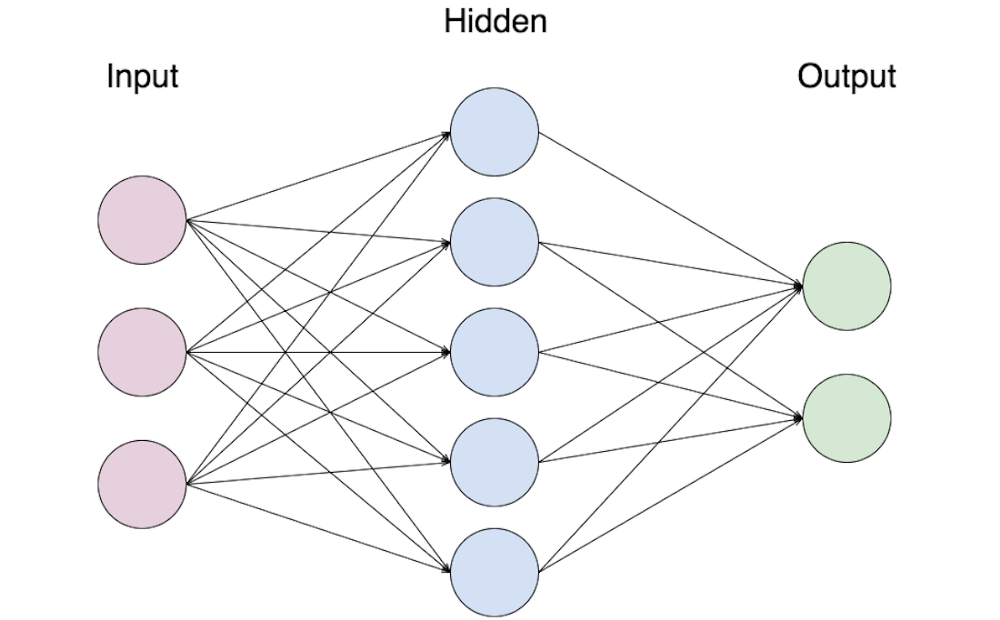
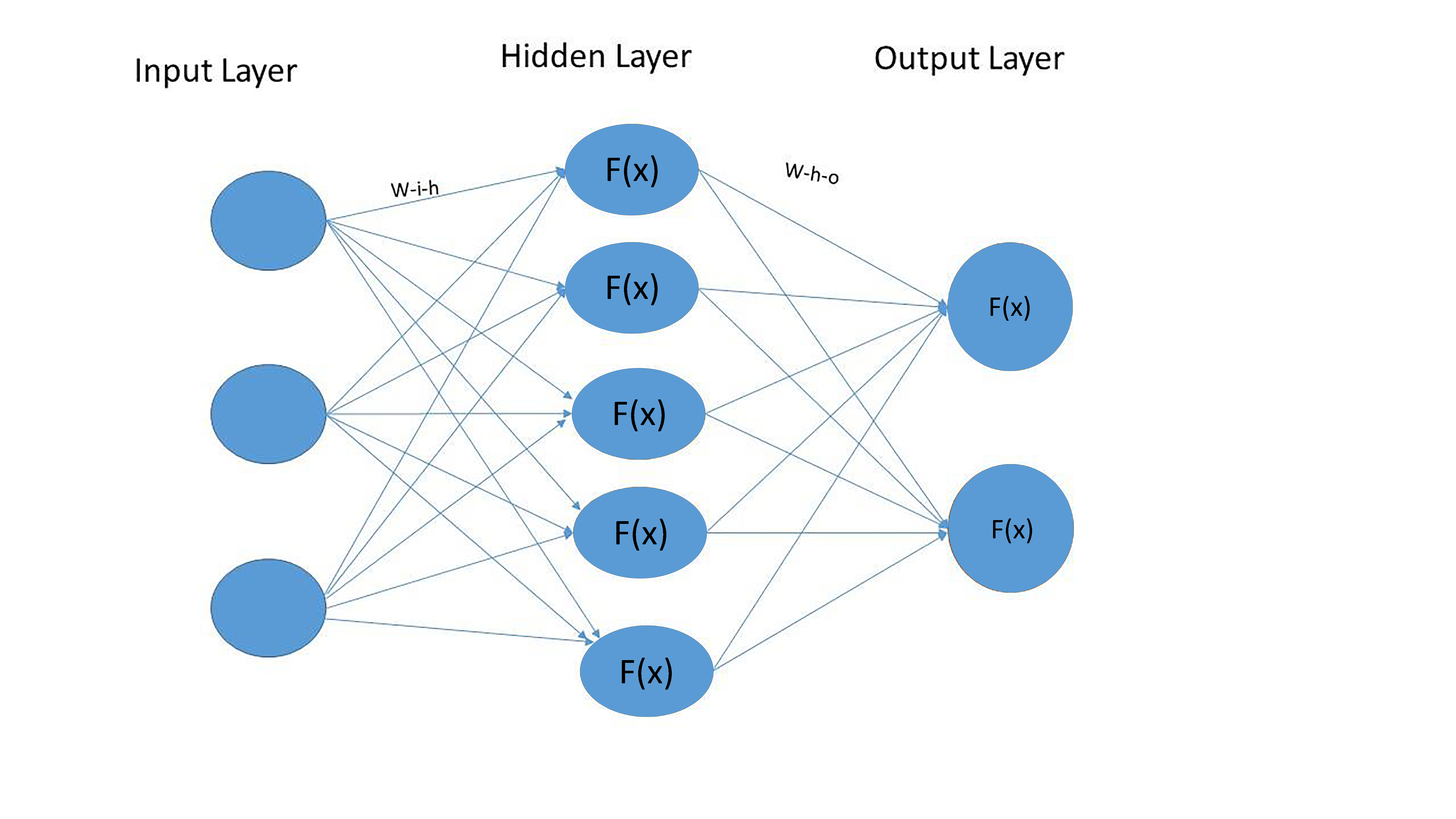
In a recurrent neural network (RNN), the hidden layer is a layer of neurons that maintains a state vector. The state vector is a representation of the internal state of the RNN at a particular timestep. The hidden layer is important because it allows the RNN to model temporal dependencies; that is, it allows the RNN to remember information about what has happened in the past and use that information to influence what happens in the future. The gradient of the hidden layer is a measure of how the hidden layer’s state vector changes over time. In other words, it is a measure of how the hidden layer learns. The gradient can be used to improve the performance of the RNN by making the hidden layer more efficient at learning. There are several ways to check the gradient of the hidden layer in an RNN. One way is to use the backpropagation algorithm. The backpropagation algorithm is a method of computing the gradient of a function by reverse-mode differentiation. Backpropagation is typically used to train neural networks, but it can also be used to compute the gradient of the hidden layer in an RNN. Another way to check the gradient of the hidden layer is to use the forward-mode differentiation. Forward-mode differentiation is a method of computing the gradient of a function by forward-mode differentiation. Forward-mode differentiation is typically used to compute the gradient of the output layer in a neural network, but it can also be used to compute the gradient of the hidden layer in an RNN. The gradient of the hidden layer can also be checked numerically. This can be done by perturbing the hidden layer’s state vector and observing how the output of the RNN changes. This method is typically used for debugging purposes, but it can also be used to check the gradient of the hidden layer.
To compute the gradient, a tensor must have its parameters requires_grad =. Partial derivatives and gradient varieties are the same. In the following example, a function for y = 2*x is used. The required_grad of the tensor – 1 is also known as the required_grad of the tensor – X. The gradient can be computed using y.
How Do You Avoid Exploding Gradients In Pytorch?

It is generally possible to avoid exploding gradient explosions by carefully configuring the network model, such as using a small learning rate, scaling the target variables, and using a standard loss function. The problem may still exist in recurrent networks with a high volume of input time steps, where exploding gradient can occur.
In neural networks, clipping gradient layers is a way to prevent gradient explosions. When the gradient becomes too large, an unstable network is formed. Because of the small size of the gradient, optimization encounters wobble gradient when it gets stuck at a certain point. A gradient clipping method is one of many methods of calculating it; however, it is more common to scale gradients to the value at which they function. To keep the gradient within a specified range, use torch.nn.clip_grad_norm. Clip-by-norm can be set using standard values found in literature, or using common vector norms or ranges discovered through experimentation and then selecting a reasonable value. As if they were concatenated into a single vector, all gradients are computed into a standard norm.
