Word2vec is a neural network that creates a distributed representation of words. It is a shallow, two-layer neural network that is trained on a large corpus of text. The word2vec model creates a vector space where each word is represented by a point in the space. The model is designed to capture the context of words, so that similar words are represented by points that are close together in the space.
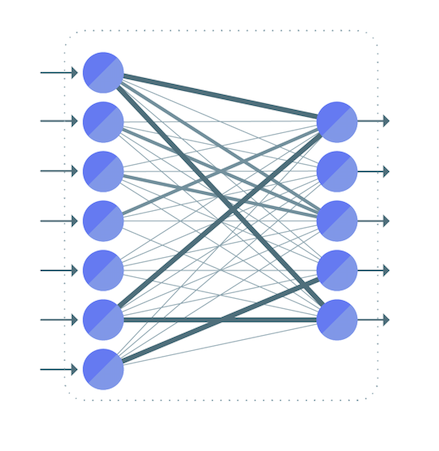
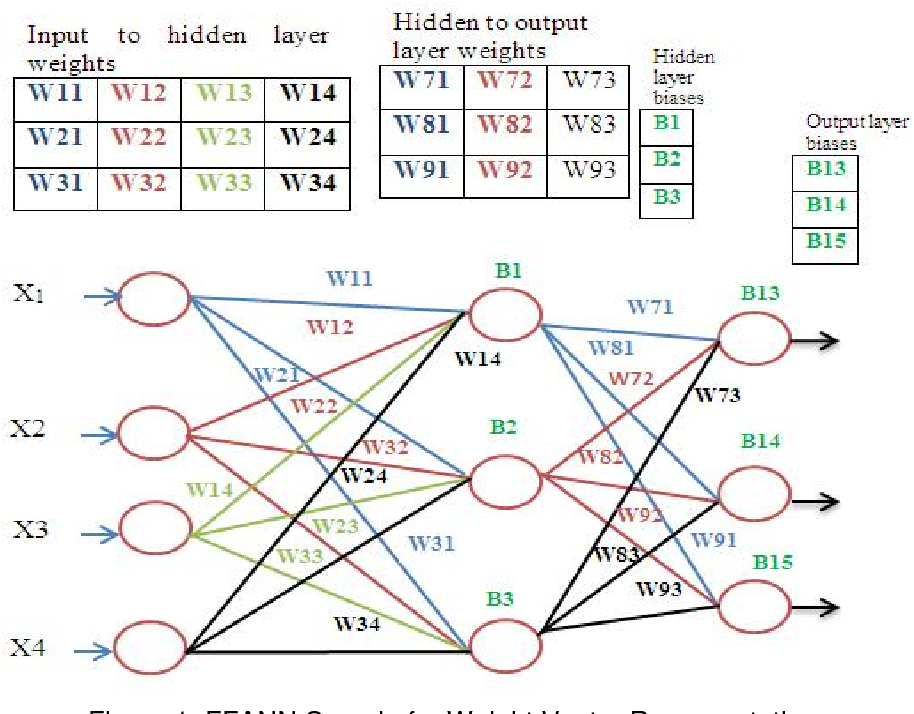
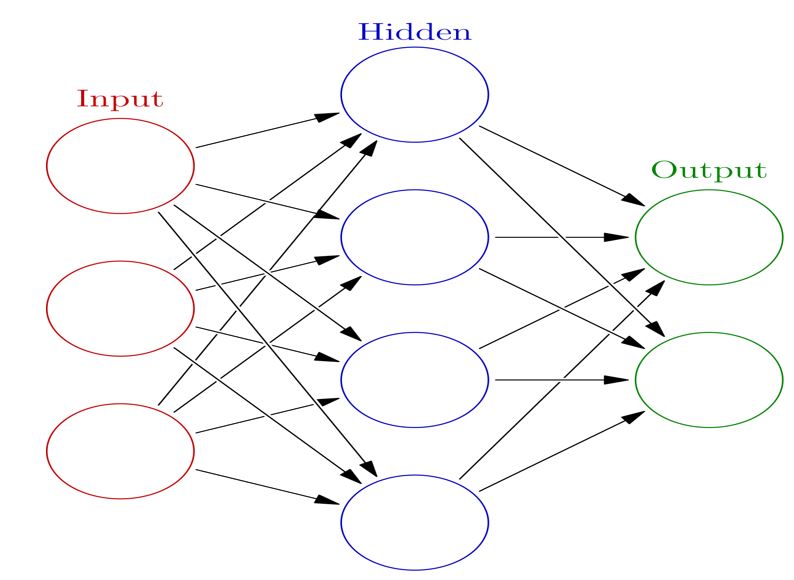
In this article, we will look at non-contextual embedding methods, which include words that do not have a relevance to the context in which they are embedded. A simple neural network will be trained using a single hidden layer on a specific task. The weights of the networks that represent embedded words will be the focus of our study. The goal of training a simple neural network with one hidden layer is to generate a task that can be performed on its own. The goal of this exercise is to calculate the weights of the hidden layer. Finally, these weights are the fruits of our labor, the words that we are attempting to learn. If we use the input word New, we can say that the output probability of words such as York and City is higher than that of the books and lightsaber.
