
Handling Missing Data: Address missing or incomplete piano rolls through techniques like interpolation.
-
Balancing: Maintain a balanced dataset to avoid bias towards any particular style or genre.
-
Version Control: Implement version control to track dataset changes and updates.
-
Documentation: Document dataset details thoroughly for reference and reproducibility.
Following these practices will set a strong foundation for training deep learning models in music generation.
-
- Are there any specific deep learning models that excel in music generation?
-
Yes, specific deep learning models excel in music generation. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and their variants, such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU), are widely used. RNNs are adept at capturing temporal dependencies in music, making them suitable for sequential data like notes in a composition.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have also shown promise. GANs consist of a generator and a discriminator, engaged in a creative adversarial process. They can produce music with high creativity and diversity.
Additionally, Transformer-based models like the OpenAI GPT series have demonstrated remarkable results in various natural language tasks and have been adapted for music generation. Their attention mechanisms allow them to learn complex patterns in music.
Ultimately, the choice of model depends on the specific music generation task, dataset, and desired outcomes. Experimentation with different models and architectures is often necessary to achieve the best results.
- How can I assess the quality and creativity of music generated by my model?
-
Assessing the quality and creativity of music generated by your model involves a multifaceted approach:
-
Human Evaluation: Enlist musicians or music enthusiasts to provide subjective assessments. Their expertise can gauge musicality, emotional resonance, and originality.
-
Objective Metrics: Utilize quantitative metrics like FID (Fréchet Inception Distance) or perplexity to measure the similarity between generated and real music. Lower FID scores indicate higher quality.
-
Diversity: Evaluate diversity by analyzing how varied and novel the generated compositions are. A lack of diversity may indicate limitations in creativity.
-
User Feedback: Solicit feedback from users to understand their preferences. This iterative process can guide improvements in line with audience tastes.
-
Comparison to Baselines: Compare your model’s output to existing AI-generated music and human compositions to assess its uniqueness and quality.
-
Genre-Specific Evaluation: Consider genre-specific criteria to ensure the model’s proficiency in diverse musical styles.
-
Emotion Elicitation: Assess if the music successfully conveys emotions or elicits specific feelings, a hallmark of creativity.
A comprehensive evaluation, combining both subjective and objective measures, provides a holistic view of your model’s music generation prowess.
-
- What are some techniques for adding human-like emotion to AI-generated music?
-
Adding human-like emotion to AI-generated music involves several techniques:
-
Sentiment Analysis: Analyze lyrics, melodies, or user-generated content to identify emotional cues. Match musical elements to specific emotions (e.g., minor chords for sadness).
-
Emotional Mapping: Assign emotions to musical features, such as tempo, dynamics, or harmonies. Craft compositions that reflect these emotional mappings.
-
Dynamic Expression: Introduce dynamic changes in volume, tempo, and articulation to mimic human expression. These nuances can evoke emotional depth.
-
Phrasing and Timing: Adjust phrasing and timing to create natural musical pauses and transitions, mimicking human performance.
-
Instrumentation: Choose instruments that resonate with specific emotions. For instance, violins for melancholy or trumpets for triumph.
-
Lyric Generation: If applicable, use natural language processing to generate lyrics that convey desired emotions and themes.
-
User Interaction: Incorporate user feedback to tailor compositions to individual emotional preferences, making the music more relatable.
By combining these techniques, AI-generated music can achieve a human-like emotional resonance that resonates deeply with listeners.
-
- Can deep learning generate music that combines different musical genres?
-
Yes, deep learning can generate music that seamlessly blends different musical genres. Deep learning models, such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), have the ability to learn diverse musical styles from training data. By exposing these models to a wide range of genres, they can capture the essence of each style.
During the generation process, the model can interpolate between learned genre representations, allowing it to create music that smoothly transitions between genres or combines elements from multiple genres. This results in innovative compositions that fuse the characteristics of, for example, classical and jazz, or rock and electronic music.
The flexibility of deep learning models and their capacity to capture intricate patterns in music make them powerful tools for generating genre-blending music, expanding creative possibilities within the music industry.
- How can user feedback be integrated into the music generation process?
-
User feedback can play a pivotal role in enhancing the music generation process. Here’s how it can be integrated effectively:
-
Feedback Collection: Establish channels for users to provide feedback on generated music, such as rating systems or comments on music platforms.
-
Sentiment Analysis: Implement sentiment analysis to gauge user emotional responses to music. Identify patterns in feedback to understand preferences.
-
Iterative Training: Continuously update the model based on feedback. Reinforce aspects users appreciate and adjust those that receive criticism.
-
Customization: Allow users to personalize generated music by expressing preferences for style, tempo, or mood. Tailor compositions to individual tastes.
-
A/B Testing: Conduct A/B testing to compare variations of generated music and determine which resonates better with users.
-
Collaborative Models: Collaborative filtering techniques can recommend music based on user history, creating a feedback loop that refines recommendations.
-
User-Generated Content: Encourage users to co-create music. Incorporate their input, such as lyrics or melodies, into the generation process.
By actively involving users and valuing their input, music generation models can evolve to produce compositions that align more closely with audience expectations and preferences.
-
- What ethical considerations should I be aware of when using AI in music creation?
-
When using AI in music creation, several ethical considerations merit attention:
-
Copyright and Plagiarism: Ensure AI-generated music respects copyright laws. Avoid using copyrighted material without proper authorization.
-
Bias and Fairness: Guard against algorithmic biases that may perpetuate stereotypes or cultural insensitivity. Strive for diversity and inclusivity in music creation.
-
Transparency: Be transparent about the involvement of AI in music production, especially when presenting it to the audience as the work of human artists.
-
Ownership and Attribution: Clarify ownership of AI-generated compositions. Provide proper attribution to human developers, AI models, and data sources.
-
User Consent: If collecting user data for music customization, obtain clear and informed consent regarding data usage and storage.
-
Quality Control: Ensure AI-generated music meets ethical quality standards and avoids generating offensive or harmful content.
-
Data Privacy: Safeguard user data used in training models. Comply with data protection regulations and respect user privacy.
-
Human-AI Collaboration: Embrace collaboration between AI and human musicians, emphasizing the complementary roles of technology and creativity.
By addressing these ethical considerations, AI-driven music creation can be a responsible and enriching endeavor that respects intellectual property, cultural values, and user rights.
-
- What does the future hold for AI-generated music, and how will it impact musicians and the music industry?
-
The future of AI-generated music promises significant changes in the music industry and for musicians:
-
Innovation and Collaboration: AI will continue to inspire new musical genres and styles, encouraging musicians to collaborate with AI systems for fresh creative inputs.
-
Efficiency in Production: Musicians will use AI tools to streamline music production, from composing melodies to mixing and mastering tracks, saving time and effort.
-
Personalization: AI-driven music platforms will offer highly personalized music recommendations and compositions tailored to individual preferences.
-
Copyright and Legal Challenges: The music industry will grapple with copyright issues surrounding AI-generated music, necessitating new legal frameworks.
-
New Revenue Streams: Musicians may find additional income sources through AI-generated music, including licensing AI compositions for various media projects.
-
Challenges to Authenticity: Musicians may face questions about the authenticity of their work when AI is involved, demanding transparency in credits.
-
Accessibility: AI-generated music may democratize music creation, allowing individuals with no musical background to produce their compositions.
While AI will bring innovation and efficiency, its impact on musicians and the music industry will require careful navigation of legal, ethical, and creative boundaries.
-