After that, we’ll create a collection of images and use the numpy library to load them into memory. In this case, we’ll use the torch function grad to calculate the gradient of the object we’ve created, MPoL, as well as the regularizer strength. Finally, we’ll use the numpy library’s optimize method to find the best regularizer for our datasets. PyTorch is a powerful computer program that computes the gradient of a function for use with inputs. The method is used to calculate the gradient of inputs based on a computational graph. An automatic differentiation can be performed in both forward and reverse modes. When the inputs are taken into account, the gradient of the function is computed as the function’s derivative. When the function’s gradient is compared to the inputs, the function’s integral is computed in reverse. The MPoL library is a Python library that computes the best image in a dataset using a gradient descent optimization method and randomization. The first step in the tutorial will be to import the torch and numpy packages. In this step, we will use the numpy library to generate an image dataset and store it in memory.
Gradient Clipping: A Popular Technique To Mitigate The Exploding Gradients Problem
Gradient clipping is a widely used method to reduce the gradient explosion in deep neural networks. Every component of the gradient vector has been assigned a value between – 1.0 and – 1.0 in this optimizer. As a result, even if the loss landscape of the model is irregular, the gradient descent is likely to behave reasonably, most likely to cliff. Clipping gradient ensures that the gradient vector has no abnormal behavior and can be distributed at most as close as possible to the threshold, which helps gradient descent to have reasonable behavior. LSTMt do not solve the problem of exploding gradient, but clipping gradient ensures that gradient vector has no abnormal behavior.
What Is Ctx In Pytorch?
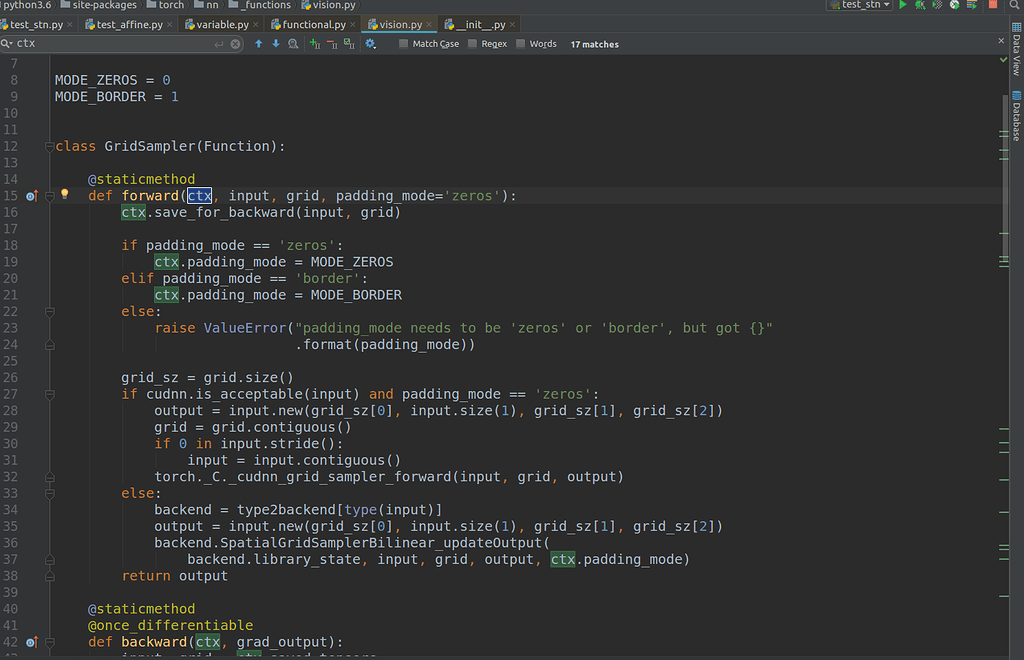
The ctx variable in pytorch is used to store the context of an object. This is useful when you want to keep track of an object’s state across multiple calls to a function. For example, if you have a list of objects and you want to keep track of the index of the object that is currently being processed, you can use the ctx variable to store the index.