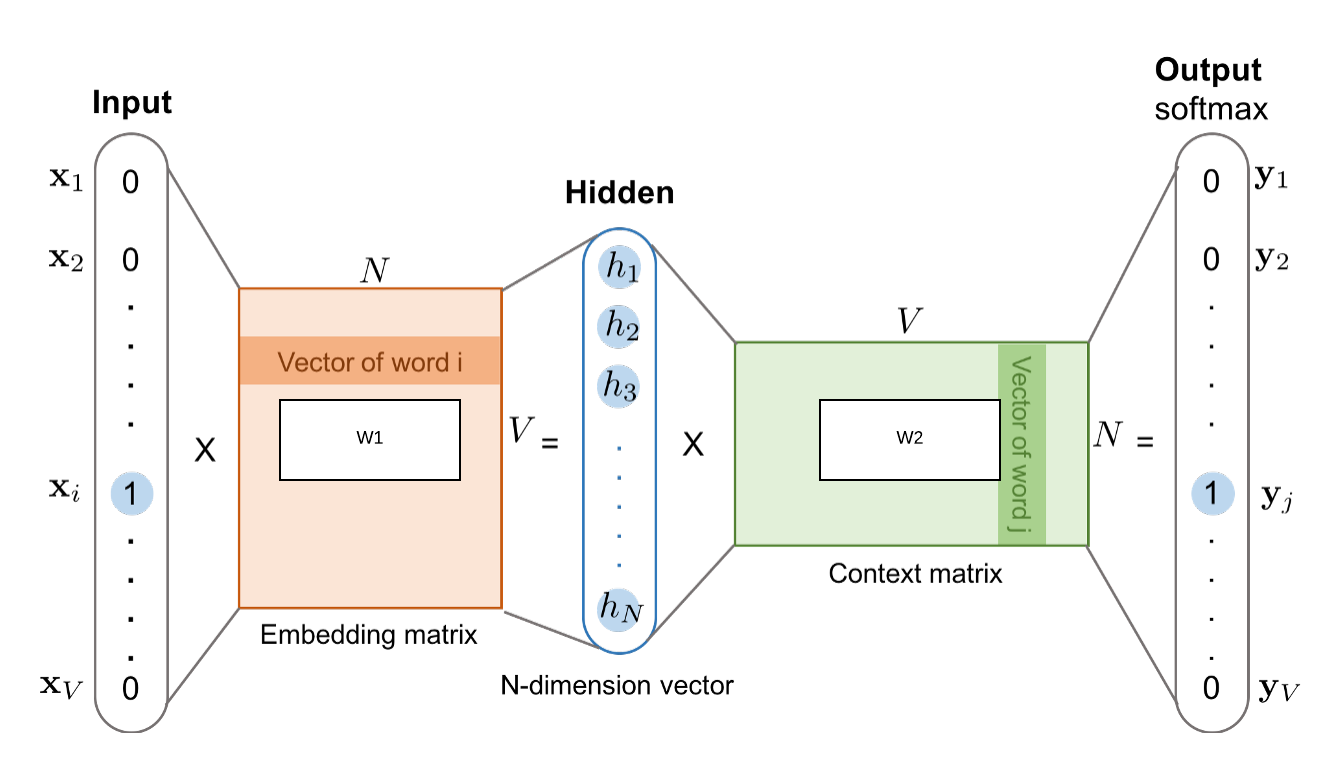
Because window_size = 1, we’re going to use the word j, giving it a target of j-1 and j-1. Only softmax neurons, not the hidden layer neurons, are activated when they are exposed. Because we use one-hot vectors, each input of our Neural Network has a dimension equal to vocab_size.