Backward Pass In Neural Networks
In the backward pass, all tensor gradient distributions within the graph are computed, but the operation is only recorded if one of its input tensors requires grad.
Pytorch Get Gradient Of Intermediate Layer
To get the gradient of an intermediate layer in Pytorch, you need to first register the layer with the module so that it becomes part of the computational graph. Once the layer is registered, you can then get the gradient by calling the .grad_fn attribute on the layer.
What Does Backward Do In Pytorch?
It computes the gradient of current Tensor w.r.t. using the Tensor Principle. This graph does not leave a mark. The chain rule is used to distinguish a graph. The function will also need to specify the gradient if the tensor is non-scalar (i.e. there are more than one element in the data).
Regularization In Pytorch
In the coming sections, we’ll look at how gradient descent can be used to optimize a function if the dataset is given, as well as the desired regularization of the function. In addition, we will look at some of PyTorch’s most common optimization strategies.
What Are Hooks In Pytorch?
Each Tensor or nn has its own PyTorch hook. Modules are triggered either forward or backward by a forward or backward pass of the module object. These hooks, according to function signatures, can modify input, output, or internal module parameters. They are commonly used for debugging purposes as well as other types of analysis.
Why Pytorch Is More Pythonic
Despite its name, PyTorch feels more like a Python application than a Java application.
Its CPU-based version is one of the most popular libraries for math and data science. PyTorch, like Numpy, runs on a GPU and can perform differentiation automatically. Using PyTorch will be a breeze if you’re familiar with numpy.
Because PyTorch is more pythonic than NumPy, it was designed to be more intuitive and similar to Python. Python developers can get started with PyTorch in a hurry. PyTorch can run on the GPU, which can also be useful for certain tasks.
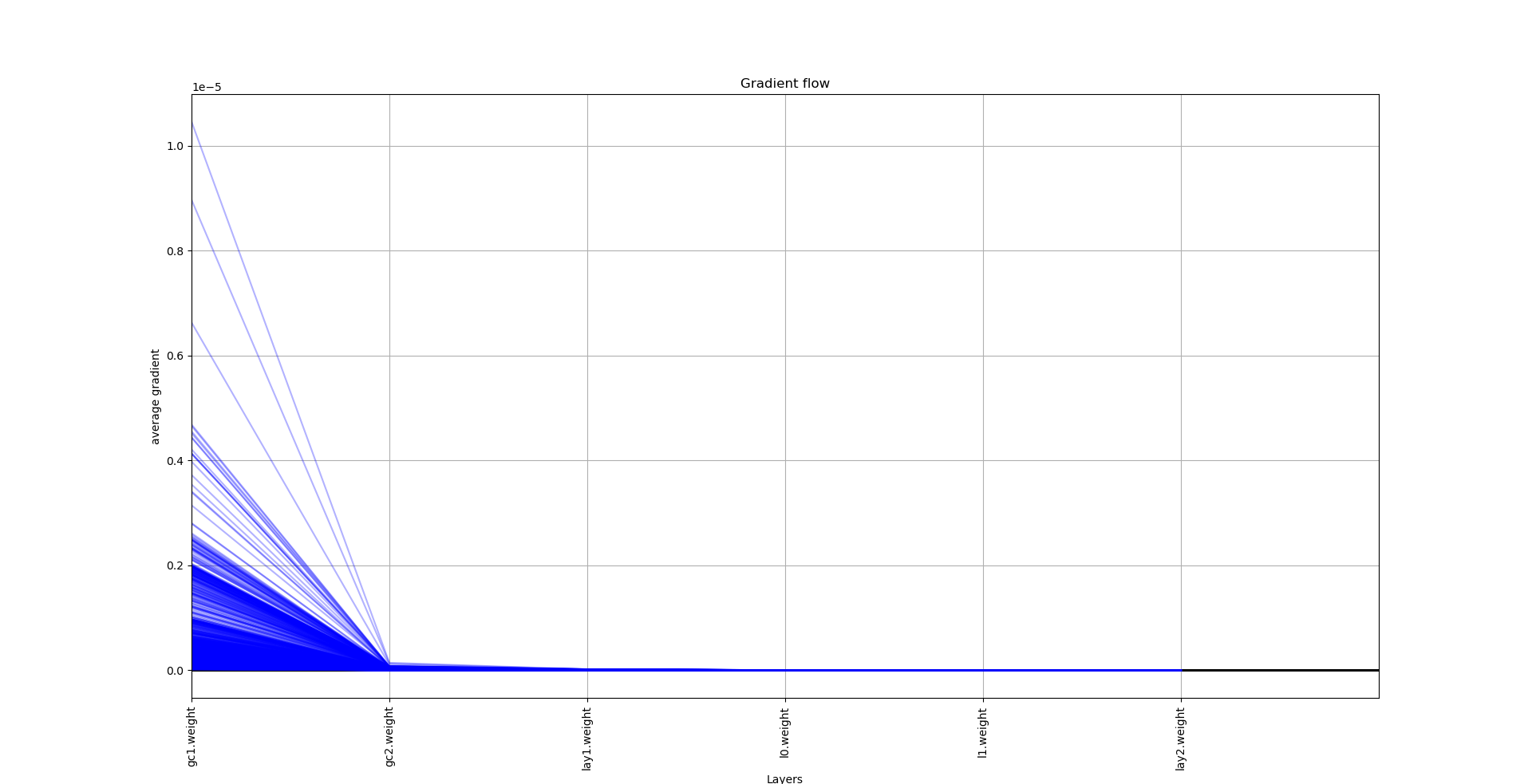
Pytorch Check Gradient Flow
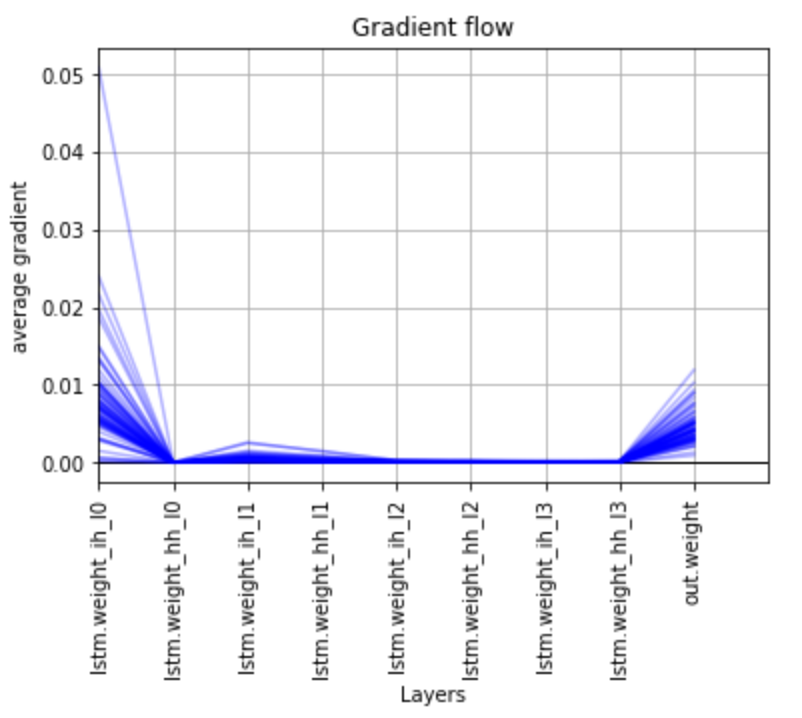
Pytorch is a popular open-source machine learning library used for both research and production. One of its key features is the ability to check the gradient flow during training. This can be useful for debugging purposes, or for understanding how the training is progressing. To check the gradient flow in Pytorch, simply call the .grad_flow() method on the relevant tensor.
Pytorch Apply Gradient
Pytorch applies gradient descent to optimize the weights of the neural network. The algorithm starts with a set of initial weights and iteratively adjusts them to minimize the loss function.
This is the PyTorch 1.13 code documentation. A function’s gradient can be calculated by including the dimensionsmathbbR*n in one or more dimensions. This gradient can be calculated by estimating each partial derivative of gg with independent precision. In practice, it is true if gg is in C3C*3 (it has at least three continuous derivatives). If the input tensor’s indices are different than the sample coordinates, spacing can be used to modify them. In this example, if spacing=2, the indices (1, 2, 3) become coordinates (2, -2, 9). If spacing is a list of one-dimensional tensors, each tensor specifies the coordinates for the corresponding dimension.