The CNN classification model with word2vec, such as the CBOW and Skip-gram algorithms, performed better than the CNN classification model with random vectors. As a result, the CNN classification model proposed by word2vec is better than the CNN classification model proposed without word2vec.
A Word2Vec model of a Word2Vec program. A predictive deep learning model based on this type of model was developed by Google in 2013. The model computes and generates high-quality, distributed, and continuous dense vector representations of words, which capture contextual and semantic similarities.
What Type Of Model Is Word2vec?
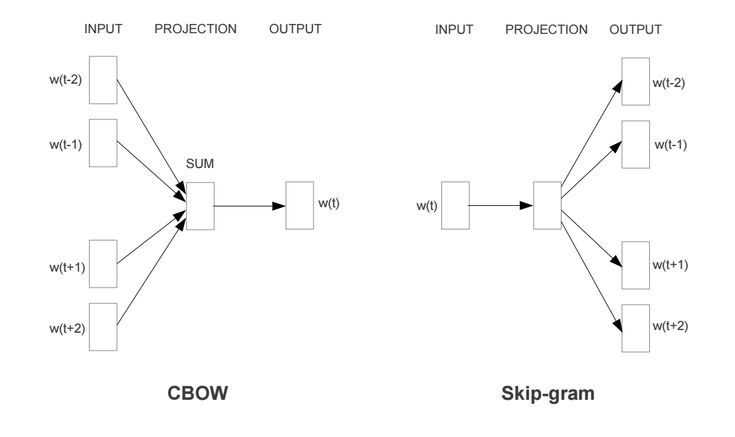
A skip-gram model and the continuous bag of words represent the two main architectures for word2vec. The skip-gram model attempts to predict the context of the input words in order to predict the words in context to the input words, whereas the CBOW model attempts to predict the missing words by taking a variety of words and attempting to predict the
Word2vec, a recent natural language processing (NLP) advancement, is a great example of this. The use of embedded words is critical to the resolution of a wide range of natural language processing problems. This series depicts how humans learn to talk to machines. Users can feed text into machine learning models by converting it into an embed, which is the most common method of processing raw text. Word2vec is typically produced by two distinct architectures. These models, as well as skip-gram and continuous bag of words models, are used. A skip-gram model is a simple neural network with one hidden layer trained in order to predict the probability of a given word appearing when an input word appears.
CBOW models attempt to predict a target word using a list of context words. This course will show you how to generate word embeddings as well as use word2vec to find similar words in a corpus. We’ll be using the Shakespeare dataset in this tutorial to create all of Shakespeare’s lines. Because we’re working with NLTK, we may need to download the following corpus for the rest of the tutorial. The embedding of a word in a natural language text is an important part ofNLP, and it depicts how humans comprehend language. Tensorflow’s user-friendly approach to word2vec allows it to appear beautiful and simple to use. It’s a great tool that allows you to interact with Word2vec’s results, so I encourage you to try it out.
Word2vec is an incredible natural language processing tool that can detect synonymous words or suggest new words for a partial sentence based on natural language processing. Google Word2vec is an excellent tool for machine learning developers looking to embed words.
Is Word2vec Deep Learning Or Machine Learning?
Word2Vec (also known as Deep Learning Word) is a method of developing a language model based on Deep Learning ideas; however, a neural network used in this method is relatively shallow (consists of only one hidden layer).
Word2Vec, as described by Google, employs deep approaches such as recurrent neural nets or deep neural nets in a similar manner. In addition, it employs some algorithms, such as hierarchical softmax, that make it more efficient. You can ask questions, get feedback, and advance your research by joining ResearchGate. Deep learning and artificial intelligence have long been buzzwords in the technology world, and their popularity has only grown. Deep learning, which is a subset of machine learning that stems from the way our brains work, is a subset of machine learning. A mesh of neural networks is used to create a network, with each layer taking on its own information at a given rate.
Every time a training example is performed, an array of vectors is generated, which are then used to predict the target word. The accuracy of the prediction is determined by the vector representation of the surrounding words that is used as a prediction vector.
Machine learning, for example, can be performed using Word2vec, a powerful tool. This program is simple to use and results are dependable.