Pytorch Rnn Example
RNNs are a type of neural network that are able to processsequences of data, such as text, audio, or time series data. PyTorch is a deep learning framework that provides a way to implement RNNs in Python. This PyTorch tutorial will show you how to create an RNN that can process text, and how to train it on a dataset.
This blog post will walk you through the various types of RNN operations within PyTorch. Vanilla RNNs are typically used in conjunction with sequential data sources such as time series or natural language processing. In bidirectional RNNs, 1 RNN is fed into the input sequence, and the other RNN reverses the order. The num_layers= 3 result will result in 3 RNN layers stacked on top of each other. We obtain values from all four batches where time-steps (seq_len) equal 5 and the number of predictions equal 2 in the out. Every batch is expected to produce two outputs. If the file size is 4, 5, 2, the grad_fn=TransposeBackward1 indicates the file size.
A torch has been concealed. The torch is lit. The product measures 0.2184 in x 0.9387 in x 0,002.5 in. [ 8], [9], [10.]], [ 11,] [12, [13], [4,], [15.]], [ 16], [17], [18], [19], [20], [22.]], [ 32.
Because we set the BATCH_SIZE = 4, we produce four batches of the product. Each batch contains five rows, which is because SEQ_LENGTH = 5 in each row. We get values from all four batches where the number of time-step (seq_len) is 5 and the number of predictions is 2, all of which have a time-step of 5. Because it is both bifunctional and adaptive, it can operate both as a RNN and as a non-RNN. There are two sets of predictions. ( batch, seq_len, num_directions, hidden_size) has the second dimension, which is Grad_fn=>SliceBackward%27 (batch, seq_len, num_directions, hidden_size). To achieve forward and backward output, use a torch. ( -4, 5, 2). [ 0.0101, -0.4025], [_SliceForward, ‘SliceMidwifery,’ [_SliceLeft, ‘SliceMiddlewyth,”sliceWyth,’]: Bottom.
How To Train An Rnn With Pytorch
The goal of recurrent neural networks (RNNs) is to be able to predict the future by repeating past values. PyTorch is a valuable tool for training RNNs. In this article, I’ll go over what you need to know about RNN training with PyTorch. We’ll start with a CUDA (GPU) device for training, which is far too long to use with a CPU (the Google CoLab notebook can be used if you don’t have one). We then set the batch size (the number of elements to see before updating the model), the learning rate for the optimizer, and the number of epochs. For example, an RNN can generate a size (seq_len, batch, num_directions, and hidden_size) using batch and num_directions. In batch_first = True, the output size is (batch, seq_len, num_directions * hidden_size). The LSTMt model is used to solve the RNN’s vanishing gradient or long-term dependence issue. Gradient vanishing refers to the loss of information in a neural network over time as connections to it continue to recur. The goal of LSTMs is to reduce the vanishing gradient by ignoring useless data and information in the network.
Pytorch Visualize Gradients
In PyTorch, visualizing gradients can be done with a few lines of code. First, we need to import the necessary packages: import torch import matplotlib.pyplot as plt Then, we can define a function that takes in an input image and outputs the gradient values for that image: def get_gradient(image): # Get the gradient values for an input image gradient = torch.autograd.grad(outputs=image, inputs=torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.0], requires_grad=True), grad_outputs=torch.ones(image.size()))[0] return gradient Finally, we can use this function to visualize the gradients for an input image: # Load in an image image = plt.imread(‘my_image.jpg’) # Get the gradient values gradient = get_gradient(image) # Visualize the gradients plt.imshow(gradient) plt.show()
It is possible to perform the same operation using PyTorch in addition to the gather and squeeze methods. We can generate a network image of the target class by starting with a random noise image and performing gradient ascent on the target class. The documentation for the gather and squeeze methods can also be found here. A convolutional network can use $I$ as its image, and $y$ as its target class. To generate an image with a high Y# class score, we need to generate $I**$. We’ll show you how to use (explicitly) L2 regularization to make the form $$ R(I) = $0.0251. You can increase the number of characters by blurring the image several times.